Six vulnerabilities have been discovered in a GPS monitoring gadget utilized by companies to observe automobile fleets, and by customers as an anti-theft gadget. If exploited, they might enable attackers to broadly disrupt fleet operations and observe particular person automobiles.
That is based on cybersecurity agency BitSight, which acknowledged in a Tuesday advisory that the gadget, the MiCODUS MV720, has vulnerabilities in each the gadget and the back-end service. These pave the best way for man-in-the-middle (MitM) assaults, authentication bypasses, and location monitoring. The vulnerabilities embrace a hard-coded gadget password that enables entry through SMS requests, and a default password on the API server, BitSight discovered.
“The exploitation of those vulnerabilities may have disastrous and even life-threatening implications,” BitSight states within the report. “For instance, an attacker may exploit among the vulnerabilities to chop gasoline to a whole fleet of business or emergency automobiles. Or, the attacker may leverage GPS info to observe and abruptly cease automobiles on harmful highways.”
The vulnerabilities embrace a hard-coded password that would enable instructions to be despatched to units, the flexibility to make use of administrator privileges for instructions, and a default password of 123456. Flaws of lesser severity embrace a mirrored cross-site scripting (XSS) problem and the flexibility to immediately entry components of the appliance. 5 of the vulnerabilities have been assigned identifiers beneath the Frequent Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) program: CVE-2022-2107, CVE-2022-2141, CVE-2022-2199, CVE-2022-34150, and CVE-2022-33944. The default password safety weak spot was not thought-about a vulnerability, and so didn’t get a CVE identifier.
GPS Bugs Stay Unpatched
Whereas the corporate has not noticed any indicators that the vulnerabilities have been exploited, the Chinese language agency that producers the gadget, MiCODUS, has not responded to makes an attempt at discussing the problems, says Stephen Boyer, co-founder and CTO for BitSight.
BitSight initially contacted MiCODUS in regards to the issues in September 2021, and after an preliminary request for extra info, the corporate refused subsequent makes an attempt to speak, based on the agency. MiCODUS didn’t instantly reply to a request for remark from Darkish Studying.
“Sadly, the hard-coded password signifies that the one actual remediation technique is to take away the MV720 gadget or take away the SIM card from the gadget,” he says. The agency shared the bug info with the Division of Homeland Safety, he added, in hopes that it may develop an applicable remediation technique.
“IoT units are stuffed with vulnerabilities, and this is not going to change going into the long run irrespective of what number of of those tales come out,” Roger Grimes, data-driven protection evangelist at KnowBe4, stated through electronic mail. “IoT units are notably exhausting to patch. They need to all be auto-patching, however most aren’t. Most require end-user interplay, and lots of occasions a bodily connection.”
He added, “For those who suppose it is exhausting to patch common software program, it is ten occasions as exhausting to patch IoT units. I am purely guessing right here, however I might speculate that 90% of susceptible GPS monitoring units will stay susceptible and exploitable if and when the seller truly decides to repair them. Hackers love these odds.”
IoT: Nonetheless No Safety by Design, Widespread Menace
The vulnerabilities underscore the dangers posed by Web of Issues (IoT) units that haven’t benefited from sufficient consideration to safety design and audits. Related units sometimes have much less safety, however are distributed all through many firms’ infrastructure and deal with bodily processes — equivalent to entry entry and energy management — not like conventional info know-how.
Involved with the shortage of safety, the US authorities has established necessities for IoT gadget safety.
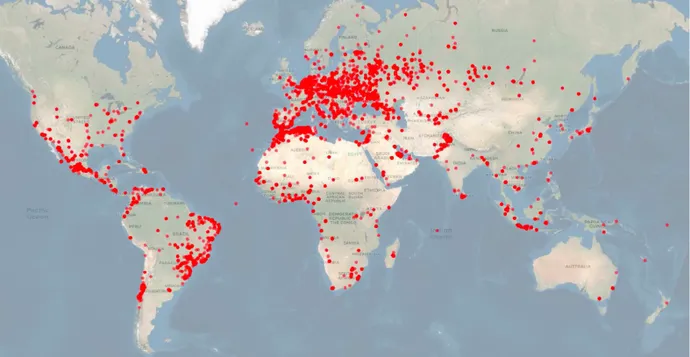
IoT units usually are additionally way more widespread than most enterprise customers acknowledge. As proven by the BitSight analysis, for instance, GPS units typically are utilized in automobiles belonging to at the least 5 Fortune 50 firms, in addition to power utilities and governments within the Center East, Europe, and North America.
BitSight couldn’t decide the prevalence of the MiCODUS MV720 particularly, however famous that MiCODUS claims that 1.5 million units are used globally. As well as, BitSight noticed practically 2.4 million connections to the MiCODUS API server from 169 international locations worldwide. The MiCODUS MV720 is a fundamental mannequin bought for $20 on-line, however different fashions may account for some, and even most, of the IoT producer’s put in base.
The BitSight report notes that two broad use circumstances exist for the units. In some international locations, knowledge means that the units are used to handle fleets of automobiles. Nonetheless, in different international locations, the big variety of particular person connections per capita means that people are utilizing the units for anti-theft purposes.
“Indonesia has many distinctive IP addresses speaking with the MiCODUS server, however principally within the GPS tracker port,” BitSight states within the advisory. “This may increasingly recommend there are a small variety of customers with a excessive variety of units, which is typical in a fleet-management state of affairs. By comparability, Mexico has a really excessive variety of connections to the net and cell ports, which may point out people are utilizing the GPS tracker as an anti-theft gadget.”
Mexico, Russia, and Uzbekistan are the international locations with essentially the most particular person customers, the corporate estimates. Russia, Morocco, and Chile seem to have the best variety of precise units.


