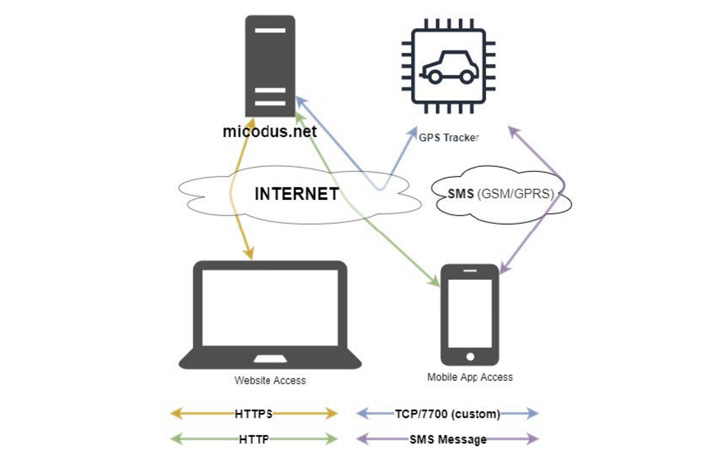
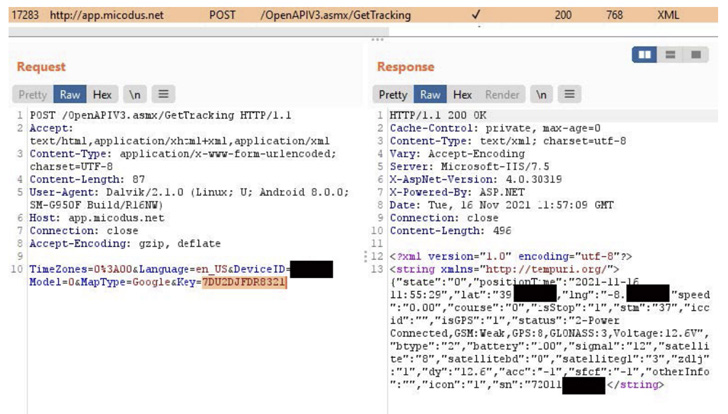
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA) is warning of a handful of unpatched safety vulnerabilities in MiCODUS MV720 World Positioning System (GPS) trackers outfitted in over 1.5 million automobiles that might result in distant disruption of vital operations.
“Profitable exploitation of those vulnerabilities could permit a distant actor to use entry and acquire management of the worldwide positioning system tracker,” CISA mentioned. “These vulnerabilities might affect entry to a car gas provide, car management, or permit locational surveillance of automobiles by which the gadget is put in.”
Accessible on sale for $20 and manufactured by the China-based MiCODUS, the corporate’s monitoring units are employed by main organizations in 169 nations spanning aerospace, vitality, engineering, authorities, manufacturing, nuclear energy plant, and transport sectors.
The highest nations with essentially the most customers embody Chile, Australia, Mexico, Ukraine, Russia, Morocco, Venezuela, Brazil, Poland, Italy, Indonesia, Uzbekistan, and South Africa.
The problems, which have been recognized throughout the course of a safety audit by BitSight, may be probably abused to trace people with out their data, disable automobiles, and even pose nationwide safety implications in gentle of the truth that militaries and regulation enforcement businesses use the trackers for real-time monitoring.
“A nation-state adversary might probably exploit the tracker’s vulnerabilities to collect intelligence on military-related actions together with provide routes, common troop actions, and recurring patrols,” BitSight researchers identified.
The listing of flaws that have been disclosed to MiCODUS in September 2021 is beneath –
- CVE-2022-2107 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – Use of a hard-coded grasp password that might allow an unauthenticated attacker to hold out adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) assaults and seize management of the tracker.
- CVE-2022-2141 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – Damaged authentication scheme within the API server that permits an attacker to regulate all site visitors between the GPS tracker and the unique server and acquire management.
- No assigned CVE (CVSS rating: 8.1) – Use of a preconfigured default password “123456” that enables attackers to entry any GPS tracker at random.
- CVE-2022-2199 (CVSS rating: 7.5) – A mirrored cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability within the internet server that might result in the execution of arbitrary JavaScript code within the internet browser.
- CVE-2022-34150 (CVSS rating: 7.1) – An entry management vulnerability stemming from Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) that might outcome within the publicity of delicate data.
- CVE-2022-33944 (CVSS rating: 6.5) – A case of authenticated IDOR vulnerability that could possibly be leveraged to generate Excel studies about gadget exercise.
In a nutshell, the issues could possibly be weaponized to acquire entry to location, routes, gas cutoff instructions in addition to the flexibility to disarm numerous options equivalent to alarms.
However with no workaround in sight, customers of the GPS tracker in query are suggested to take steps to attenuate publicity or alternatively stop utilizing the units and disable them altogether till a repair is made obtainable by the corporate.
“Having a centralized dashboard to observe GPS trackers with the flexibility to allow or disable a car, monitor pace, routes and leverage different options is helpful to many people and organizations,” the researchers mentioned. “Nevertheless, such performance can introduce severe safety dangers.”