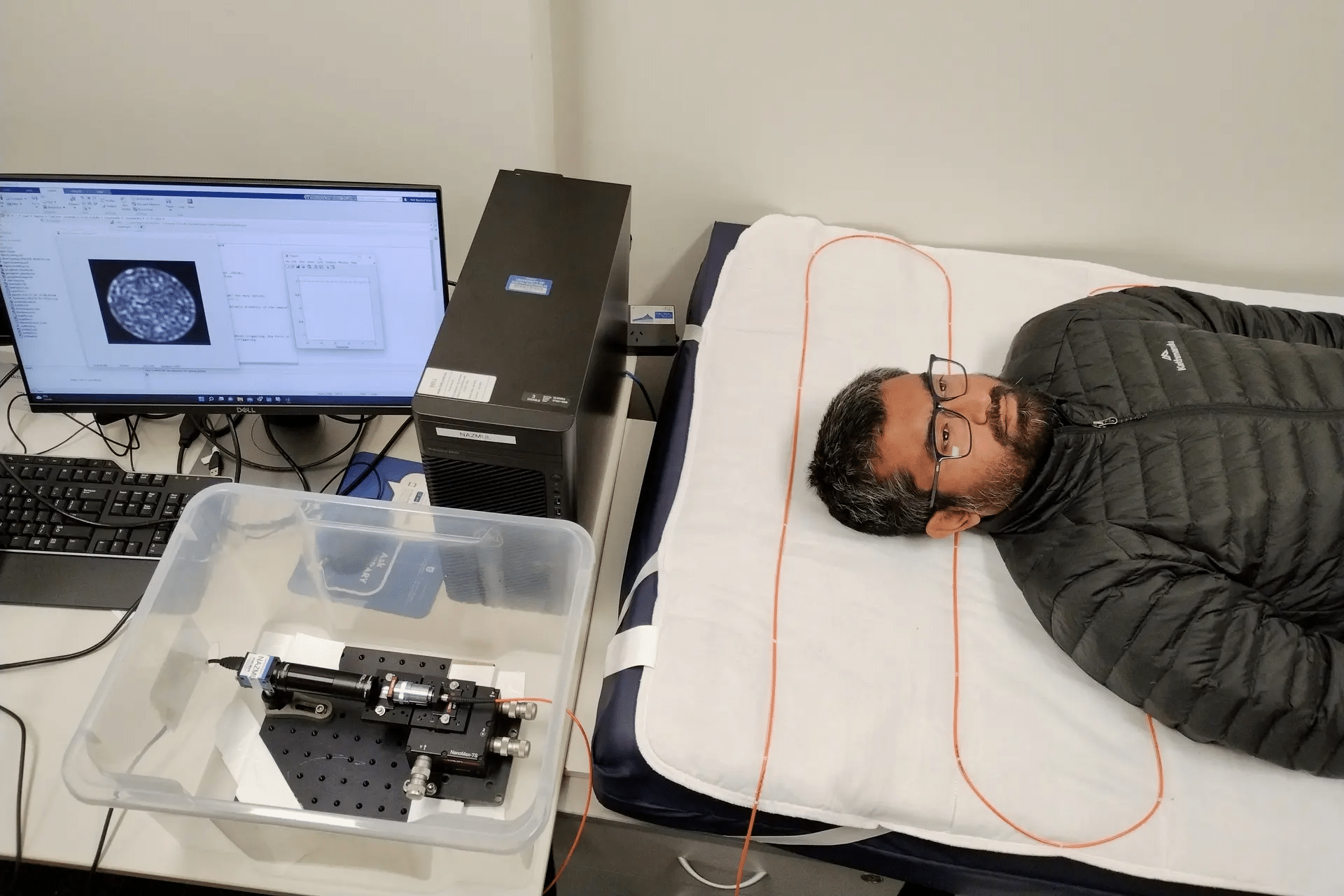
Researchers at College of South Australia have developed a Multimode Optic Fiber (MMF) sensor to observe vitals of sufferers.
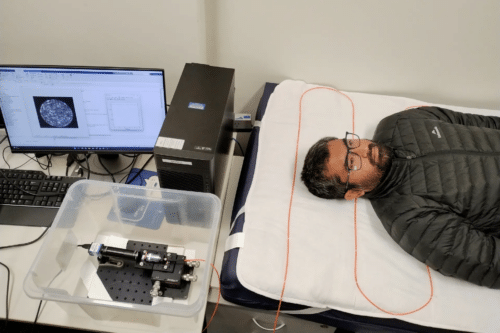
The sensors are embedded within the higher portion of the affected person’s mattress. This reduces the possibility of bedsore, prevents falling, screens affected person’s coronary heart charges and likewise reduces the necessity for guide monitoring.
The good mattress sensor is mixed with seven MMF cables, bundled on the enter and output areas of the sensor. The sensor is then built-in with a single laser gentle supply and a digicam by the mounted ends. A visual single gentle of wavelength 633 nm is generated from the laser supply, which is collimated to yield a beam of three.4mm diameter roughly. This beam is then directed to the tip face of the MMF bundle which distributes the beam equally throughout all seven fibers. The opposite finish of the bundle is imaged onto a CCD digicam.
The coherent gentle generates a speckle output whereas propagating. Any change within the fiber similar to pressure, change within the size of MMF modes and bleeding causes change within the output. The change within the patterns are quantified with an algorithm to determine the bodily perturbation.
“Respiration charges are sometimes the primary signal {that a} affected person is deteriorating. This usually requires units to be connected to the affected person, both on the chest, as a masks on the face, or ventilator. These might be restrictive and generally inappropriate in an aged care setting,” Warren-Smith, a researcher mentioned. “Monitoring important indicators repeatedly, unobtrusively, and cheaply through the mattress-embedded sensors is a much better resolution for each affected person and nurse.”
The good mattress sensor makes a distinction because it doesn’t require any further sensor components to perform. Additionally the sensitivity and spatial radiation of the sensor is perhaps elevated with none further price. It may be achieved by multiplexing and machine studying algorithms.