Tokyo Metropolitan College researchers have discovered the method underlying the short growth of ultra-thin nanowires or “whiskers” in natural substances. Understanding how these “whiskers” develop is important for purposes since nanowires are each a fascinating technical development and a danger once they quick electronics.
Nanowires are extraordinarily skinny crystalline filaments with thrilling new makes use of in electronics, catalysis, and power manufacturing. Moreover, they may develop by chance in undesirable places, bridging insulating boundaries and shorting digital circuits. Understanding how they develop is a big technological problem, however the exact mechanism remains to be a thriller.
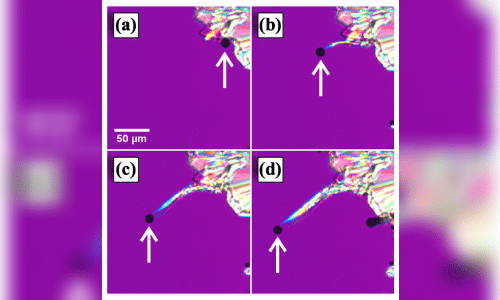
Professor Rei Kurita, Assistant Professor Marie Tani, and Takumi Yashima from Tokyo Metropolitan College have been inspecting crystal development within the widespread natural compounds o-terphenyl and salol. These two substances each exhibit “whisker crystals,” that are skinny filaments that develop rapidly from crystalline fronts when the fabric is cooled. They examined the filaments intently and located that every had slightly bubble on the tip.
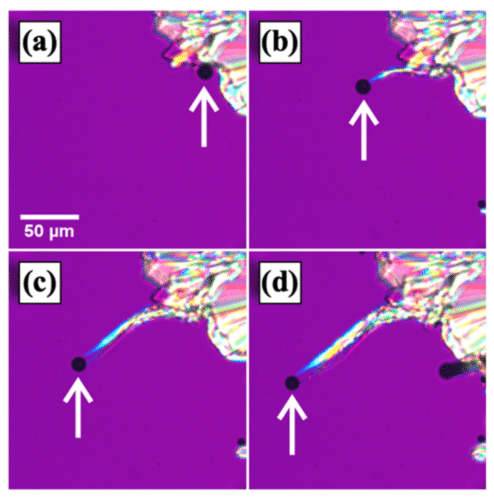
They have been capable of show that this bubble was certainly slightly capsule of gasoline fabricated from the identical natural substance reasonably than simply an impurity or air blended in. A radically completely different situation from the everyday depiction of freezing in liquids was noticed, as molecules within the liquid transferred to the gasoline contained in the bubble earlier than being linked to the tip of the filament, versus merely depositing onto a rising entrance as in typical crystal formation. Consequently, nanowires grew at an extremely fast charge.
The scientists found that the numerous density differential between the crystal and liquid in these compounds performed a job within the bubble manufacturing itself. Once they repeated the trials in liquids with smaller variations, they found no whisker development. They reasoned that the crystalline entrance was prone to have important density inhomogeneities, which might finally trigger cavitation—the spontaneous creation of gasoline bubbles that finally give rise to whiskers.
To forestall cavitation, slightly amount of impurity was launched to the fabric. As bubbles subsided, the whiskers adopted go well with, permitting for the slower however whisker-free formation of sizable chunks of homogeneous crystallisation. The workforce’s research offers novel methods to develop nanofilaments for technological purposes and new strategies to guard electronics and batteries from probably harmful shorts brought on by whisker crystals.
Click on right here to view their research.