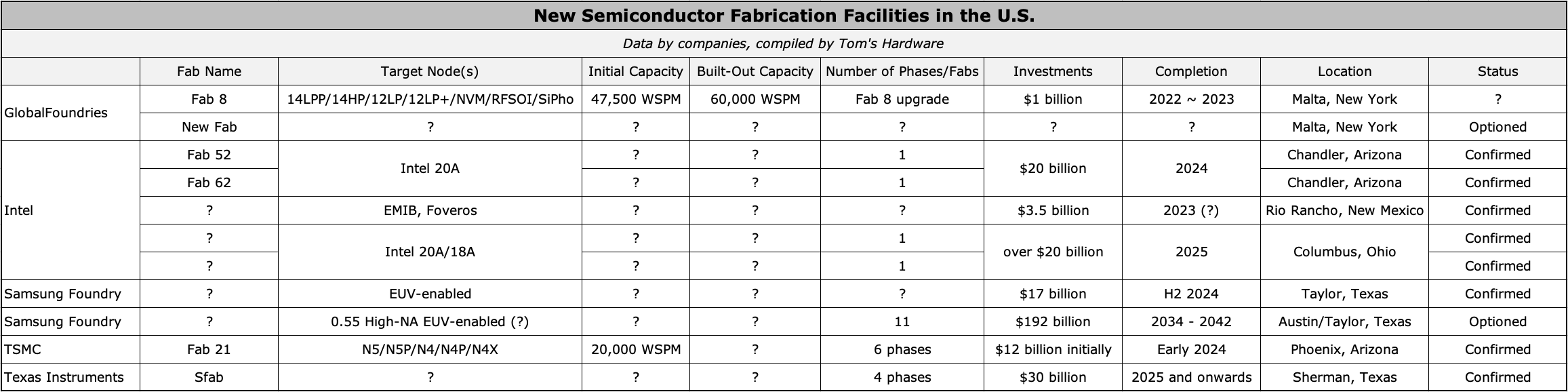
The U.S. share of worldwide semiconductor manufacturing capability has decreased from 37% in 1990 to 12% in 2021, in line with the Semiconductor Business Affiliation (SIA), however some 47% of the chips bought worldwide are designed within the U.S. This disparity poses main dangers to American nationwide safety and the economic system, which is why each business insiders and politicians just lately started to name for constructing semiconductor fabs within the USA.
Their calls have been heard, and as we speak 5 main chipmakers — GlobalFoundries, Intel, Samsung Foundry, TSMC, and Texas Devices — are constructing new semiconductor manufacturing services within the U.S. These efforts will inevitably be bolstered by a brand new wave of funding offered by the newly-approved CHIPS act . This U.S. subsidy initiative will pump $52 billion into new US-based chip fabs and supply contemporary tax incentives. These funds will spur a wave of recent funding over the approaching years, and its sorely wanted.
There are lots of explanation why international locations like Taiwan, South Korea, and Singapore turned main producers of logic and reminiscence chips within the Nineteen Nineties and 2000s. Along with decrease labor prices in these states, these governments and their native authorities offered varied incentives to chipmakers, which is why it was considerably cheaper to construct fabs in Asia than within the U.S. and Europe.
New York and Saratoga County authorities understood this early and provided AMD important incentives in 2006 when the corporate made plans for what’s now often known as GlobalFoundries Fab 8. Sadly, different states and the federal authorities weren’t that agile, which is why the deployment of brand-new fabs turned a uncommon prevalence in America. In actual fact, Intel even adjusted its manufacturing capability technique, culminating in it delaying the Fab 42 tools transfer in by 5 years and its coming on-line by six years.
Whereas we won’t say that the semiconductor manufacturing business within the U.S. did not add capability lately — each Intel and GlobalFoundries steadily expanded their manufacturing capacities within the late 2010s — brand-new modern fabs have not been deployed within the U.S. for some time. That is about to alter. Here is how and the place these modifications will happen.
Intel: Spending Over $40 Billion on Chip Services within the U.S.
Intel is actually one of many oldest chipmakers within the U.S. and one of many world’s largest. It additionally occurs to be the one firm spending greater than $40 billion on new semiconductor fabs within the U.S. In contrast to a few of its business friends that set long-term plans and possibility new fabs, Intel is investing tens of billions of {dollars} into 4 U.S. fabs that can come on-line in three years. Presently, Intel is constructing 4 chip manufacturing crops, two in Arizona and two in Ohio, and one superior packaging facility in New Mexico.
Arizona
Intel broke floor on Fab 52 and Fab 62 within the Ocotillo campus close to Chandler, Arizona, in late September 2021, and the development of these buildings is effectively underway. The fabs are designed to supply chips utilizing Intel’s 20A fabrication know-how each for Intel and its Intel Foundry Providers prospects.
(Picture credit score: Intel)
Intel’s 20A manufacturing node would be the firm’s first course of to include RibbonFET gate-all-around field-effect transistors (GAAFETs) and PowerVia bottom energy supply. These radical enhancements are anticipated to carry important energy, efficiency, and space (PPA) enhancements.
Intel’s Fab 52 and Fab 62 will come on-line in 2024 and price round $20 billion. These fabs might be instrumental for Intel’s IDM 2.0 technique that can discover the corporate manufacturing chips for different corporations, a primary.
Ohio
Intel is constructing two fabs in Ohio which might be but to be named, however their significance for Intel and the U.S. chip business is difficult to overestimate. For years, Intel has steadily expanded its mega websites in Arizona, New Mexico, and Oregon. Increasing present campuses makes plenty of sense for the reason that semiconductor provide chain could be very advanced. Intel wants assist from companions (e.g., uncooked supplies suppliers, elements, and so forth.) with an area presence.
(Picture credit score: Intel)
In Ohio, Intel desires to ascertain yet one more mega website that can home as much as eight semiconductor manufacturing services (we would come with a complicated packaging facility, too, however Intel has not confirmed this). The location would require investments of round $100 billion to be totally constructed over the subsequent decade . Moreover, the brand new campus would require Intel’s companions to ascertain an area presence, which basically means a significant growth of the U.S. semiconductor provide chain. Really, of all of the chipmakers constructing new crops within the U.S., solely Intel is keen to construct a brand new mega-site from scratch.
The primary two new fabs are close to Columbus, Ohio, and are anticipated to supply chips on Intel’s 18A/20A nodes someday in 2025 once they come on-line. Intel’s 18A manufacturing know-how was meant to be the primary fabrication course of to benefit from ASML’s Twinscan EXE 0.55 Excessive-NA excessive ultraviolet (EUV) lithography scanners. Nonetheless, earlier this yr, Intel mentioned it may preserve utilizing current-gen Twinscan NXE 0.33 NA EUV instruments for 18A by adopting multi-patterning. However even with out Excessive-NA instruments, the brand new know-how guarantees to carry a wide range of energy, efficiency, and space (PPA) benefits as it’ll depend on Intel’s 2nd-Gen GAA RibbonFETs.
Intel’s mega fab undertaking will initially price over $20 billion and might be Ohio’s largest financial improvement undertaking in historical past. To lure Intel to Ohio, the state had to supply Intel with about $2.1 billion in varied incentives . As well as, Intel is requesting funding from the federal authorities as a part of the CHIPS act, nevertheless it is not clear how a lot funding it’ll obtain.
In actual fact, authorities funding is essential for Intel’s Ohio mega website undertaking. Fab buildings usually are not costly (however have the longest lead time), however semiconductor manufacturing instruments are (e.g., one EUV scanner prices about $160 million). Intel can construct shells, however then it must equip them with instruments in a well timed method to satisfy its manufacturing schedules. Equipping a fab for a modern node means shopping for every kind of lithography (together with immersion and EUV scanners), coating, etching, deposition, resist elimination, inspection, and different instruments, which price billions of {dollars}.
If it takes too lengthy to equip a brand-new chip plant as a result of an absence of economic sources, Intel can add additional instruments to an present facility to supply chips on a sure new node. However because of this Intel should put its new constructing on maintain and wait for an additional alternative to equip it, which implies that it’s going to generate prices with out producing any earnings.
Whereas Intel formally considers spare fab shells as a ‘good capital technique’ that offers it flexibility in how and when it brings further capability and instruments on-line, it’s nonetheless higher to equip the buildings after they’re constructed. That is why Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger warned the U.S. authorities and legislators that if the CHIPS act invoice was not handed and the corporate did not get monetary incentives and assist from the federal government, he may transfer the corporate’s subsequent mega website undertaking to Europe .
New Mexico
Intel’s superior packaging facility in New Mexico will allow the corporate and its shoppers to construct sophisticated multi-chiplet designs (a-la Meteor Lake ) that can turn into widespread within the coming years within the U.S.
(Picture credit score: Intel)
Since refined packaging applied sciences like embedded multi-die interconnect bridge (EMIB) and Foveros require a cleanroom, it’s protected to name the packaging operations in New Mexico a fab. In actual fact, the tools for the packaging facility will price Intel $3.5 billion, the value of a brand new fab a few many years in the past.
The superior packaging operations might be instrumental for producing refined designs within the U.S. when it turns into operational in 2023 ~ 2024, so that is yet one more Intel undertaking whose significance for the U.S. semiconductor business is difficult to overrate.
TSMC: 5nm Coming to the U.S.
TSMC made fairly a splash when it introduced plans to construct its 5nm-capable fab close to Phoenix, Arizona, in mid-2020. All through its historical past, the corporate has solely constructed two fabs exterior of Taiwan — the WaferTech plant in Camas, Washington (which nonetheless processes 200-mm wafers utilizing mature nodes) and Fab 16 in Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China (which makes chips utilizing TSMC’s 28nm nodes). Due to this fact, the intention to construct a reasonably superior fab in Arizona was thought of a significant shift in technique.
(Picture credit score: TSMC)
Being the world’s largest contract chipmaker, TSMC actually has lots of of consumers within the USA, so bringing a fab nearer to them is perhaps useful. But, the primary section of the fab may have a capability of round 20,000 WSPM (wafer begins per 30 days) when it turns into operational in early 2024, which is considerably decrease than the fabs that TSMC operates in Taiwan. Consequently, many observers view the undertaking as a technique to deal with some very particular prospects serving the U.S. authorities and army establishments, in addition to a option to please the U.S. authorities that wishes to diversify chip provide chains amid its tensions with China.
Later, it transpired that TSMC considers its Fab 21 undertaking as yet one more multi-phase fab, albeit co-financed by the state of Arizona and the U.S. authorities. TSMC will construct its Fab 21 in six phases over a few years to return. The primary section will come on-line in early 2024 and produce chips utilizing TSMC’s N5 (N5, N5P, N4, N4P, N4X) household of course of applied sciences, however it’s logical to count on subsequent phases to undertake extra superior nodes.
In any case, a TSMC fab coming to Arizona will strengthen the U.S. semiconductor business. In the meantime, it’s vital to notice that the world’s No. 1 foundry selected Arizona as a result of this state already hosts an Intel mega website, which implies entry to skilled expertise and a wide range of related suppliers.
GlobalFoundries: New Services for Specialty Chips
Since 2012, when GlobalFoundries’s accomplished its Fab 8, the corporate has been steadily rising the manufacturing capability of the ability both by increasing its cleanroom area or by putting in extra superior tools with increased productiveness.
(Picture credit score: GlobalFoundries)
Final yr, the corporate introduced plans to take a position $1 billion to extend Fab 8’s capability from 47,500 wafer begins per 30 days (WSPM) to 60,000 WSPM. Curiously, GlobalFoundries solely shipped 35,700 wafers from Fab 8 in 2021.
GlobalFoundries’s Fab 8 processes wafers utilizing a bunch of fabrication applied sciences, together with varied FinFET-based nodes (14LPP, 14HP, 12LP, 12LP+) in addition to NVM, RFSOI, and Silicon Photonics, that are necessary nodes not just for GloFo’s U.S.-based prospects but additionally for the nation’s nationwide safety because the army makes use of lots of GF’s chips.
As well as, GlobalFoundries mentioned it might construct an all-new fab in Malta, New York, in a private-public partnership to assist rising demand. The corporate hasn’t revealed any details about this upcoming manufacturing facility, however given GlobalFoundries’s concentrate on specialty nodes, count on the brand new chip plant to be aimed toward varied superior specialty manufacturing applied sciences.
Just lately Thomas Caulfield, chief govt of GlobalFoundries, mentioned that GloFo would wish monetary assist from the U.S. authorities offered below the CHIPS act to construct and equip the brand new fab in New York rapidly.
Samsung Foundry: SF’s Main-Edge Nodes Return to the U.S.
The Samsung Foundry division was quietly established within the U.S. in 2005 (with U.S.-based Qualcomm being the primary buyer). Since 2009, it has produced chips for Samsung and third-party prospects in Austin, Texas.
(Picture credit score: Samsung)
Since Samsung was part of IBM’s widespread platform alliance (along with AMD/GlobalFoundries, Chartered, Freescale, and Infineon), in some unspecified time in the future, it made sense for Samsung Foundry to supply chips utilizing modern applied sciences co-developed with its companions at its S2 plant in Austin, Texas. Consequently, Samsung made its superior 32nm, 28nm, and 14nm SoCs in Texas. In actual fact, cross-fab compatibility (and therefore flexibility) between S2, S1 (Giheung, South Korea), and GF’s Fab 8 offered Samsung with many benefits and put the Texas manufacturing facility in a novel place with its 14nm node.
Since IBM’s fab membership basically ceased to exist and Samsung wanted EUV lithography each for its DRAM and SoCs, it will definitely moved its modern node manufacturing to South Korea, leaving its S2 fab in Texas with older trailing nodes (14nm/11nm ~ 65nm). However Samsung nonetheless has many shoppers within the U.S. that want modern nodes, so in late 2021 the corporate introduced plans to construct an all-new fab close to Taylor, Texas . The undertaking will price $17 billion, and the brand new facility will come on-line within the second half of 2024.
Samsung hasn’t formally disclosed which course of applied sciences it’ll use at its new fab in Texas. In the meantime, the corporate indicated that it might use the ability to fabricate chips for 5G, cell, high-performance computing (HPC), and synthetic intelligence (AI) purposes beginning within the second half of 2024. Timing and goal purposes clearly point out that we’re coping with a complicated fab.
Whereas that is pure hypothesis, we might count on Samsung to make use of its Taylor fab to supply chips on varied 3nm-class fabrication nodes that depend on GAA transistors. Consequently, Samsung will carry its modern nodes again to Texas, which is sweet information for the corporate’s prospects within the U.S. and the nation’s semiconductor business.
However Samsung Foundry apparently has large plans for Texas that span by means of 2042. The contract chipmaker just lately filed 11 purposes looking for tax breaks in Austin and Taylor for constructing new chip crops within the Manor and Taylor faculty districts. The whole price of the fabs is $192 billion (i.e., $17.5 billion per fab). The preliminary services will come on-line in 2034, whereas the remaining will begin operations by 2042.
For now, the purposes appear to be a method to safe incentives below the Chapter 313 incentives program that expires this yr. Additionally, it is a good option to show to numerous authorities the intentions to spend money on the U.S. semiconductor business. But, these purposes can hardly be thought of whilst optioned fabs as semiconductor fabrication services will price considerably extra within the looming Excessive-NA EUV period.
Texas Devices: $30 Billion for Specialty and Trailing Nodes
Though Texas Devices is often credited for inventing the microprocessor practically concurrently with Intel, the corporate has by no means turn into a provider of general-purpose mass-market CPUs. It even wound down its OMAP cell SoC enterprise in 2012. However Texas Devices is the world’s largest maker of analog chips. For instance, Apple’s shiny new MacBook Professional comes with TI’s audio amplifiers and USB-C energy supply controllers (these energy controllers are used very extensively nowadays). With a portfolio of over 45,000 merchandise, Texas Devices serves just about all possible purposes that want analog chips.
(Picture credit score: Texas Devices)
Texas Devices runs its personal fab in addition to outsources among the parts it provides. Like different chipmakers, TI confronted unprecedented demand for its gadgets throughout the pandemic and is dealing with robust demand pushed by up to date business megatrends (5G, AI, HPC, edge computing, autonomous autos). To satisfy the rising demand for its merchandise, Texas Devices began to construct its new large fab close to Sherman, Texas , this Could.
The brand new chip plant might be in-built 4 phases, with the primary fab coming on-line in 2025. The endeavor would be the largest financial undertaking ever in Texas; it’ll price TI about $30 billion and span a decade. Native authorities accredited an incentive bundle that abates 90% of TI’s property taxes for the fab’s first 30 years to encourage TI to spend money on Sherman and Grayson County.
There have been different explanation why TI most well-liked Texas over different places, although. The corporate already has three 300-mm semiconductor manufacturing services within the state (together with DMOS6 in Dallas, RFab Part 1 in Richardson, and the soon-to-be-completed RFab Part 2 in Richardson), so it might share engineering expertise between the websites. Moreover, the corporate’s suppliers are situated regionally too, so will probably be simpler to get supplies and different items for the brand new chip plant.
Abstract
After years of stagnation, the U.S. is lastly getting brand-new chip crops. Intel, GlobalFoundries, TSMC, and Samsung Foundry are set to spend effectively over $70 billion on U.S. fabs by 2025. If Texas Devices’s large fab undertaking (that comes on-line in 2025 and spans for a number of extra years as new phases are constructed) and subsequent TSMC Fab 21 phases are added, we’re taking a look at investments that may hit the $200 billion mark (and even exceed it) over the subsequent decade.
(Picture credit score: GlobalFoundries)
To a big diploma, such large investments are made potential by a number of elements: incentive packages from native authorities, authorities subsidies enabled by the CHIPS act, availability of engineering expertise, and the present semiconductor manufacturing provide chain. Different causes embrace geopolitical tensions and the need to diversify manufacturing bases.
The large query is whether or not the brand new American fabs are sufficient to compete in opposition to the large upcoming Gigafab initiatives in South Korea and Taiwan. The reply is not clear but – new chip crops within the U.S. will construct chips principally developed within the U.S. and such centralization may carry some attention-grabbing rewards that we but have to acknowledge. In the meantime, the forthcoming fabs in Asia will produce chips designed within the U.S. and China, as South Korea and Taiwan (as international locations) have not but developed their very own chip designing capabilities.