Readers will recall that cloud communications agency Twilio disclosed on August 7 2022 that hackers had accessed person information following a refined social engineering assault that noticed staff focused with SMS-phishing (“smishing”) textual content messages.
Attackers despatched present Twilio workers and former staff SMS textual content messages that purported to return from the corporate’s IT division, telling them that their passwords had expired.
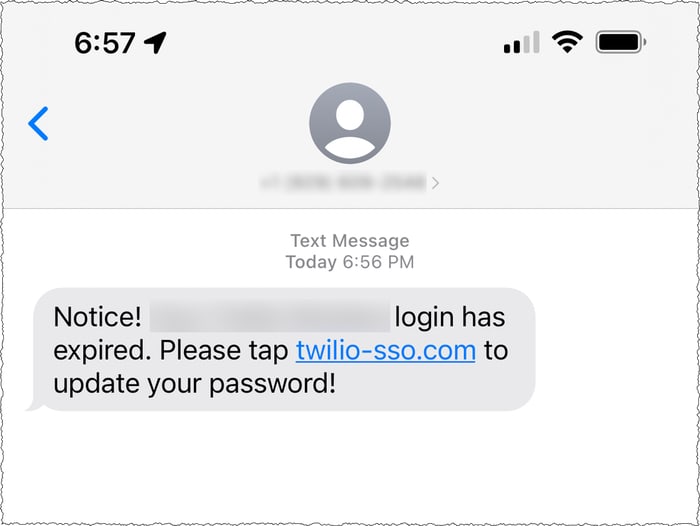
Clicking on the hyperlink within the messages had taken unsuspecting people to a pretend Twilio login web page, the place they entered their credentials and allowed hackers to realize entry to buyer information.
Now, following the conclusion of an investigation into that incident, Twilio has revealed that the identical malicious hackers had tricked an worker into offering their password by a voice-phishing assault on June 29 2022:
“Our investigation additionally led us to conclude that the identical malicious actors probably had been answerable for a short safety incident that occurred on June 29, 2022. Within the June incident, a Twilio worker was socially engineered by voice phishing (or ‘vishing’) to supply their credentials, and the malicious actor was capable of entry buyer contact data for a restricted variety of clients.”
After all, it issues little if a safety incident was “temporary” or not, in case your attackers handle to get away with the knowledge that they needed.
And there are nonetheless some troubling issues to learn in Twilio’s incident report. As an illustration, the corporate first introduced that it had suffered a safety breach on August 7 2022, however has solely this week disclosed that it “final noticed unauthorised exercise” on its methods a full two days afterward August 9.
Concluding its investigation into the breaches, Twilio says that 209 clients and 93 finish customers of its Authy two-factor authentication app had their accounts impacted by the assault.
The assaults towards Twilio had been a part of a a lot bigger marketing campaign, dubbed “0ktapus” by safety researchers, that compromised over 130 organisations.
The encrypted messaging service Sign, as an illustration, reported that roughly 1,900 of its customers may doubtlessly have been affected on account of the Twilio breach, though their message historical past and make contact with lists would have remained secure.
Twilio says it has taken steps to scale back the efficacy of smishing and vishing assaults in future, by putting in extra safety measures together with:
- Implementing stronger two issue precautions and distributing FIDO2 tokens to all staff;
- Implementing extra layers of management inside our VPN;
- Eradicating and limiting sure performance inside particular administrative tooling;
- Growing the refresh frequency of tokens for Okta-integrated functions;
- Conducting supplemental obligatory safety coaching for all staff concerning assaults primarily based on social engineering strategies.
Twilio says it’s “very dissatisfied and annoyed” concerning the incident, and has apologised to clients. It says it’s “making long run investments to proceed to earn again the belief of our clients.”


