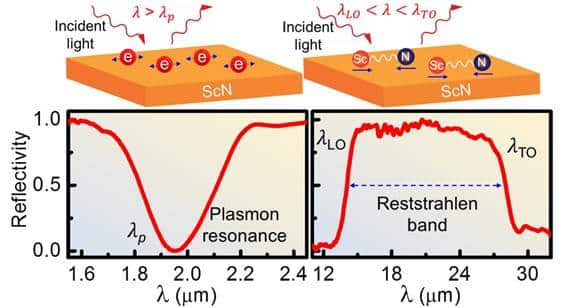
Scientists primarily based in Bengaluru have reportedly discovered a fabric that converts infrared gentle into renewable power. They’ve found a brand new materials which may emit, detect, and modulate infrared gentle with excessive effectivity making it helpful for photo voltaic and thermal power harvesting and likewise for optical communication gadgets. In accordance with a information launch scientists at Bengaluru’s Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Superior Scientific Analysis (JNCASR) have discovered a novel substance termed “single-crystalline scandium nitride” that may rework infrared gentle into renewable power. Scientists from the Centre for Nano Science and Engineering from the College of Sydney and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) additionally took half on this analysis that was launched lately within the scientific journal Nano Letters.
The electromagnetic waves are a renewable power supply used for the era of electrical energy, telecommunication, defence and safety applied sciences, sensors, and healthcare providers. Though infrared radiation is invisible to people, they’ll really feel its warmth. It’s utilized by evening imaginative and prescient goggles. The researchers used a scientific phenomenon known as “polariton excitations” to have the ability to convert it into renewable power. Assistant Professor at JNCASR Dr Bivas Saha, mentioned that from electronics-to-healthcare, defence and security-to-energy applied sciences, there’s a large want for infrared sources, sensors and emitters. He added that the work right here on infrared polaritons in scandium nitride can be set to allow its functions in lots of such gadgets.
The researchers used a scientific phenomenon known as “polariton excitations” to attain this feat. Assistant Professor at JNCASR, Dr Bivas Saha, mentioned that from electronics to healthcare, defence and safety to power applied sciences, there’s a large want for infrared sources, sensors and emitters. He added that the work right here on infrared polaritons in scandium nitride can be set to allow its functions in lots of such gadgets. Scientists from the Centre for Nano Science and Engineering from the College of Sydney and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) additionally took half on this analysis that was launched lately within the scientific journal Nano Letters.
The article will be discovered right here.