[Ed. note: While we take some time to rest up over the holidays and prepare for next year, we are re-publishing our top ten posts for the year. Please enjoy our favorite work this year and we’ll see you in 2025.]
On this period of exponential acceleration that AI has introduced forth, the common VS Code or Jetbrains developer advantages from a toolkit stacked with fashionable, state-of-the-art elements. From IDEs to extensions to CLIs, in the event you cease and contemplate all of the instruments you employ weekly, which might you guess is the oldest? That’s, which device do you work together with usually (say, an hour per week) that hasn’t substantively modified in years?
Since IDEs are refreshed each few years, perhaps you’ve got guessed that your oldest device in energetic use is “git.” It was first launched almost 20 years in the past, again in 2005. Or perhaps you favor to code with the basic old-school textual content editors, like Elegant Textual content (2008) or vim (1991).
In keeping with our analysis at GitClear, the oldest device most builders are nonetheless actively utilizing—greater than an hour per week—hasn’t modified since earlier than the Berlin Wall got here down. In 1986, an unheralded Tucson pc science professor named Eugene Myers published his seminal research paper and the “Myers Diff Algorithm” was born. Few builders at this time know the algorithm by identify, however they’ll acknowledge the acquainted red-and-green byproduct of Myers algorithm, which is the default diff generator of git, and thus, git platforms like GitHub:
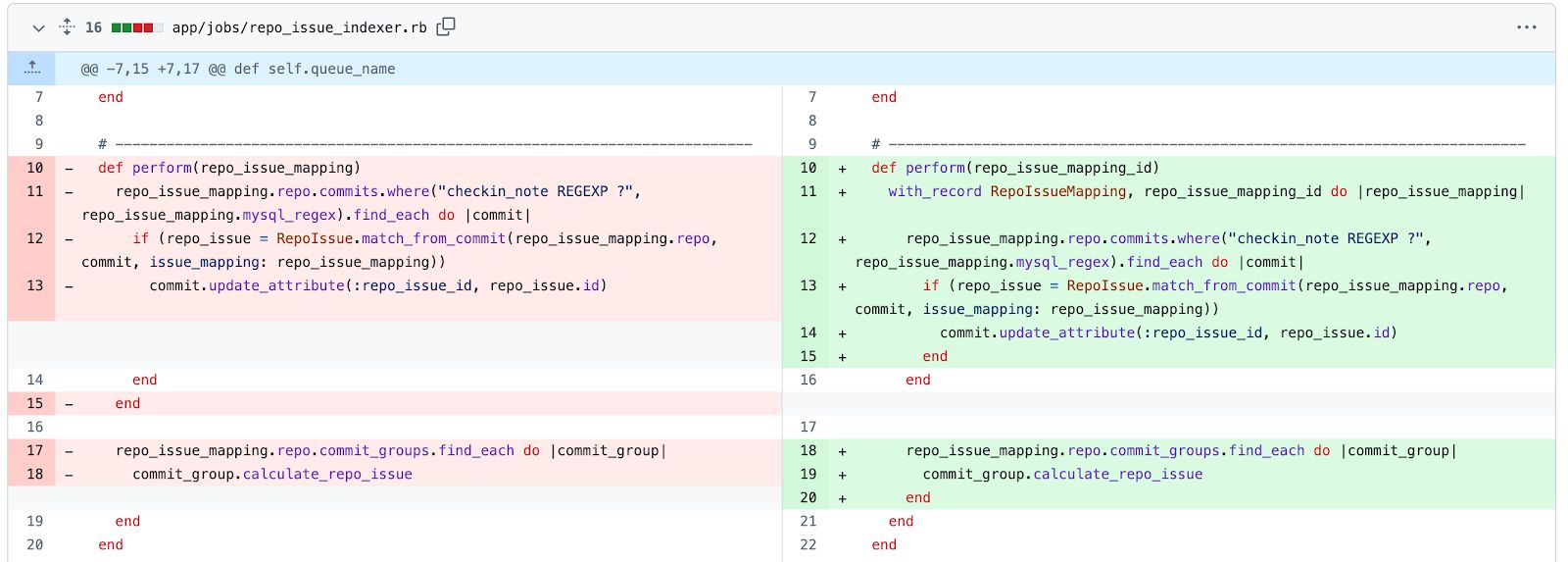
How did GitHub designate which traces to paint crimson and inexperienced? By implementing the formulation of Eugene Myers, who provided what grew to become the canonical resolution for representing the distinction between the state of a git repo “earlier than” and “after” a developer’s git commit.
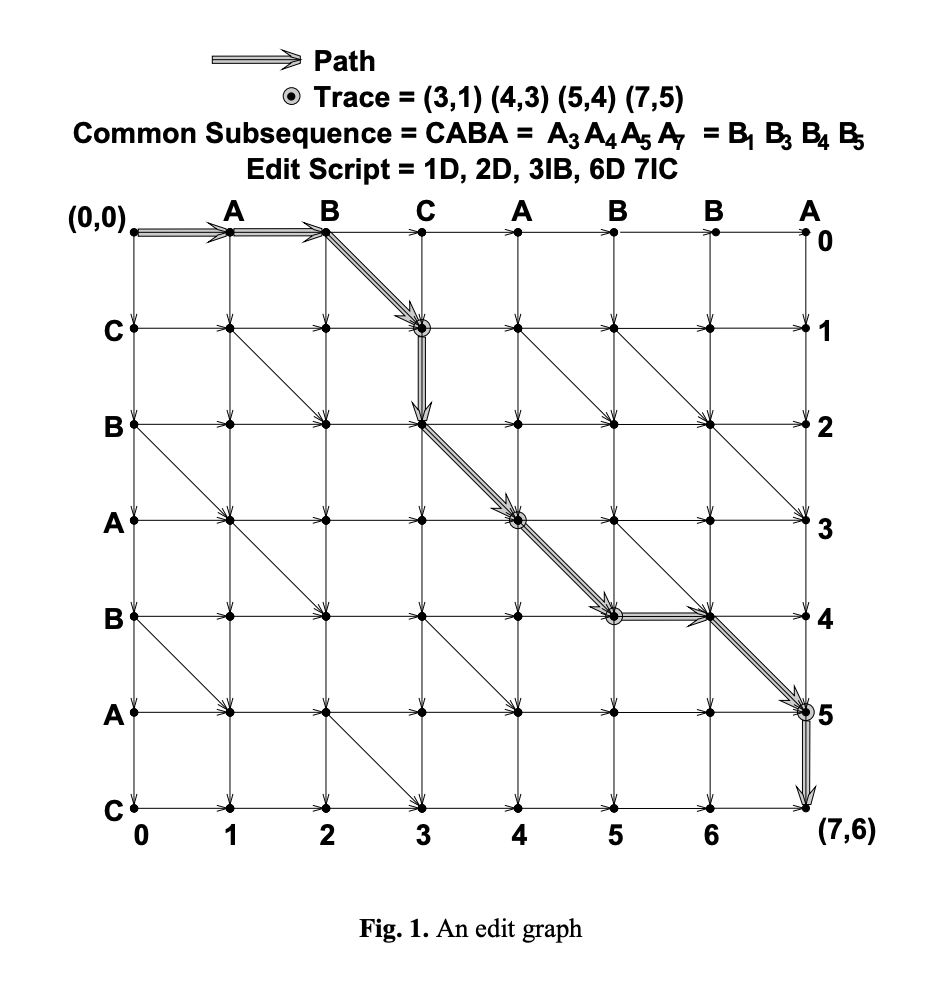
Is it attainable to enhance upon this methodology, or did Professor Myers knock it out of the park? New analysis we’ve undertaken assessments an up to date set of “diff operators” that stretch the standard “add” and “delete” to incorporate “transfer,” “replace,” “discover/exchange,” and others. Their aim is to measure whether or not it is attainable to use a deeper lexicon of diff operators to condense how a commit is represented. Can change be proven extra concisely than what was attainable almost 40 years in the past?
Our work adopted tangent traces of investigation: one empirical, one observational. We’ll summarize the 2 sides of the analysis beneath. The headline discovering ought to come as welcome information for builders: 30% Less is More: Exploring Strategies to Reduce Pull Request Review Time. The analysis comes accompanied by examples and videos to substantiate the “30% less code to review in pull requests” discovering.
Earlier than we might decide how a lot time might be saved, we needed to set up a baseline: how a lot time was being spent on code evaluate within the 2020s?
In keeping with CodeGrip’s 2022 online survey of “1,000+ CxOs and builders,” code evaluate is utilized by round 84% of firms. The identical survey discovered that the median developer in 2022 spent two to 5 hours per week on code evaluate. Thirty p.c of respondents report spending extra than 5 hours per week on evaluate. Thus, in a 40-hour work week, greater than 10% of all the week is consumed by code evaluate.
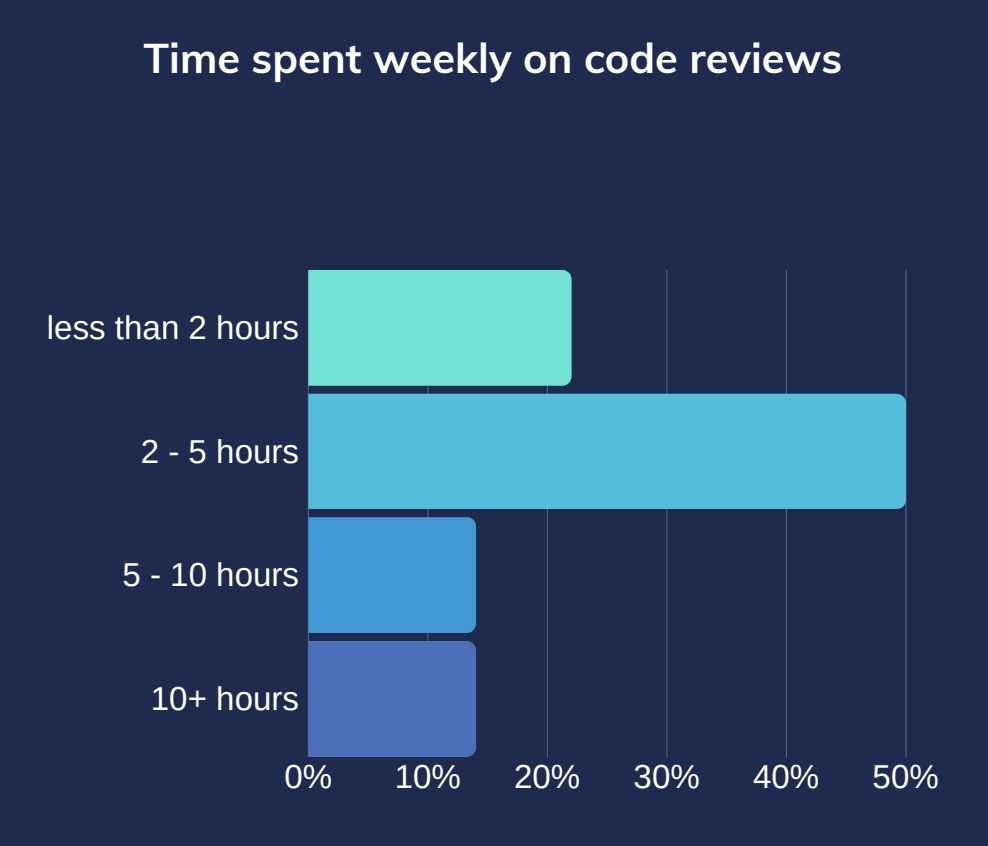
The first correlate of “code evaluate time” is “traces of code to evaluate.” And the upper a corporation’s contributor depend rises, the extra possible that builders’ burden of “code to evaluate” will turn out to be 20% or extra of their complete hours obtainable per week.
To grasp how GitClear’s “Commit Cruncher” diff algorithm can generate a extra exact diff than Myers, let’s contemplate a pair particular examples.
The Myers diff algorithm classifies all code change traces as binary: both “add” or “delete.”
The Commit Cruncher algorithm examined acknowledges 3 times extra sorts of modified operations: Added, Deleted, Up to date, Moved, Discover/Changed, and Copy/Pasted (examples of recognized code operations here). The latter operation (Copy/Paste) featured prominently in GitClear’s popular AI Code Quality research from earlier in 2024, which was cited by greater than ten developer media sources, together with Stack Overflow’s podcast.
The extent to which Commit Cruncher reduces traces to learn vs. Myers algorithm relies on the content material of a given pull request. The extra refactoring a pull request contains, the larger the potential financial savings of “traces to evaluate.” Just a few examples the place Commit Cruncher can specific a diff extra concisely comply with.
One instance the place Myers requires extra work by a reviewer is when a code change includes white area, just like the change proven earlier on this publish:

The identical diff, by means of the lens of Commit Cruncher:
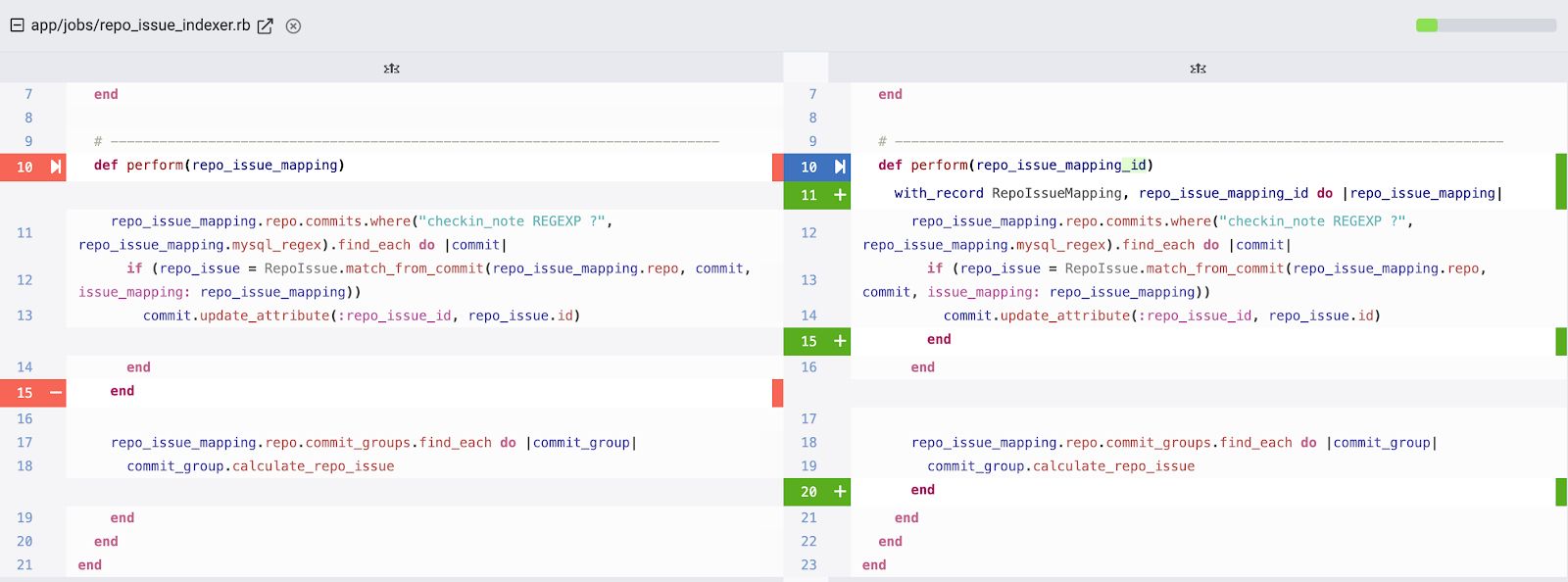
By recognizing whitespace modifications as trivial updates, a diff viewer can focus consideration on the subset of traces the place significant modifications occurred.
One other instance comes from a pull request comparability posted to GitClear’s Youtube channel. It reveals a case the place a file was renamed and a block of code that had initially been within the physique of a React element was extracted to a standalone perform. In GitHub’s Myers-based diff presentation, the change is proven as a brand new, 30+ line, added methodology:
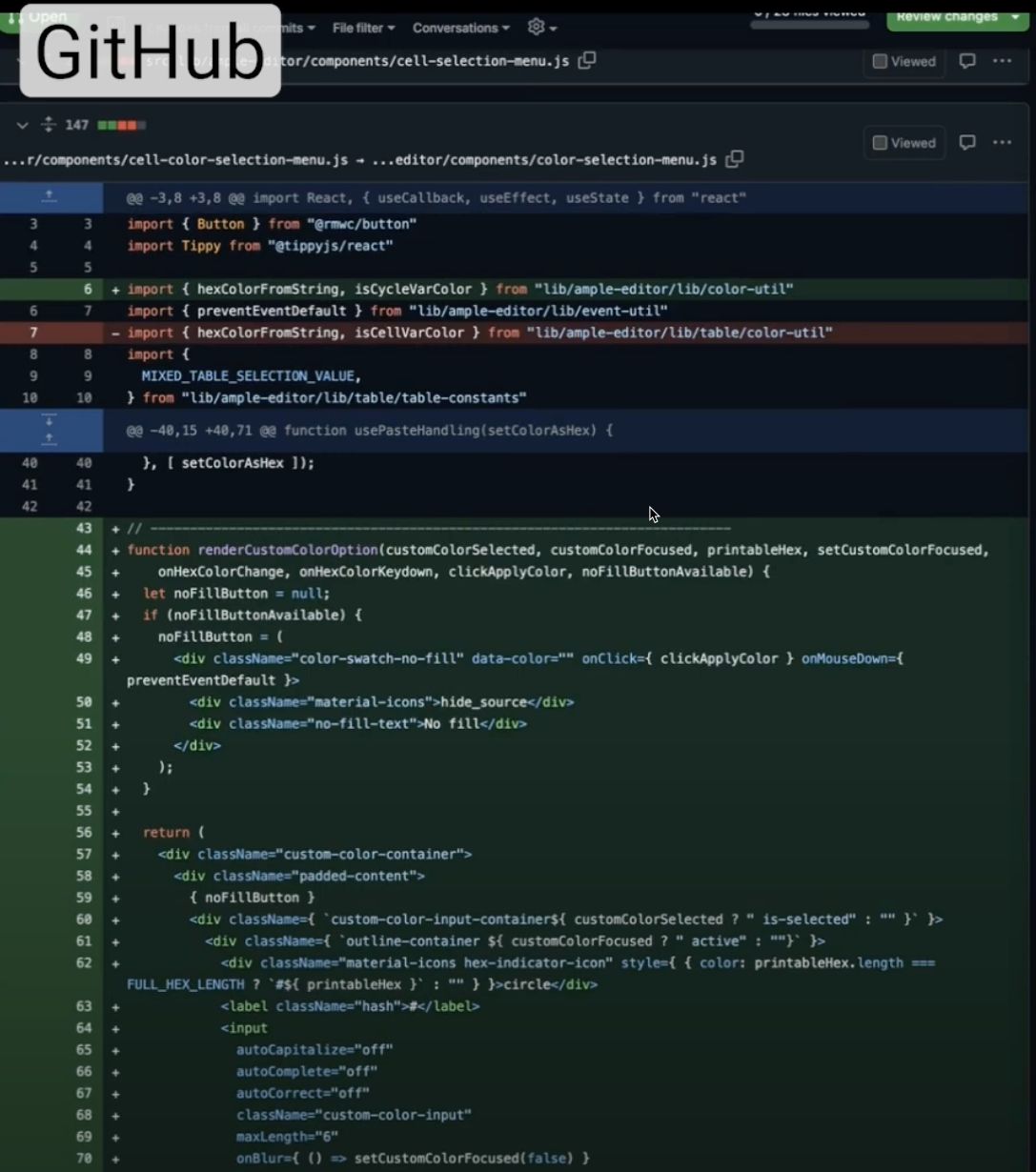
The identical diff, processed by Commit Cruncher, is much less thrilling:
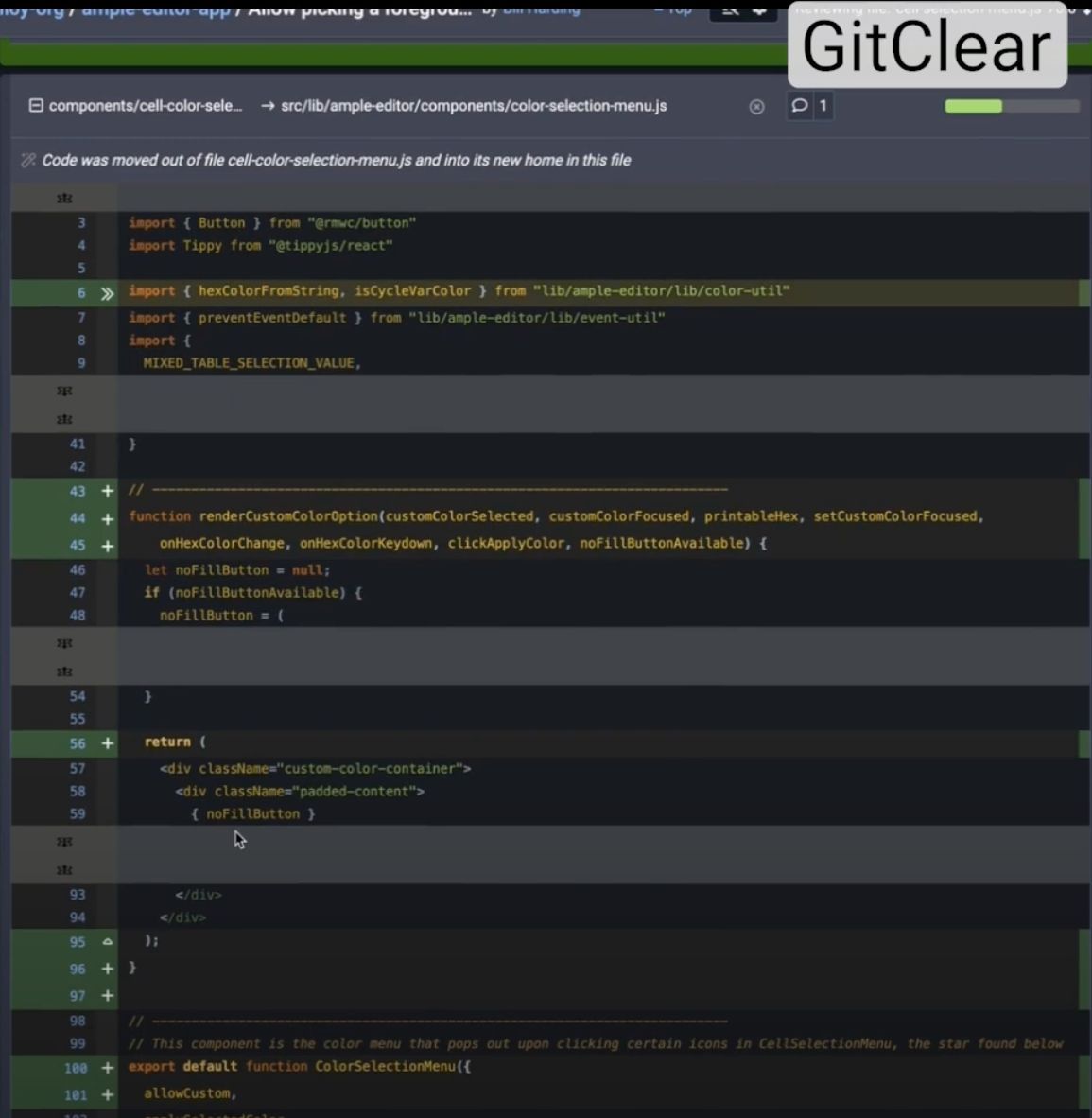
“Much less pleasure” reviewing pull requests is exactly what the common code reviewer seeks. By eliding the no-op modifications to the relocated methodology, the Commit Cruncher presentation conserves a reviewer’s consideration for traces with extra substantive content material variations.
One other line discount alternative is introduced when traces obtain an incremental modification, like this trivial change from a current React commit:
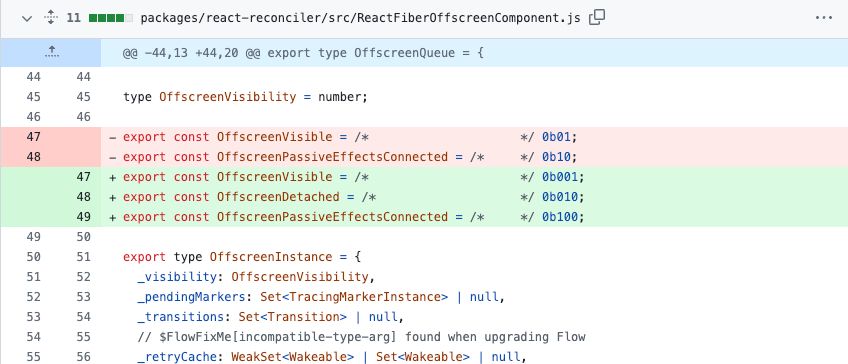
The identical diff by means of a GitClear lens condenses the incremental replace to a single line, the place the brand new (or eliminated) characters are proven inline:
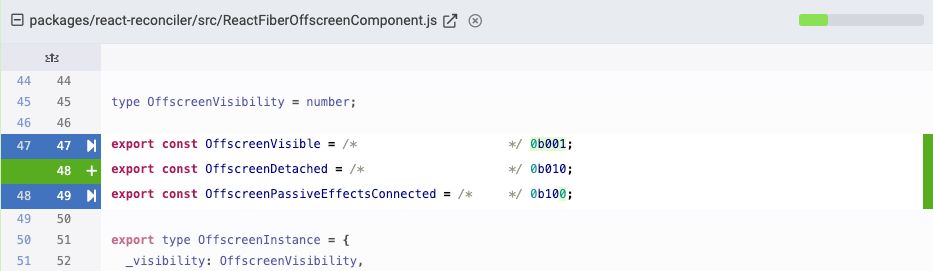
Within the GitClear database, containing multiple billion line modifications, round 10-15% of these modifications are incremental updates like this. These small enhancements add up.
Commit Cruncher employs one other, extra delicate distinction in the way it derives which traces modified in comparison with Myers. To grasp this distinction, contemplate a pull request that features a set of commits, [A, B, C] being proposed for merge.
The Myers diff algorithm works by inspecting two inputs: the repo state earlier than commit A and the state after commit C. The one info that this diff algorithm has obtainable to assemble a visible diff is the state of the repo at two cut-off dates. Contemplate a case the place Commit B renames a file, adopted by Commit C including and eradicating just a few traces from the renamed file. A comparability that considers solely [A, C] would present on the “earlier than” facet the pre-rename model of the renamed file as deleted traces. On the “after” facet, the a whole bunch or hundreds of traces from the renamed file can be introduced as if the file had been newly created.
In distinction, Commit Cruncher employs the extra computationally intensive method of following every modified line by means of every commit that it seems inside, to construct what’s labeled a “Commit Group”:
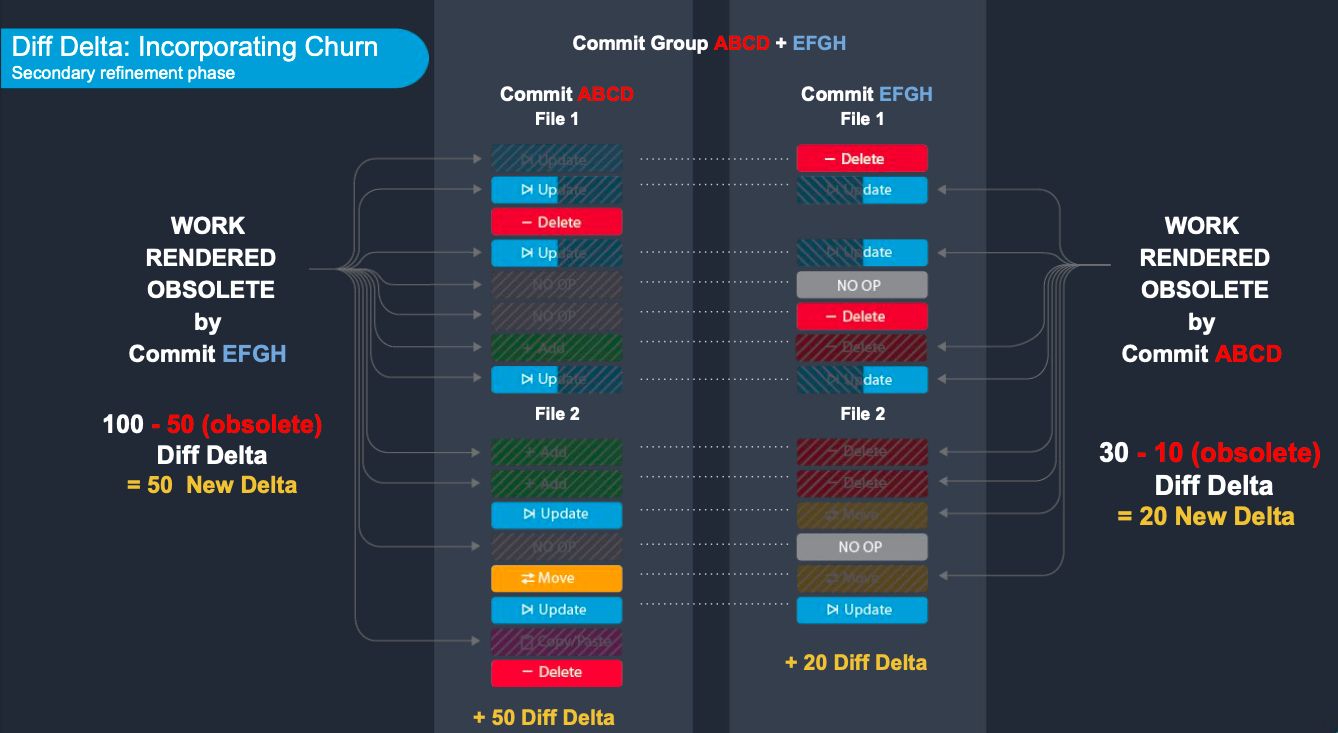
From GitClear Commit Group PDF explainer
There are just a few advantages that emerge from doing the added work of traversing every line by means of its complete commit historical past.
One profit is that, when hovering on the road, the developer can entry a historic document of the commit messages, which regularly elucidates why a specific line advanced into its remaining kind. From GitClear’s video:
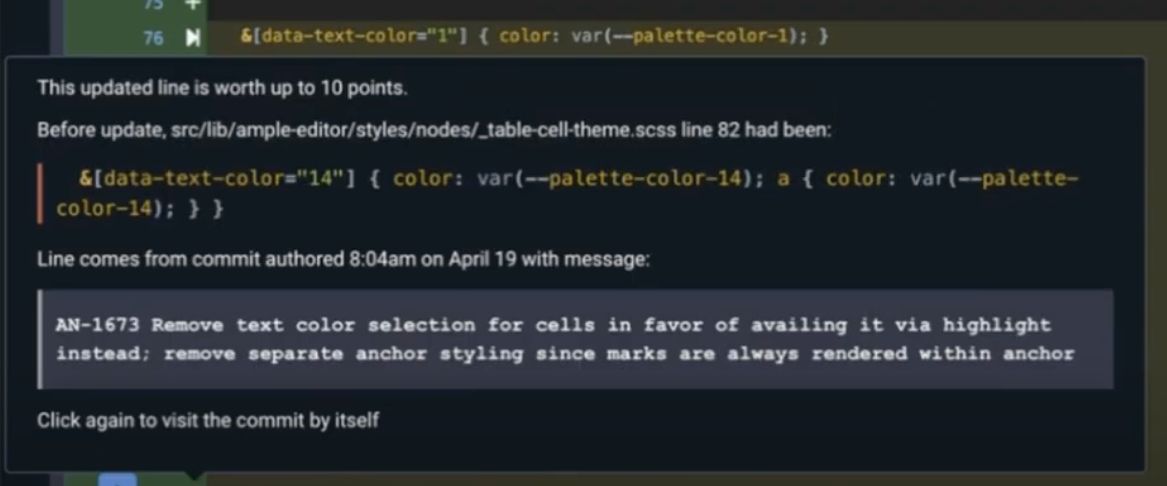
One other profit is that, when a line undergoes a number of modifications like being moved and having a discover/exchange utilized, Commit Cruncher can nonetheless present the reviewer the unique location of the multi-updated line. This implies much less uncertainty about how this line will carry out in a manufacturing surroundings (because it was already deployed within the authentic kind).
To evaluate the real-world affect of utilizing the Commit Cruncher diff algorithm vs. basic Myers, GitClear analyzed 12,638 pull requests that it processed through the second half of Could 2024. The pull requests’ diffs have been processed by GitClear and in comparison with their GitHub equal. The contributing repos have been about 25% common open-source initiatives (React, VS Code, Chromium, Tensorflow) and roughly 75% SaaS clients who had opted into anonymized knowledge sharing.
GitClear used the GitHub API’s compare endpoint to seize the depend of “added” and “deleted” traces that GitHub would present for every pull request. It then recorded the depend of modified traces per pull request, as derived by Commit Cruncher.
Our metric for comparability was the variety of inexperienced or crimson highlighted traces in both the basic Myers diff as used on GitHub (and elsewhere) versus the highlighted traces on GitClear (utilizing up to date diff algorithm). We lumped add, take away, and others right into a single worth, as that’s what any code reviewer would see.
Right here have been the 12,638 pull requests, with common and median modified line counts for variously-sized pull requests:
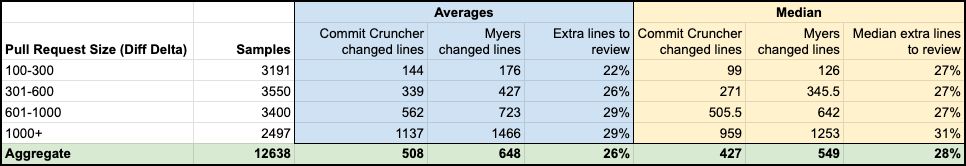
The information reveals that builders reviewing with GitClear and its “Commit Cruncher” algorithm have been introduced with, on common, 22% to 29% fewer modified traces to evaluate per pull request.
The median distinction between “Myers” and “Commit Cruncher” ranges from 27% to 31%, relying on the entire magnitude of the change set. This suggests that updating git diff processing instruments might cut back the quantity of traces requiring evaluate by nearly a 3rd. An in depth description of the database queries that have been used to supply these numbers is obtainable within the “Appendix” section A6.
Whereas the uncooked line counts recommend that Commit Cruncher-processed pull requests would require fewer traces to be reviewed, Lead builders, CTOs, and VPs of engineering could pretty marvel if there are much less fascinating modifications coupled with a brand new diff processor.
To analysis these questions, 48 developer analysis members have been recruited randomly from the online platform CodeMentor. Every participant was assigned to evaluate two completely different pull requests in a programming language acquainted to them. Every pair of pull requests alternated which git platform it was proven on. For instance, the primary participant would evaluate PR #1 on GitHub and PR #2 on GitClear. The second participant would evaluate PR #1 on GitClear and PR #2 on GitHub.
The analysis supplies tabular outcomes for these 48 developer interviews, gathering knowledge to guage:
1) Do reductions in “traces to evaluate” truly translate to a corresponding discount in “real-world time to evaluate“?
2) Does reviewing pull requests in much less time correlate with damaging or optimistic impacts to “proportion of bugs found“?
A study by Bacchelli and Bird that helps the rivalry that, when reviewing code, most understanding and a focus is spent searching for “Discovering Defects”:
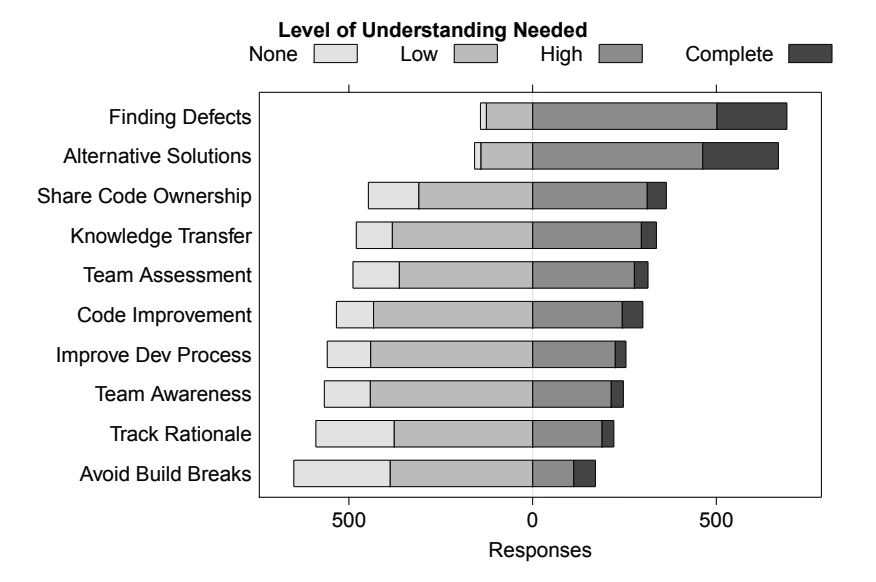
Statements from GitClear’s survey members help this interpretation for “code evaluate motivation”:
- “Probably the most tough factor when doing a code evaluate is knowing the rationale for the change.”
- “Understanding the code takes many of the reviewing time.”
- “In a profitable code evaluate submission, the writer is bound that his friends perceive and approve the change.”
To shorten the code evaluate course of, a device must speed up the speed at which a developer evolves from “encountering code” to “contextualizing it” to “evaluating whether or not it satisfies the writer’s objectives.”
Our interviews discovered reductions in every of three pull request programming languages examined:
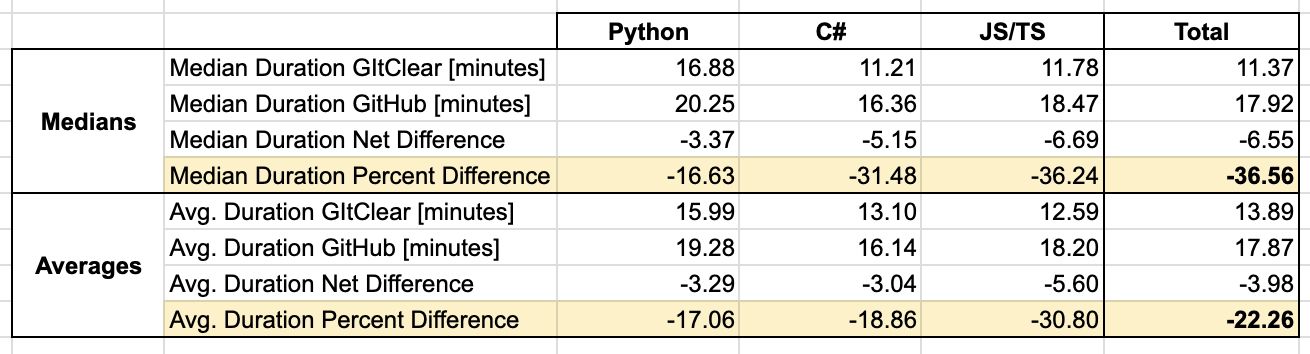
This is how the aggregated knowledge seems to be in graph kind, with the yellow bars illustrating absolutely the distinction between the 2 knowledge factors:
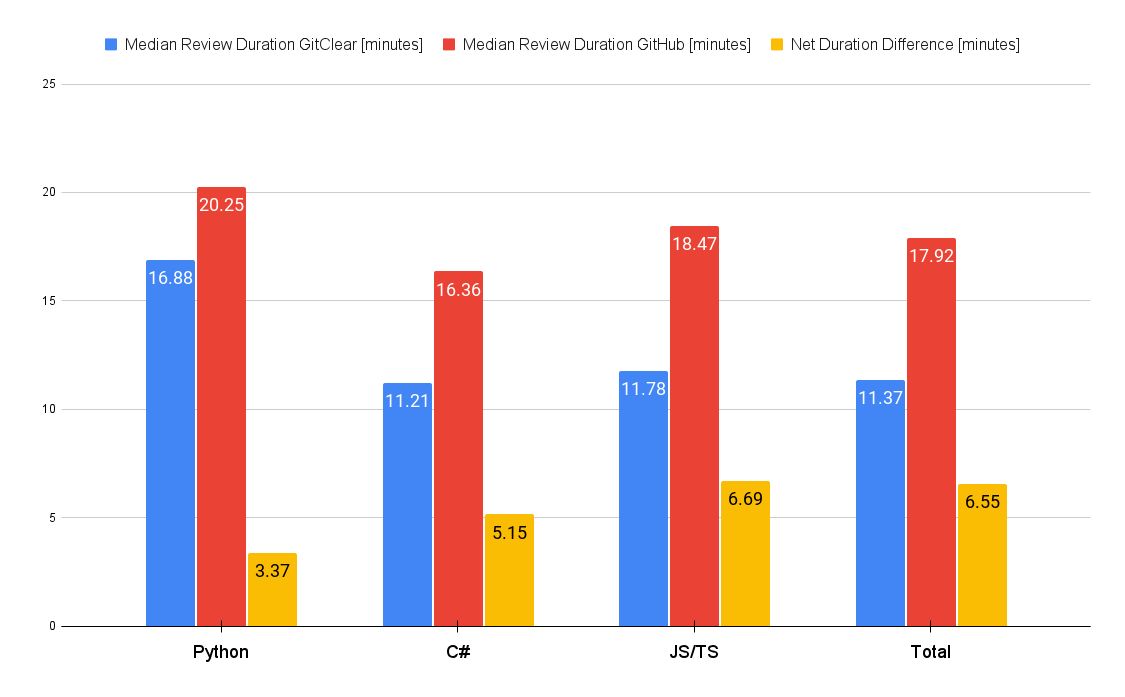
Probably the most notable distinction was for the pull request #25610, with a 42% lower (13.2 common minutes with GitClear’s Commit Cruncher vs. 22.7 minutes with GitHub).
GitClear’s analysis discovered pull request comprehension throughout the margin of error for GitClear and GitHub reviewers.
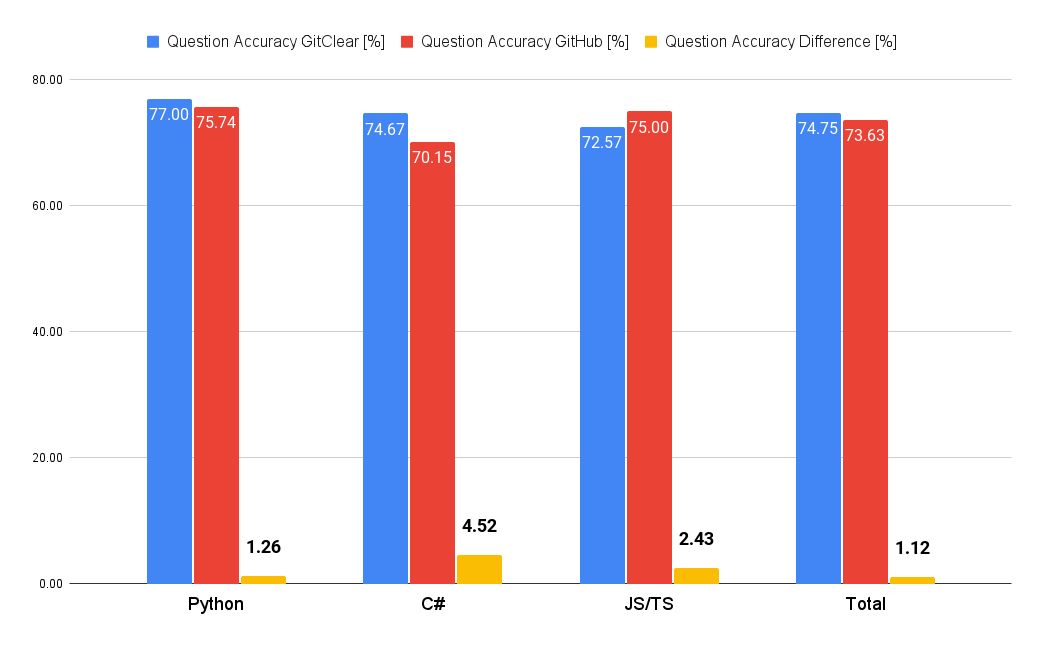
Query accuracy percentages have been lower than 5% completely different. A statistically insignificant profit was present in favor of Commit Cruncher diffs when evaluated throughout all the pool outcomes.
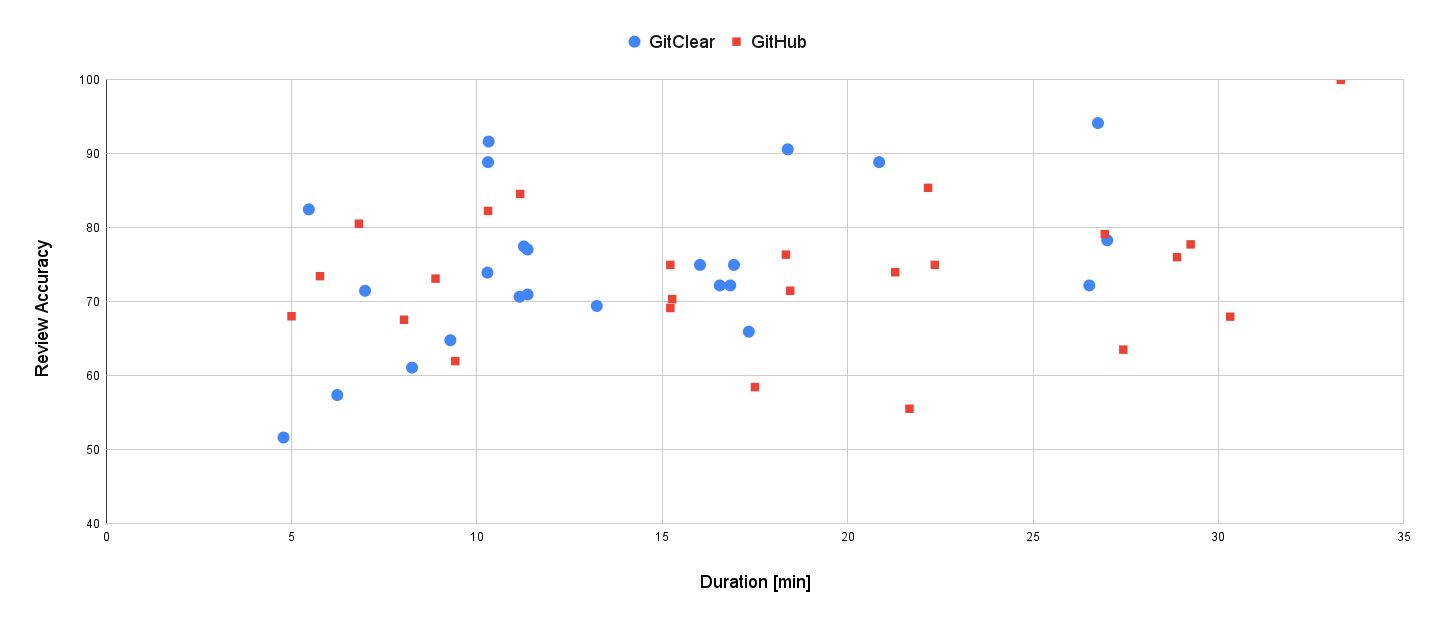
The uncooked knowledge of the analysis metrics for every particular person session was plotted utilizing a scatter chart, evaluating query accuracy scores in opposition to the code evaluate period, as seen within the determine beneath. The code evaluate period lower is visually outlined by the elevated frequency of blue (GitClear) dots on the left facet of the chart.
Maybe probably the most substantive query that involves thoughts whereas studying this analysis: how has diff viewing advanced to be extra homogenous than any of “developer IDE,” “git platform,” or “system OS”? In comparison with the innumerable programming languages which have come and gone within the many years because the Myers algorithm was created, how did so many merchandise converge on an answer developed 40 years in the past? We provide two concepts on this puzzler.
The primary chance is that almost all builders don’t even acknowledge that it’s attainable to signify a diff with out Myers. Since diffs have seemed the identical since their profession started, no person thinks to go in search of different choices.
The second motive is that Myers is a a lot “cleaner” algorithm than any successor can be. Selecting Myers gives an immediately obtainable, multi-generation-tested means to point out a diff. And in relation to reviewing a diff, getting each line proper, each time, is extremely vital.
Whereas Commit Cruncher reveals important enchancment over Myers on this analysis, it depends upon a set of iteratively tuned heuristics. Not one of the massive git platforms can afford to imperil person belief as they iterate on a extra granular illustration of what modified inside a commit. Very like all supply management suppliers herded to git as soon as it was confirmed dependable at enterprise-scale, no single firm is more likely to evolve their diff device till they’ve robust incentives to take action. As future analysis corroborates {that a} financial savings of greater than 20% is feasible in pull request evaluate time, the present stasis could finish.
The proof introduced herein raises new questions for the oldest device nonetheless broadly utilized by modern builders.
The implications of a 28% drop in code evaluate time might be important. Scale the 2022 CodeGrip code review survey outcome to a 10-member group and the maths works out to about 50 hours per week spent reviewing code. If the mixed developer and supervisor salaries common $150,000, then a 10-developer group invests round $16,000 monthly of wage towards code evaluate. This doesn’t embody the difficult-to-measure (however acquainted to any developer) time wanted to context shift into and out of “code evaluate mode.”
A discount of the magnitude noticed right here would imply this 10-developer group might reallocate 40 hours monthly for extra coding, much less reviewing (one hour/week * 4 weeks/month * 10 builders). Contemplating that code review is often one of the most unpleasant, high-willpower chores included in a developer’s tasks, the morale enchancment gained by lowering code evaluate time could rival the positive factors in “time saved.”
The complete textual content and citations of GitClear’s newest analysis is out there to obtain free: 30% Less is More: Exploring Strategies to Cut Pull Request Review Time. The pull request device will be trialed without charge by visiting our Best GitHub Alternative Pull Request Review Tool web page, which permits pasting a pull request URL from GitHub to permit a direct, side-by-side comparability of the competing diff algorithms.


