Reminiscence is an important a part of fashionable microprocessor programs reminiscent of computer systems, smartphones, networking units, sensible devices and even rockets and satellites. Since their introduction within the late 1960’s, Semiconductor Recollections are the popular alternative of reminiscence overtaking magnetic (tapes and discs) and optical codecs. There are two kinds of semiconductor reminiscences: Unstable (RAM) and Non-Unstable (ROM). On this information, we are going to check out two several types of risky reminiscences i.e., SRAM and DRAM. We’ll perceive their primary operation and discover out the variations between SRAM vs DRAM.
Overview of Semiconductor Reminiscence
The primary essential query is what precisely is Reminiscence in microprocessor programs? Reminiscence is a tool or system that has the power to retailer digital data (both quickly or completely).
Within the early days of computing, engineers used magnetic tapes and discs to retailer data. The polarities of the magnetic discipline (north and south) on a round substrate signify the digital logic values (0 and 1).
However the technological developments in semiconductor design and manufacturing gave rise to Semiconductor Reminiscence. On this system, we retailer the knowledge utilizing built-in circuits (involving transistors, capacitors, fuses and so on., on a single semiconductor substrate).
In contrast to magnetic tapes or discs, semiconductor reminiscence doesn’t have any mechanical or transferring elements. Therefore, we additionally name semiconductor as Stable-State Reminiscence (as transistors, that are the constructing blocks of many semiconductor units, are referred to as Stable-State Gadgets).
Earlier than continuing additional, we have to perceive a few essential terminology related to Reminiscence. We confer with the knowledge saved in reminiscence as Knowledge and the smallest potential information is a Bit (a logic 1 or logic 0).
Once we place an information into the reminiscence, we name this operation as Writing information. Equally, after we retrieve information from reminiscence, we name it as Studying information.
Classification of Semiconductor Reminiscence
Allow us to now see alternative ways during which we are able to classify semiconductor reminiscences.
Unstable vs Non-Unstable Reminiscence
We will classify Semiconductor Reminiscence (as that is the principle subject of debate, we are going to keep on with Semiconductor Recollections and ignore different kinds of reminiscences) into two classes based mostly on whether or not they retain information after we take away energy to them. They’re Unstable and Non-Unstable Recollections.
The time period Unstable Reminiscence refers to these reminiscence units that can’t maintain the information within the occasion of energy off (both the system is shut down manually or attributable to an influence failure).
Non-Unstable Reminiscence means a reminiscence gadget that may maintain information even after we take away the facility. As Unstable Reminiscence doesn’t must trouble about storing the information completely, it’s barely sooner than non-volatile counterpart. Therefore, we use risky reminiscence to carry important system data whereas the system is working. Non-Unstable reminiscence can also be essential, in spite being slower because it holds start-up instructions, the OS (working system) or firmware (in case of embedded programs) and likewise purposes.
Learn Solely vs Learn/Write
One other technique to classify semiconductor relies on how we entry the information. They’re: Learn Solely and Learn/Write. A Learn Solely Reminiscence or ROM is a type of reminiscence which shouldn’t be altered whereas the system is working because it holds important system information and purposes.
In distinction, we are able to learn and write to a Learn/Write Reminiscence even when the system is working, because it holds short-term information.
Random Entry vs Sequential Entry
The ultimate technique to classify semiconductor reminiscence relies on entry location. They’re Random Entry and Sequential Entry. With Random Entry Reminiscence or RAM, we are able to entry any reminiscence location at any time.
However this isn’t potential with Sequential Entry Reminiscence. Because the identify suggests, we are able to entry information solely sequentially and all reminiscence areas usually are not accessible instantly. An instance of sequential entry reminiscence is magnetic tapes. With the intention to entry a location, the system has to spin the tape spool to that location by passing by all of the earlier areas.
An essential level right here is that the majority semiconductor reminiscences are Random Entry Recollections. That is the place we have now a confusion with respect to the phrases RAM and ROM.
The time period ROM (Learn Solely Reminiscence) technically means a reminiscence that can not be modified whereas the system is working. We one way or the other related it with Non-Unstable Reminiscence.
Coming to RAM (Random Entry Reminiscence), it technically means we are able to entry information from any reminiscence location nearly instantaneously (in distinction to sequential reminiscence the place we have now to attend till we attain that location). Once more, we one way or the other related RAM with Unstable Reminiscence.
For the remainder of the dialogue, we are going to ignore the true that means of the phrases and proceed to affiliate RAM with Unstable Reminiscence and ROM with Non-Unstable Reminiscence.
Some widespread and well-liked non-volatile reminiscence applied sciences are:
- ROM (Learn Solely Reminiscence)
- MROM (Masks Learn Solely Reminiscence)
- PROM (Programmable Learn Solely Reminiscence)
- EPROM (Erasable Programmable Learn Solely Reminiscence)
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Learn Solely Reminiscence)
- Flash Reminiscence
There are solely two children of Unstable Reminiscence Applied sciences. They’re:
- SRAM (Static Random Entry Reminiscence)
- DRAM (Dynamic Random Entry Reminiscence)
Within the subsequent couple of sections, we are going to be taught briefly about SRAM and DRAM and likewise examine SRAM vs DRAM.
What’s SRAM?
SRAM is brief for Static Random Entry Reminiscence. It’s a kind of Unstable Reminiscence that’s primarily used as embedded reminiscence (inside registers of microprocessor and cache). SRAM is just like a bistable Flip-Flop, the place we retailer information by setting or clearing the state of the flip-flop.
The time period static in SRAM implies that it doesn’t want a reminiscence refresh and as soon as the information is written, it stays till energy is provided. That is in distinction to DRAM, which wants periodic refresh to maintain the reminiscence even when it’s linked to energy (because it shops the information as a cost on a capacitor – we are going to be taught extra within the subsequent part).
As SRAM is deeply embedded into the structure of the microprocessor, the fabrication course of is just like that of a CPU core.
Construction of SRAM
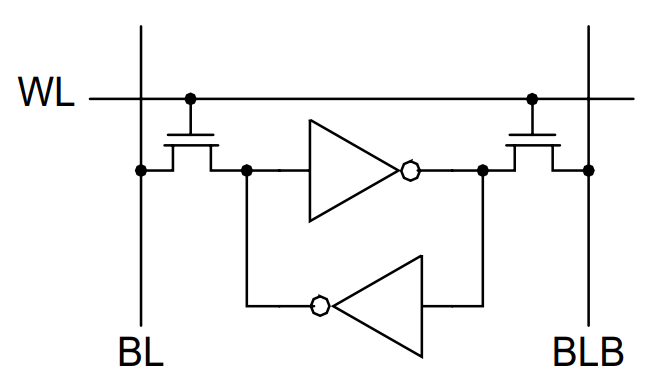
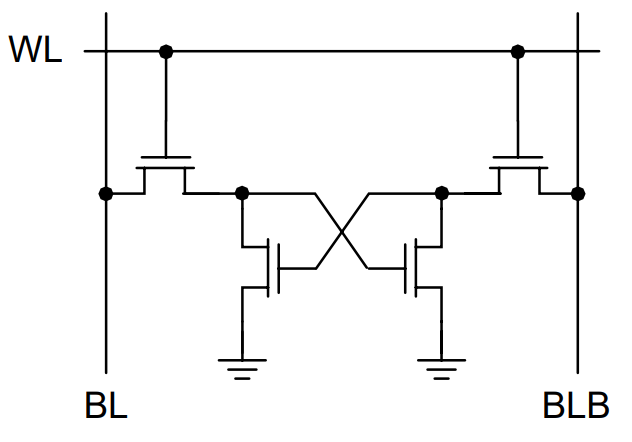
The next reveals a primary construction of a 1-bit SRAM Reminiscence Cell. Right here, a Reminiscence Cell is the smallest group of elements that may maintain 1-bit of information.
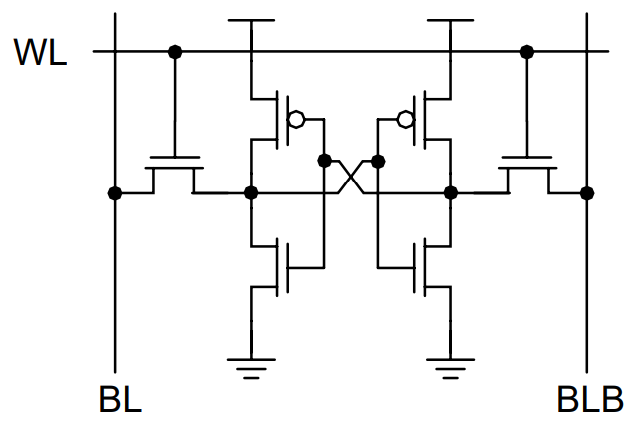
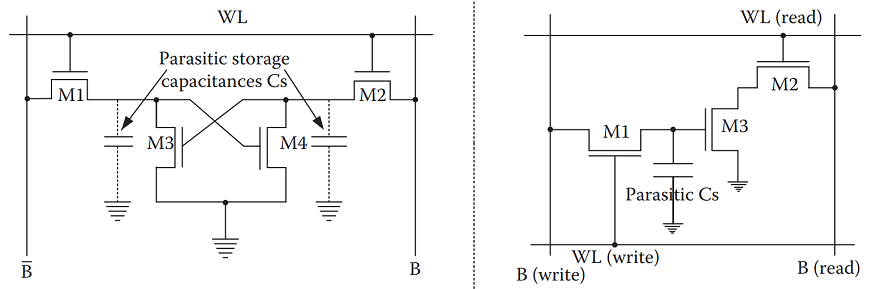
From the picture, the circuit appears just a little bit advanced however truly it’s a cross-coupled inverter with two go transistors. Following picture reveals the break-up of the inverters with NMOS and PMOS transistors. This circuit is barely simpler to grasp.
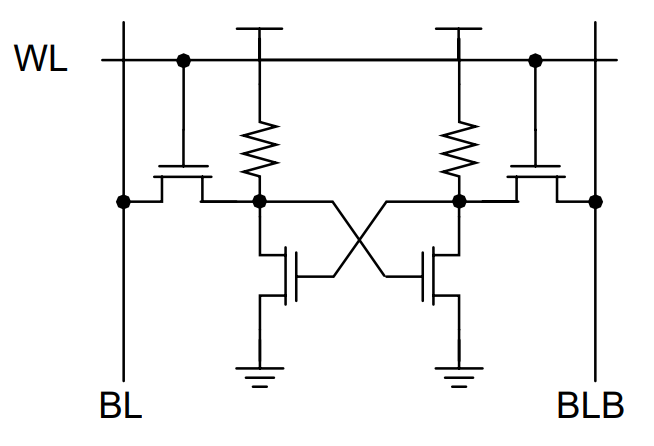
The 2 PMOS transistors within the inverters act as pull-ups and the 2 NMOS transistors act as pull-downs. Whereas early SRAM designs used all 6 transistors – 6T (4 in cross-coupled inverters and two go transistors), one other well-liked design was utilizing Polysilicon Load Resistors as pull-ups as a substitute of PMOS Transistors.
This considerably diminished the dimensions of the reminiscence cell because it basically has solely 4 transistors whereas the load resistors (that are of excessive resistance) are made up of a polysilicon layer on prime of the transistors.
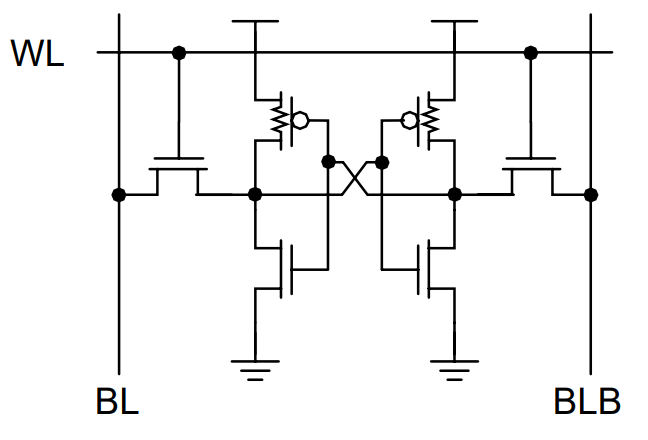
There are a pair extra designs of SRAM Reminiscence cell. One changed the big poly-load resistors (as they wanted to be barely bigger to beat leakage present) with polysilicon PMOS. Some great benefits of this design are that they will nonetheless be fabricated with Poly-PMOS layer on prime of the NMOS layer and the general traits are higher than poly-load resistor design counterparts.
As the dimensions of cache built-in throughout the CPU die is growing, having a layer on prime of the common silicon grew to become advanced. The end result was a 4 transistor (4T) design with no pull-up load. This considerably diminished the dimensions of the reminiscence cell because it had solely 4 transistors however designers needed to take further care with respect to leakage currents.
Of all these designs, the 6T SRAM Reminiscence Cell continues to be the favored alternative from fabrication standpoint because of the complexities of poly-load layer. You may need heard of CPU Cache Reminiscence. It’s truly an SRAM kind reminiscence embedded on the die of the CPU.
What’s DRAM?
Whereas we examine the SRAM circuit with a bistable latching circuit, issues are fairly completely different in terms of DRAM. For starters, a DRAM Cell (we are going to see particulars later), we use the cost saved (or the dearth of cost) on a capacitor to signify the binary information.
The rationale such kind of reminiscence is called “Dynamic” is as a result of the cost on the capacitor slowly leaks away even when the circuit is linked to energy provide. To beat this leakage, we have now to recharge (referred to as Reminiscence Refresh) the capacitor periodically.
Even with the extra complexity of the reminiscence refresh circuit, the benefit of DRAM is its low value per bit, excessive reminiscence density and excessive capability. Because of this, DRAM grew to become the “primary reminiscence” of contemporary microprocessor programs. The RAM sticks that we use in our desktop and laptops (DIMMs and SODIMMs) are literally DRAM.
Construction of DRAM
Earlier DRAM designs (within the Nineteen Seventies) had 4 or three transistors with one or two parasitic storage capacitors. These have been giant with important chip space and excessive value per bit. Added to the fundamental circuit is the extra circuit to refresh the cost on the capacitor in a periodic interval.
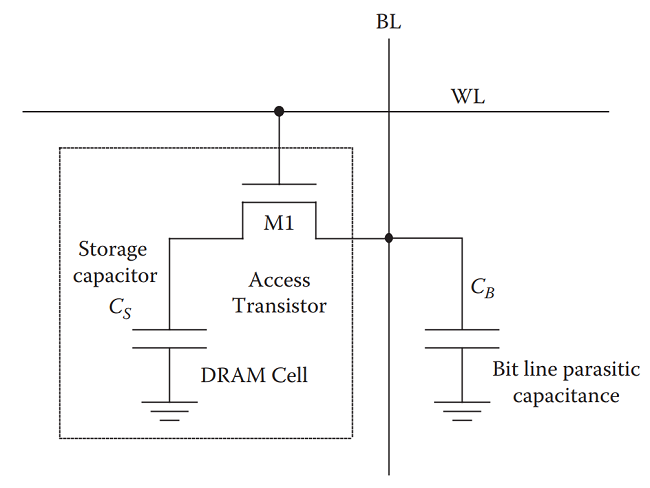
Engineers and scientists have been in a position to scale back the dimensions of the DRAM cell dramatically with a brand new one transistor one capacitor (1T-1C) design. The next picture reveals the favored 1T DRAM Cell with a storage capacitor.
As a single DRAM cell wants only one transistor (and a capacitor) to retailer 1-bit, the world of DRAM cell may be very lower than a SRAM Cell (which requires 6 transistors to retailer 1-bit). Therefore, the reminiscence density of DRAM is considerably larger than SRAM. Additionally, the price of fabrication can also be much less in case of DRAM.
All the pc reminiscence that we add to motherboard utilizing DIMM (Twin in-line Reminiscence Module) and SO-DIMM (Small Define DIMM) sticks is definitely DRAM. Technically, it’s DDR SDRAM (Double Knowledge Fee Synchronous Dynamic Random Entry Reminiscence) with DDR4 and DDR5 being the newest iterations.
Comparability of SRAM vs DRAM
Allow us to now examine SRAM vs DRAM with respect to value, efficiency, density and different essential parameters.
| SRAM | DRAM |
| Static Random Entry Reminiscence or SRAM is a sort of Unstable Reminiscence. | Dynamic Random Entry Reminiscence can also be a sort of Unstable Reminiscence. |
| It’s carried out utilizing six transistors (6T) to type a bistable latching circuit (just like a flip-flop) that holds the information. | DRAM is carried out utilizing one transistor and one capacitor (1T1C) and the cost on the capacitor (or lack thereof) represents the binary information. |
| As it’s a risky reminiscence, it retains/holds information so long as there’s energy to the circuit with none further circuitry. Therefore, it’s Static. | Even DRAM is a risky reminiscence. Which suggests it could maintain/retain information so long as there’s energy. However for the reason that cost on the capacitor slowly leaks away, there can be further circuit to periodically refresh the cost and preserve the information intact. Therefore, it’s Dynamic. |
| SRAM wants 6 transistors to retailer 1-bit information. | DRAM wants just one transistor (and a capacitor) to retailer 1-bit information. |
| This implies, the dimensions of 1 SRAM Cell may be very giant. | With 1T1C design, the dimensions of 1 DRAM Cell is comparatively very small. |
| Massive cell measurement means low reminiscence density (variety of reminiscence cells per unit space). | Reminiscence Density of DRAM is considerably excessive attributable to is small measurement. |
| The price of fabricating SRAM is excessive attributable to 6T design. | Despite the fact that including capacitor requires separate manufacturing approach, the price of general fabrication of DRAM may be very much less. |
| The pace of entry (learn or write) may be very excessive. In truth, in reminiscence hierarchy, they’re on the prime with CPU Registers, CPU Cache. | Entry occasions are comparatively sluggish than SRAM. They’re subsequent in line to SRAM in reminiscence hierarchy. |
| Energy consumption of SRAM is mostly much less as there aren’t any parasitic leakages. | The leakage of capacitor and the requirement of periodic cost refresh implies that general energy consumption of DRAM is barely extra. |
| On account of their low reminiscence density and excessive fabrication value, SRAM capability is usually restricted to few megabytes (MBs). | The reminiscence capability of DRAM may be very giant, usually in gigabytes (GBs). |
| The widespread software is on-chip cache reminiscence (L2, L3) in microprocessors or SRAM (that acts as a brief storage) in microcontrollers. | DRAM is usually obtainable as DIMM sticks for computer systems (that sit on the motherboards). Small units (some laptops, telephones, tablets and so on.) have DRAM modules soldered instantly on the PCB. |
NOTE: We didn’t delve deep into the workings of SRAM and DRAM as this information focuses on the fundamentals of SRAM vs DRAM. In case you are , we are able to do in-depth guides on the working of each SRAM and DRAM.
Conclusion
SRAM and DRAM are two essential kinds of semiconductor reminiscence in fashionable computing programs. Whereas they each are risky in nature, the way in which they retailer the information is totally completely different. On this information, we noticed the fundamentals of semiconductor reminiscences, SRAM, DRAM together with their respective buildings. We additionally noticed an in depth SRAM vs DRAM comparability.