Routing administration is a vital part of networking. Other than routing packets from supply to vacation spot it entails advanced administration of packets to keep up efficiency of the community. The protocols which monitor efficiency of the community and work on detection and removing of redundant hyperlinks are equally necessary at layer 2 operations. It tends to resolve problems with community efficiency degradations when techniques use shared telecommunication channels on native space networks.
As we speak we glance extra intimately about RSTP – Speedy Spanning tree protocol, its options and the way it’s configured in a community.
What’s RSTP-Speedy Spanning Tree Protocol?
Speedy Spanning Tree Protocol is a quick convergent and superior model of STP or Spanning Tree protocol. It’s used to forestall loops in bridges and broadcast storms in LANs redundant networks. It achieves quicker convergence by bypassing the blocking and listening state of STP and allowing just one energetic path between two gadgets. Disabled connections are used as backup / redundant paths to help energetic connection in occasion of failure. The IEEE normal for Speedy Spanning Tree protocol is 802.1w.
Commonalities between STP and RSTP
- Lowest bridge ID is elected as root bridge in each STP and RSTP connection
- In STP and RSTP BPDUs are forwarded between switches
- Each in STP and RSTP root and designated ports are elected in comparable method
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Speedy Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) are distinguished by their functionality to forestall loops in community topologies containing redundant hyperlinks. Whereas the STP was initially developed to deal with this situation, it has sure limitations, together with a prolonged convergence time and an incapability to adapt swiftly to modifications in community topology. The RSTP, then again, overcomes these drawbacks and supplies a extra environment friendly resolution for loop prevention whereas being aware of dynamic alterations within the community setup.
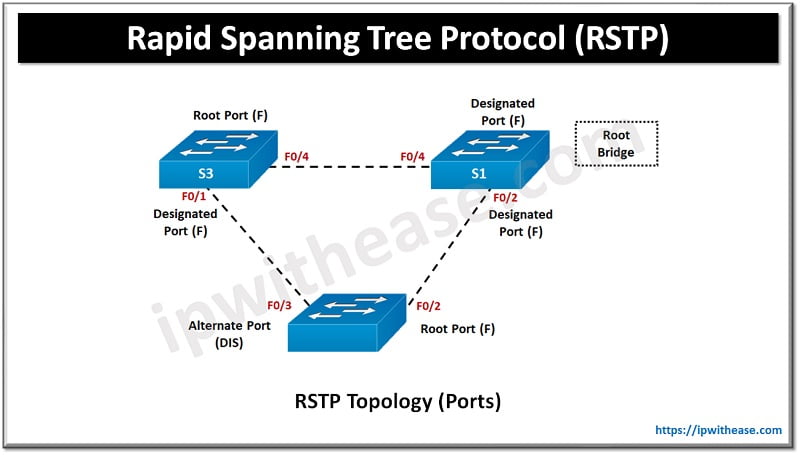
RSTP Port Roles
RSTP has 4 port roles as below:
- Root port is greatest path port to ahead knowledge to bridge.
- Designated port is a non-root port used as forwarded port for every LAN section.
- Backup port is backup path to section to which one other bridge port connection is established.
- Alternate port is a backup port having much less fascinating value of path. They continue to be in block state.

RSTP helps three port states as below:
- Discarding – No knowledge transport occurs on this state
- Studying – Ports find out about MAC deal with however no frames are forwarded
- Forwarding – ports ship knowledge and are in full operational state



Options of RSTP
- Community loops prevention
- Prevention of redundancy
- It supplies quicker convergence
- Backward appropriate with STP
- No synthetic ahead delay timers required
Speedy Spanning Tree Protocol: Configuration
Step 1: To configure RSTP – Speedy Spanning Tree protocol it must be enabled.
s1# configure terminal
Present configuration command, one per line, Finish with CNTL/Z.
s1(config)#spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
s1(config)#interface fa0/2
s1(config)#spanning-tree link-type point-to-point
s1(config)#finish
s1(config)#clear spanning-tree detected protocols
s1(config)#
To test if swap runs RSTP use beneath command
S1(config)#present spanning-tree
Step 2: Configure S1 because the ROOT bridge for VLAN1 and 5
s1# configure terminal
Present configuration command, one per line, Finish with CNTL/Z.
s1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 root major
s1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 5 root major
s1(config)#finish
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
s1#
s1(config)#Present spanning-tree vlan 1
VLAN001
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp
Root ID Precedence 24577
Handle 0014.f2d2.4180
Value 9
Port 216 (Port-channel21)
Hey Time 3 sec Max Age 15 sec Ahead Delay 12 sec
Bridge ID Precedence 32766 (precedence 32765 sys-id-ext 1)
Handle 001c.57d8.9000
Hey Time 3 sec Max Age 15 sec Ahead Delay 12 sec
Growing old Time 300 sec
Interface Position Sts Value Prio.Nbr Kind
——————- —- — ——— ——– —————————
Po21 Root FWD 9 128.216 P2p
Po23 Altn BLK 9 128.232 P2p
s1(config)#Present spanning-tree vlan 5
VLAN005
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp
Root ID Precedence 24586
Handle 0014.f2d2.4180
Value 9
Port 216 (Port-channel21)
Hey Time 2 sec Max Age 15 sec Ahead Delay 12 sec
Bridge ID Precedence 32777 (precedence 32767 sys-id-ext 10)
Handle 001c.57d8.9000
Hey Time 2 sec Max Age 15 sec Ahead Delay 12 sec
Growing old Time 300 sec
Interface Position Sts Value Prio.Nbr Kind
——————- —- — ——— ——– —————————
Po21 Root FWD 9 128.216 P2p
Po23 Altn BLK 9 128.232 P2p
Proceed Studying:
High 50 STP Interview Questions
Varieties of Digital Non-public Community (VPN) & its Protocol