Cybersecurity researchers have taken the wraps off a beforehand undocumented spyware and adware focusing on the Apple macOS working system.
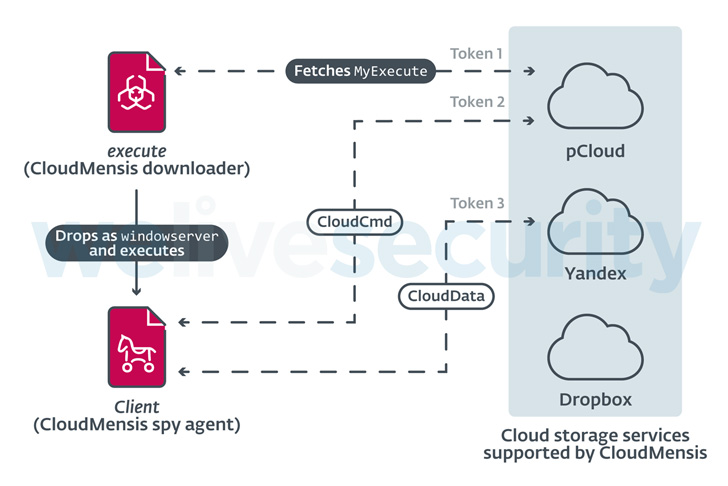
The malware, codenamed CloudMensis by Slovak cybersecurity agency ESET, is alleged to solely use public cloud storage companies similar to pCloud, Yandex Disk, and Dropbox for receiving attacker instructions and exfiltrating information.
“Its capabilities clearly present that the intent of its operators is to assemble info from the victims’ Macs by exfiltrating paperwork, keystrokes, and display captures,” ESET researcher Marc-Etienne M.Léveillé stated in a report revealed right this moment.
CloudMensis, written in Goal-C, was first found in April 2022 and is designed to strike each Intel and Apple silicon architectures. The preliminary an infection vector for the assaults and the targets stay unknown as but. However its very restricted distribution is a sign that the malware is getting used as a part of a extremely focused operation directed in opposition to entities of curiosity.
The assault chain noticed by ESET abuses code execution and administrative privileges to launch a first-stage payload that is utilized to fetch and execute a second-stage malware hosted on pCloud, which, in flip, exfiltrates paperwork, screenshots, and e mail attachments, amongst others.
The primary-stage downloader can be recognized to erase traces of Safari sandbox escape and privilege escalation exploits that make use of 4 now-resolved safety flaws in 2017, suggesting that CloudMensis could have flown beneath the radar for a few years.
The implant additionally comes with options to bypass the Transparency, Consent, and Management (TCC) safety framework, which goals to make sure that all apps receive person consent earlier than accessing information in Paperwork, Downloads, Desktop, iCloud Drive, and community volumes.
It achieves this by exploiting one other patched safety vulnerability tracked as CVE-2020-9934 that got here to mild in 2020. Different features supported by the backdoor embody getting the listing of working processes, capturing screenshots, itemizing information from detachable storage gadgets, and working shell instructions and different arbitrary payloads.
On high of that, an evaluation of metadata from the cloud storage infrastructure exhibits that the pCloud accounts had been created on January 19, 2022, with the compromises commencing on February 4 and peaking in March.
“The final high quality of the code and lack of obfuscation exhibits the authors is probably not very conversant in Mac growth and are usually not so superior,” M.Léveillé stated. “Nonetheless lots of sources had been put into making CloudMensis a robust spying software and a menace to potential targets.”