Information Science
Grasp it at this time — SQL Queries to wash the info and put together it for evaluation
“No information is clear, however most is helpful.”
— Dean Abbott
Actual world information is sort of all the time messy. And as a knowledge scientist or analyst it’s good to uncover the information in regards to the information. To take action, the info have to be tidy and free from errors. Therefore, the very first step is to wash the info.
Due to this fact, I summarized 5 suggestions which you’ll be able to apply to wash messy information in SQL.
It’s a fast learn, which you’ll be able to end along with your espresso and grasp a few of the fascinating tips to wash the soiled information.
You may simply navigate to your favourite half utilizing this index.
· Discover Lacking Values in Your Information
· Flag Sure Data
· Clear Up Messy Values
· Bucket Values into Segments or Bins
· Right Information Sorts
Word: I’m utilizing SQLite and a self created Dummy_Sales_Data created utilizing Faker which you will get on my Github repo for Free below MIT license!!
Okay, let’s get began…
The issue of lacking worth is kind of widespread in lots of real-life datasets. Lacking worth can bias the outcomes of knowledge evaluation or the machine studying fashions or scale back the accuracy of the mannequin or can merely make the info evaluation troublesome.
Use these ready-to-go queries to search out out lacking values from the info in addition to to verify if any patterns are related to the info.
- Lacking information in a specific column
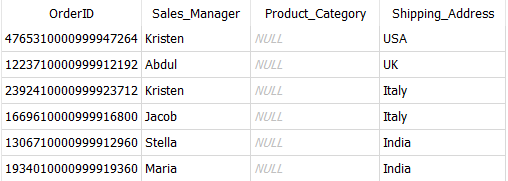
As an illustration, discovering out the OrderIDs the place Product_Category is lacking.
SELECT OrderID,
Sales_Manager,
Product_Category,
Shipping_Address
FROM Dummy_Sales_Data_v1
WHERE Product_Category IS NULL
Furthermore, yow will discover out if the dataset follows any tendencies when some column has lacking values.
- Patterns related to Lacking Information
For an occasion, in our instance, let’s attempt to discover out if information follows any particular sample when the values within the column Product_Category are lacking.
SELECT Shipping_Address,
OrderID,
Amount,
Product_Category
FROM Dummy_Sales_Data_v1
WHERE Product_Category IS NULL
GROUP BY Shipping_Address, OrderID, Amount

On this manner, you’ll be able to look at, is there any particular sample adopted by the info when Product_Category is lacking. You may cross any variety of columns in WHERE clause and get the patterns related to these lacking values.
Moreover, as a substitute of lacking values, you’ll be able to all the time uncover patterns in information when a column has particular worth, as proven under.
SELECT Shipping_Address,
OrderID,
Amount
FROM Dummy_Sales_Data_v1
WHERE Product_Category LIKE 'Healthcare'
GROUP BY Shipping_Address, OrderID, Amount
ORDER BY Amount DESC

On this instance, you came upon the Amount and Transport deal with patterns related to Healthcare merchandise and clearly see the highest 5 delivery addresses by order Amount.
One other greatest apply is to create a easy binary column to flag some information. This can be utilized within the later levels whereas performing information evaluation.
For instance, suppose you need to mark all of the information as Dirty_Data if the Delivery_Time is lacking within the dataset.
SELECT OrderID,
Sales_Manager,
Shipping_Address,
Delivery_Time,
CASE WHEN Delivery_Time IS NULL THEN 1
ELSE 0
END AS Dirty_data
FROM Dummy_Sales_Data_v1

A brand new column, Dirty_Data will get added to the output with values as 0 and 1. When this output is taken out as excel or any editor, it’s going to definitely make additional duties straightforward reminiscent of discovering out the Orders the place Delivery_Time is lacking.
On this manner you’ll be able to embrace as many alternative situations to outline soiled information and flag it.
Subsequent, let’s see find out how to clear up the info which is simply too granular than requirement.
Top-of-the-line method to clear up granular values is to standardize them.
Typically, column values can be found at extra granular degree than required. In such situations, it makes extra sense to standardize them at a better degree.
For instance, a delivery deal with column in accommodates names of nations, which will be standardized to area names reminiscent of Europe, North America and so forth, as proven within the under question.
SELECT OrderID,
Shipping_Address,
CASE WHEN Shipping_Address IN ('Germany','UK') THEN 'Europe'
ELSE 'Different'
END AS area
FROM Dummy_Sales_Data_v1

So, the knowledge on delivery deal with on nation degree was granular, so that you standardized it at area degree.
For simplicity, I used just one WHEN assertion inside CASE, nonetheless, we will anytime create extra values in area column through the use of a number of WHEN statements.
Going a step forward and making the question a bit bit advanced, you’ll be able to analyze the info throughout a number of information.
That is traditional use-case of CASE assertion in SQL. The CASE assertion is SQL’s manner of dealing with if-then logic.
You may get deeper insights into the CASE assertion from my newest article — 5 Superior SQL Ideas You Ought to Know in 2022.
Let’s see, how this can be utilized to bucket values into bins.
Suppose, you need to categorize the Shipping_Cost into Low, Medium and Excessive relying on the worth.
SELECT OrderID,
Shipping_Cost,
CASE WHEN Shipping_Cost < 25 THEN 'Low'
WHEN Shipping_Cost BETWEEN 25 AND 32 THEN 'Medium'
WHEN Shipping_Cost > 32 THEN 'Excessive'
END AS cost_range
FROM Dummy_Sales_Data_v1

Because of this, a brand new column cost_range will get created containing values Low, Medium, Excessive relying on the column shipping_cost.
Effectively, these bins serves the aim for categorizing the delivery price. Nonetheless, if you wish to order the information as per cost_range both in ascending (from low to excessive) or descending order (from excessive to low), these bins should not working. See under,
SELECT OrderID,
Shipping_Cost,
CASE WHEN Shipping_Cost < 25 THEN 'Low'
WHEN Shipping_Cost BETWEEN 25 AND 32 THEN 'Medium'
WHEN Shipping_Cost > 32 THEN 'Excessive'
END AS cost_range
FROM Dummy_Sales_Data_v1
ORDER BY cost_range DESC

The information are ordered in descending order of cost_range and Medium comes on the highest, which is inaccurate.
The right output would have the rows with cost_range excessive on high, adopted by Medium and Low. And to get this appropriate outcome, it’s good to identify your bins well.
One of many easiest method you’ll be able to obtain it’s, use numbers as proven under.
SELECT OrderID,
Shipping_Cost,
CASE WHEN Shipping_Cost < 25 THEN '1. Low'
WHEN Shipping_Cost BETWEEN 25 AND 32 THEN '2. Medium'
WHEN Shipping_Cost > 32 THEN '3. Excessive'
END AS cost_range
FROM Dummy_Sales_Data_v1
ORDER BY cost_range DESC
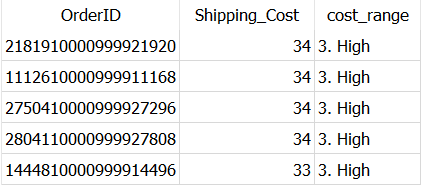
Now, you bought it appropriate. Right here, word the usage of 3, 2, 1 to reorder the values.
Going forward, incorrect information sorts for columns will be one of many important impediment in information extraction and evaluation. Let’s see how one can take care of it in SQL.
In the actual world, typically, the info kind of the column shouldn’t be precisely assigned or the info kind assigned initially not serves the aim on your job.
For instance, a date-time column is usually saved as textual content column or the column with float values is assigned the info kind integer.
Solely extraction of knowledge kind won’t have any downside with incorrect information sorts, nonetheless, if you happen to want to be part of the tables and the info kind of the widespread column in each tables is totally different, the question will return an error.

CAST operate !!!
In SQL, CAST operate is used to explicitly convert a given information kind to a special information kind in a SQL database. It has the best syntax as,
CAST(column_name AS new_data_type)
the place column_name is the identify of the column whose information kind you need to change.
An fascinating truth about CAST is, it moveable throughout totally different Database Administration Methods reminiscent of Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle and can work the identical on every of them.
Let’s rapidly undergo an instance.
Suppose, you need to convert the Shipment_Cost to drift worth, which is initially saved as an integer.
SELECT Shipping_Cost,
CAST(Shipping_Cost AS REAL) AS Shipping_Cost_float
FROM Dummy_Sales_Data_v1

Easy it’s!
Nonetheless, it additionally has some limitations. You cannot merely convert the column from one to different information kind.
for an occasion, the date column can’t be transformed into float. The 2 information sorts — current and new one — needs to be comparable in nature.
Microsoft has offered an fascinating chart, which can be utilized as fast reference to grasp which information sorts are suitable with one another, which you’ll be able to obtain from right here.
That’s all!








