Proof-of-concept (Poc) code has been launched for a now-patched high-severity safety flaw within the Home windows CryptoAPI that the U.S. Nationwide Safety Company (NSA) and the U.Ok. Nationwide Cyber Safety Centre (NCSC) reported to Microsoft final yr.
Tracked as CVE-2022-34689 (CVSS rating: 7.5), the spoofing vulnerability was addressed by the tech big as a part of Patch Tuesday updates launched in August 2022, however was solely publicly disclosed two months afterward October 11, 2022.
“An attacker might manipulate an present public x.509 certificates to spoof their id and carry out actions equivalent to authentication or code signing because the focused certificates,” Microsoft stated in an advisory launched on the time.
The Home windows CryptoAPI presents an interface for builders so as to add cryptographic companies equivalent to encryption/decryption of knowledge and authentication utilizing digital certificates to their functions.
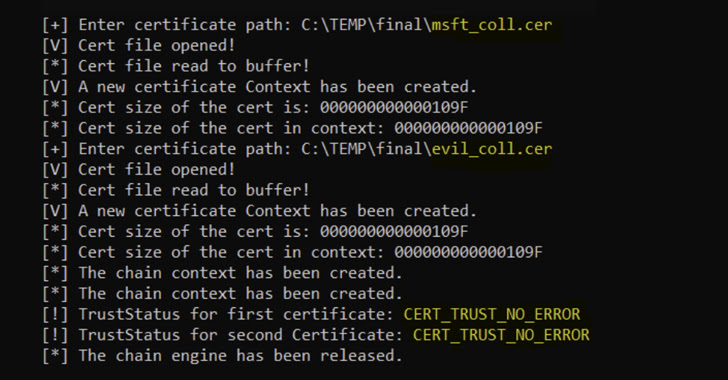
Net safety firm Akamai, which launched the PoC, stated CVE-2022-34689 is rooted in the truth that the weak piece of code that is designed to simply accept an x.509 certificates carried out a test that solely relied on the certificates’s MD5 fingerprint.
MD5, a message-digest algorithm used for hashing, is actually cryptographically damaged as of December 2008 owing to the chance of birthday assaults, a cryptanalytic technique used to seek out collisions in a hash perform.
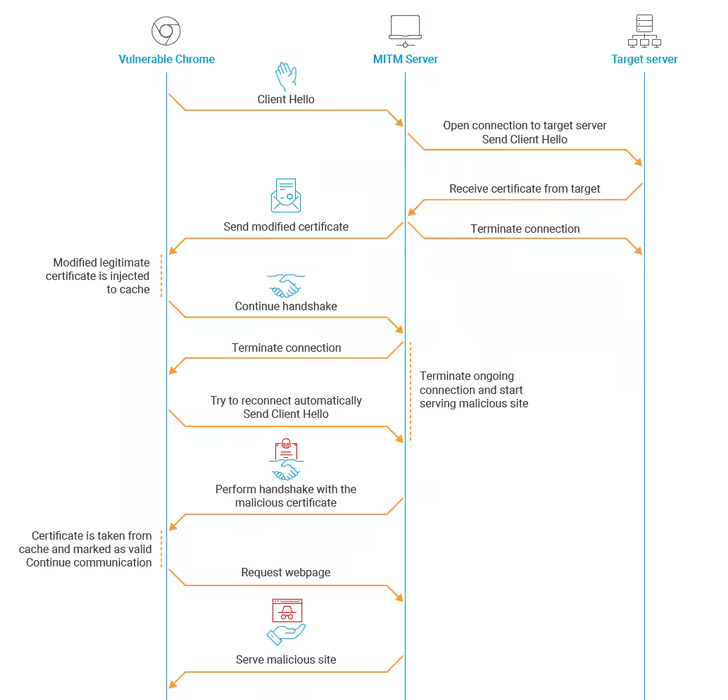
The online impact of this shortcoming is that it opens the door for a foul actor to serve a modified model of a authentic certificates to a sufferer app, after which create a brand new certificates whose MD5 hash collides with the rigged certificates and use it to masquerade as the unique entity.
In different phrases, the flaw could possibly be weaponized by a rogue interloper to stage a mallory-in-the-middle (MitM) assault and redirect customers counting on an previous model of Google Chrome (model 48 and earlier) to an arbitrary web site of the actor’s selecting just because the prone model of the online browser trusts the malicious certificates.
“Certificates play a significant function in id verification on-line, making this vulnerability profitable for attackers,” Akamai stated.
Though the flaw has a restricted scope, the Massachusetts-headquartered agency identified “there’s nonetheless loads of code that makes use of this API and is likely to be uncovered to this vulnerability, warranting a patch even for discontinued variations of Home windows, like Home windows 7.”