LockBit ransomware assaults are continuously evolving by making use of a variety of methods to contaminate targets whereas additionally taking steps to disable endpoint safety options.
“The associates that use LockBit’s providers conduct their assaults in keeping with their desire and use totally different instruments and methods to realize their aim,” Cybereason safety analysts Loïc Castel and Gal Romano stated. “Because the assault progresses additional alongside the kill chain, the actions from totally different circumstances are inclined to converge to related actions.”
LockBit, which operates on a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) mannequin like most teams, was first noticed in September 2019 and has since emerged as probably the most dominant ransomware pressure this yr, surpassing different well-known teams like Conti, Hive, and BlackCat.
This includes the malware authors licensing entry to associates, who execute the assaults in trade for utilizing their instruments and infrastructure and earn as a lot as 80% of every profitable ransom fee obtained from the victims.
LockBit additionally makes use of the favored strategy of double extortion to exfiltrate huge quantities of information previous to encrypting the belongings of the goal, netting the cybercriminal syndicate no fewer than 850 victims on its knowledge leak website as of Might 2022.
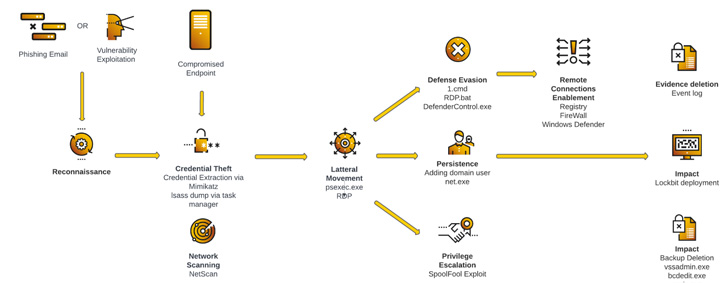 |
| Assault Life Cycle – Case Examine 1 |
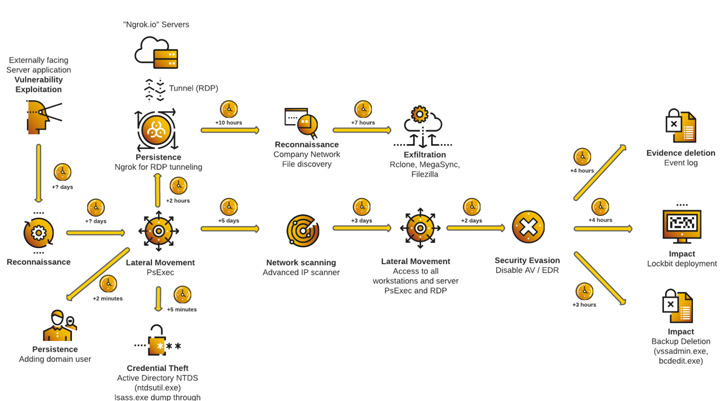 |
| Assault Life Cycle – Case Examine 2 |
In keeping with a leak website knowledge evaluation by Palo Alto Networks Unit 42, LockBit accounted for 46% of all ransomware-related breach occasions for the primary quarter of 2022. In June alone, the group has been tied to 44 assaults, making it probably the most lively ransomware pressure.
LockBit ransomware assaults are recognized to make use of a number of avenues for preliminary an infection: Exploiting publicly-exposed RDP ports, counting on phishing emails to obtain malicious payloads, or leveraging unpatched server flaws that enable the associates to realize distant entry to the focused community.
Following this step are reconnaissance and credential theft actions, which allow the actors to maneuver laterally throughout the community, set up persistence, escalate privileges, and launch the ransomware. That is additionally accompanied by working instructions to delete backups and subvert detection by firewalls and antivirus software program.
Within the three years since LockBit appeared on the scene, the RaaS scheme has obtained two notable upgrades, with the risk actors debuting LockBit 2.0 in June 2021 and launching the third installment of the service, LockBit 3.0, final month with help for Zcash cryptocurrency fee choices and a bug bounty program — the primary for a ransomware group.
The initiative claims to supply rewards of as much as $1 million for locating safety blind spots in its web site and locker software program, submitting sensible concepts, doxing the top of the gang’s associates program, or figuring out ways in which may expose the IP of the server internet hosting the web site on the TOR community.
The bug bounty program is one more signal that hacker teams are more and more functioning as legit IT enterprises, incorporating HR departments, common function releases, and even bonuses for fixing difficult issues.
Nevertheless, indications are that LockBit 3.0, additionally referred to as LockBit Black, is impressed by one other ransomware household generally known as BlackMatter, a rebranded model of DarkSide that shuttered in November 2021.
“Giant parts of the code are ripped straight from BlackMatter/Darkside,” Emsisoft researcher Fabian Wosar stated in a tweet earlier this week. “Guess it’s clear that LockBit obtained their soiled fingers on one other group’s code.”



