A .NET-based evasive crypter named DarkTortilla has been utilized by menace actors to distribute a broad array of commodity malware in addition to focused payloads like Cobalt Strike and Metasploit, seemingly since 2015.
“It could actually additionally ship ‘add-on packages’ resembling extra malicious payloads, benign decoy paperwork, and executables,” cybersecurity agency Secureworks mentioned in a Wednesday report. “It options strong anti-analysis and anti-tamper controls that may make detection, evaluation, and eradication difficult.”
Malware delivered by the crypter contains data steakers and distant entry trojans (RATs) resembling Agent Tesla, AsyncRat, NanoCore, and RedLine Stealer. “DarkTortilla has versatility that related malware doesn’t,” the researchers famous.
Crypters are software program instruments that use a mixture of encryption, obfuscation, and code manipulation of malware in order to bypass detection by safety options.
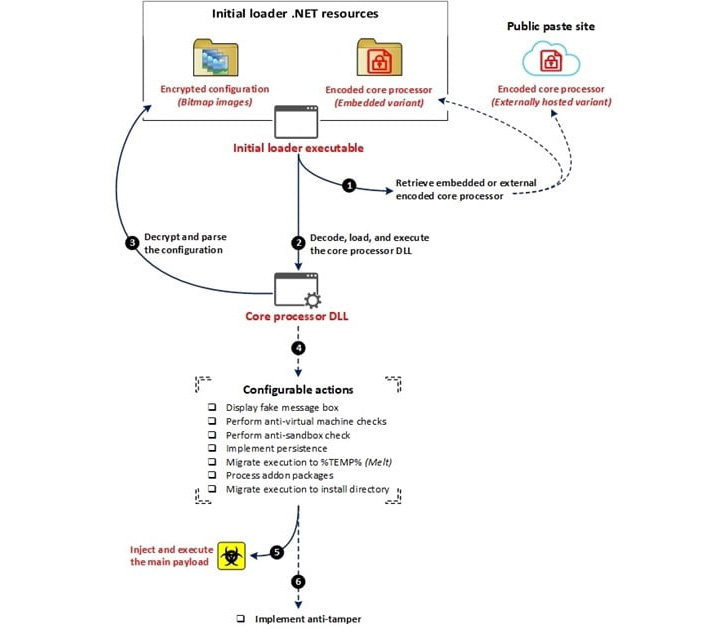
The supply of DarkTortilla happens by way of malicious spam emails which include archives with an executable for an preliminary loader that is used to decode and launch a core processor module both embedded inside itself or fetched from textual content storage websites resembling Pastebin.
The core processor is then chargeable for establishing persistence and injecting the first RAT payload into reminiscence with out leaving a path on the file system via an elaborate configuration file that additionally permits it to drop add-on packages, together with keyloggers, clipboard stealers, and cryptocurrency miners.
DarkTortilla is additional noteworthy for its use of anti-tamper controls that guarantee each the processes used to execute the parts in reminiscence are instantly rerun upon termination.
Particularly, the persistence of the preliminary loader is achieved via a second executable known as a WatchDog that is designed to maintain tabs on the designated course of and rerun it ought to it’s killed.
This method is harking back to an analogous mechanism adopted by a menace actor referred to as Moses Employees, which, earlier this yr, was discovered counting on a watchdog-based method to stop any interruption to its payloads. Additionally employed are two different controls to ensure the continued execution of the dropped WatchDog executable itself and the persistence for the preliminary loader.
Secureworks mentioned it recognized a median of 93 distinctive DarkTortilla samples being uploaded to the VirusTotal malware database per week over a 17-month interval from January 2021 to Might 2022.
“DarkTortilla is able to evading detection, is very configurable, and delivers a variety of widespread and efficient malware,” the researchers concluded. “Its capabilities and prevalence make it a formidable menace.”