Amazon Internet Companies (AWS) has resolved a cross-tenant vulnerability in its platform that may very well be weaponized by an attacker to realize unauthorized entry to sources.
The problem pertains to a confused deputy drawback, a kind of privilege escalation the place a program that does not have permission to carry out an motion can coerce a more-privileged entity to carry out the motion.
The shortcoming was reported by Datadog to AWS on September 1, 2022, following which a patch was shipped on September 6.
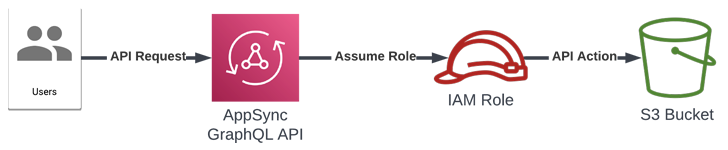
“This assault abuses the AppSync service to imagine [identity and access management] roles in different AWS accounts, which permits an attacker to pivot right into a sufferer group and entry sources in these accounts,” Datadog researcher Nick Frichette mentioned in a report printed final week.
In a coordinated disclosure, Amazon mentioned that no prospects have been affected by the vulnerability and that no buyer motion is required.
It described it as a “case-sensitivity parsing problem inside AWS AppSync, which might probably be used to bypass the service’s cross-account position utilization validations and take motion because the service throughout buyer accounts.”
AWS AppSync provides builders GraphQL APIs to retrieve or modify knowledge from a number of knowledge sources in addition to routinely sync knowledge between cellular and internet functions and the cloud.
The service can be used to combine with different AWS companies via particular roles designed to carry out the mandatory API calls with the required IAM permissions.
Whereas AWS does have safeguards in place to forestall AppSync from assuming arbitrary roles by validating the position’s Amazon Useful resource Title (ARN), the issue stems from the truth that the verify may very well be trivially bypassed by passing the “serviceRoleArn” parameter in a decrease case.
This conduct might then be exploited to offer the identifier of a job in a unique AWS account.
“This vulnerability in AWS AppSync allowed attackers to cross account boundaries and execute AWS API calls in sufferer accounts by way of IAM roles that trusted the AppSync service,” Frichette mentioned.
“Through the use of this technique, attackers might breach organizations that used AppSync and acquire entry to sources related to these roles.”