A brand new encryption normal for Web of Issues (IoT) ought to assist advance safety for these linked gadgets in companies, producers, vital infrastructure, and different sectors working this tools.
However many of those gadgets proceed to lag behind in cybersecurity capabilities and practices.
On Feb. 7, the Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Expertise (NIST) introduced it had chosen a gaggle of cryptographic algorithms, generally known as Ascon, to be the formal encryption normal for “light-weight” digital gadgets and their communications. The usual ought to assist gadgets makers and their prospects higher safe the info and gadgets from attackers more and more concentrating on operational expertise though such gadgets have restricted processing energy and storage.
The algorithms enable encryption protections for even the smallest gadgets, NIST pc scientist Kerry McKay stated within the announcement of the usual.
“The world is transferring towards utilizing small gadgets for plenty of duties starting from sensing to identification to machine management, and since these small gadgets have restricted sources, they want safety that has a compact implementation,” she stated. “These algorithms ought to cowl most gadgets which have these types of useful resource constraints.”
Why IoT Is Exploding
Linked gadgets in enterprise and industrial settings are a quickly rising software pushed by two main forces over the previous three years. Initially, the pandemic spurred the necessity to help distant operations, whereas the present issues of a recession are pushing firms to automate operations utilizing linked gadgets.
For instance, the Industrial Web of Issues (IIoT) — an umbrella time period for linked gadgets that monitor and management bodily programs and industrial processes — is predicted to develop dramatically. The variety of industrial IoT connections — a measure of the variety of gadgets deployed — is predicted to greater than double to 36.8 billion in 2025, up from 17.7 billion in 2020, in line with Juniper Analysis.
Nonetheless, the huge development additionally brings an enormous assault floor space. Vulnerabilities within the so-called Prolonged Web of Issues (XIoT), which incorporates each gadgets and the programs that handle these gadgets, jumped 57% within the first half of 2022 persevering with a dramatic rise from the prior yr. On the enterprise facet, safety researchers demonstrated 63 exploitable vulnerabilities in a wide range of linked gadgets at this yr’s Pwn2Own, akin to printers and network-attached storage.
In the meantime, enterprise and industrial IoT gadgets and programs are sometimes used for many years with out common updates, not like standard IT environments, that are changed each three to 5 years and up to date often in between, says Invoice Malik, vice chairman of infrastructure methods at cybersecurity agency Pattern Micro.
“Proper now, tens of 1000’s of business IoT environments are open to the Web, both via carelessness or a lack of information of the dangers,” he says. “Many of those programs ship with default passwords, that are hardly ever modified by the use, and people programs are sometimes incapable of being up to date.”
Light-weight — however Not Mild — Safety
The NIST normal goals to provide even low-power gadgets a base stage of cybersecurity by encrypting saved knowledge and communications. The method took a number of years, beginning with 57 candidates in March 2019, which had been whittled all the way down to 10 finalists in 2021.
“The power to supply safety was paramount, however we additionally needed to take into account components akin to a candidate algorithm’s efficiency and suppleness by way of pace, measurement, and vitality use,” NIST’s McKay acknowledged within the Feb. 7 announcement. “Ultimately, we made a variety that was a superb all-around selection.”
Implementing the NIST normal will take time, as many IoT distributors are nonetheless catching as much as cybersecurity finest practices, with gadgets typically missing robust authentication capabilities, no straightforward solution to distribute and set up patches, and poor visibility into exercise, together with weak or nonexistent logging, Pattern Micro’s Malik says.
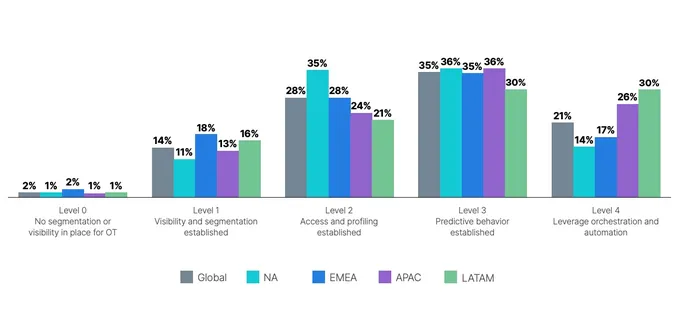
The extent of maturity for the economic sector in North America, for instance, continues to lag behind different another international locations. In comparison with the worldwide common of 57%, solely half the businesses (50%) within the area have adopted applied sciences that search for anomalous habits or use automation and orchestration to handle and safe gadgets, thought-about the highest two tiers of safety maturity for operational expertise, in line with Fortinet’s “2022 State of Operational Expertise and Cybersecurity Report.”
The dangers to linked enterprise and industrial gadgets is rising, particularly in opposition to the manufacturing sector, which accounted for 68% of noticed assaults in opposition to industrial programs within the third quarter of 2022, in line with Dragos, a cybersecurity companies agency. Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has created a web-based battlefield with risk actors on either side concentrating on a wide range of programs and gadgets, aiming at inflicting bodily injury and disruption via cyberattacks.
As enterprises and industries proceed to maneuver towards ubiquitous monitoring and management, enabling sensible factories, sensible cities, and sensible infrastructure, cyberattacks will grow to be extra impactful, Deloitte acknowledged in its “Business 4.0 and Cybersecurity” report.
Detection Alone Is “Not Sufficient”
Specializing in detection, nevertheless, is just not sufficient, says Keao Caindec, a principal analyst with Farallon Expertise Group and chair of the Safety Working Group on the Business IoT Consortium (IIC).
“Plenty of the safety controls that we use as we speak, focus extra on detection and remediation, quite a lot of monitoring after which prioritizing occasions and alerts,” he says. “The issue is that leaves you at all times only one step behind the attacker, so firms want to actually give attention to addressing preliminary entry, stopping compromised entry, stopping unauthorized discovery and reconnaissance and stopping lateral assaults.”
But the flexibility to guard enterprise and industrial IoT stays with firms, which ought to search to realize as a lot visibility as potential into what gadgets are linked to their environments, Caindec says. He factors to an already-pursued defensive framework, zero-trust architectures, as maybe the finest present method to securing enterprise and industrial IoT gadgets and programs.
As well as, firms have to have the highest resolution makers on their facet. Cybersecurity efforts are a major funding, particularly in the event that they embody changing gadgets, so that you want govt help, says Wendy Frank, cyber IoT chief with consultancy Deloitte.
“I believe quite a lot of this comes down to actually speaking to your boards, ensuring they’re conscious of the particular issues round gadgets, as a result of they do not do that for a residing,” she says.


