The Ursnif malware has turn into the newest malware to shed its roots as a banking trojan to revamp itself right into a generic backdoor able to delivering next-stage payloads, becoming a member of the likes of Emotet, Qakbot, and TrickBot.
“This can be a important shift from the malware’s unique objective to allow banking fraud, however is in keeping with the broader menace panorama,” Mandiant researchers Sandor Nemes, Sulian Lebegue, and Jessa Valdez disclosed in a Wednesday evaluation.
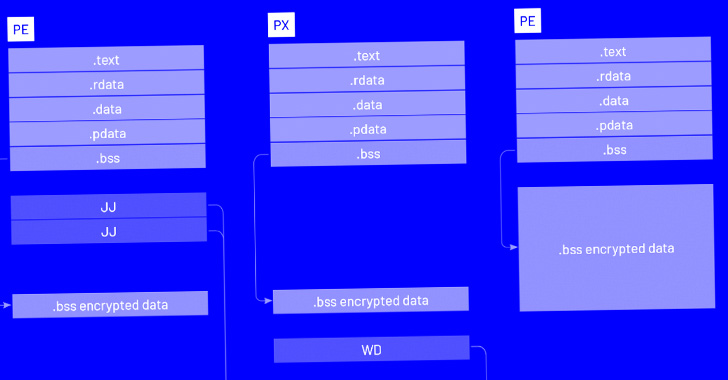
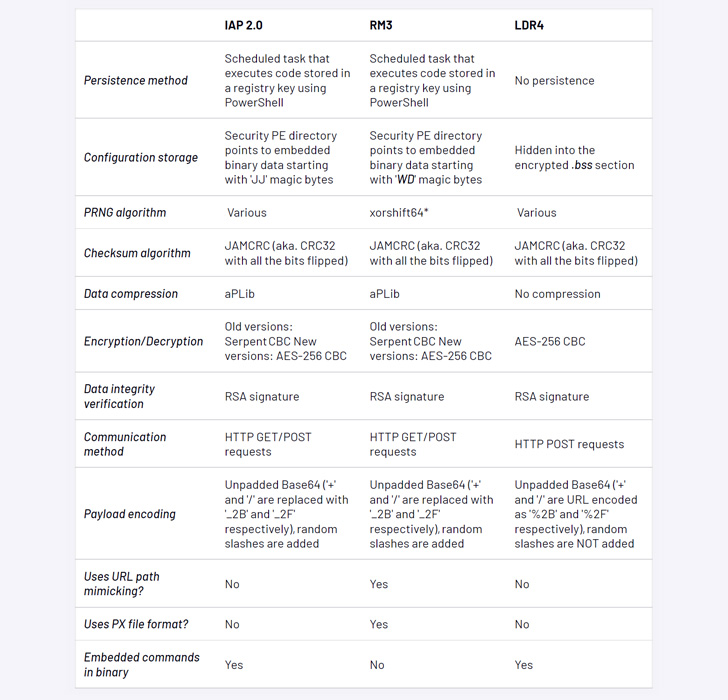
The refreshed and refactored variant, first noticed by the Google-owned menace intelligence agency within the wild on June 23, 2022, has been codenamed LDR4, in what’s being seen as an try to put the groundwork for potential ransomware and knowledge theft extortion operations.
Ursnif, additionally referred to as Gozi or ISFB, is likely one of the oldest banker malware households, with the earliest documented assaults going way back to 2007. Test Level, in August 2020, mapped the “divergent evolution of Gozi” over time, whereas stating its fragmented growth historical past.
Nearly a 12 months later in late June 2021, a Romanian menace actor, Mihai Ionut Paunescu, was arrested by Colombian legislation enforcement officers for his position in propagating the malware to no fewer than 1,000,000 computer systems from 2007 to 2012.
The most recent assault chain detailed by Mandiant demonstrates the usage of recruitment and invoice-related e mail lures as an preliminary intrusion vector to obtain a Microsoft Excel doc, which then fetches and launches the malware.
The most important refurbishment of Ursnif eschews all its banking-related options and modules in favor of retrieving a VNC module and gaining a distant shell into the compromised machine, that are carried out by connecting to a distant server to acquire mentioned instructions.
“These shifts might replicate the menace actors’ elevated focus in direction of collaborating in or enabling ransomware operations sooner or later,” the researchers mentioned.