Client electronics maker Lenovo on Tuesday rolled out fixes to include three safety flaws in its UEFI firmware affecting over 70 product fashions.
“The vulnerabilities could be exploited to realize arbitrary code execution within the early phases of the platform boot, probably permitting the attackers to hijack the OS execution circulation and disable some necessary security measures,” Slovak cybersecurity agency ESET stated in a sequence of tweets.
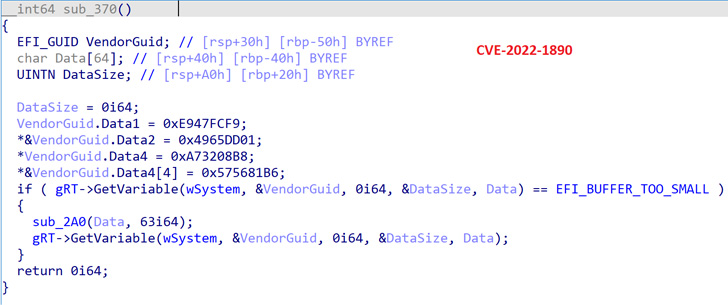
Tracked as CVE-2022-1890, CVE-2022-1891, and CVE-2022-1892, all three bugs relate to buffer overflow vulnerabilities which have been described by Lenovo as resulting in privilege escalation on affected methods. Martin Smolár from ESET has been credited with reporting the failings.
The bugs stem from an inadequate validation of an NVRAM variable referred to as “DataSize” in three completely different drivers ReadyBootDxe, SystemLoadDefaultDxe, and SystemBootManagerDxe, resulting in a buffer overflow that may very well be weaponized to realize code execution.
That is the second time Lenovo has moved to handle UEFI safety vulnerabilities for the reason that begin of the 12 months. In April, the corporate resolved three flaws (CVE-2021-3970, CVE-2021-3971, and CVE-2021-3972) — additionally found by Smolár — that would have been abused to deploy and execute firmware implants.
Customers of impacted gadgets are extremely beneficial to replace their firmware to the newest model to mitigate potential threats.