A brand new covert Linux kernel rootkit named Syslogk has been noticed below growth within the wild and cloaking a malicious payload that may be remotely commandeered by an adversary utilizing a magic community site visitors packet.
“The Syslogk rootkit is closely based mostly on Adore-Ng however incorporates new functionalities making the user-mode software and the kernel rootkit laborious to detect,” Avast safety researchers David Álvarez and Jan Neduchal stated in a report revealed Monday.
Adore-Ng, an open-source rootkit out there since 2004, equips the attacker with full management over a compromised system. It additionally facilitates hiding processes in addition to customized malicious artifacts, information, and even the kernel module, making it tougher to detect.
“The module begins by hooking itself into numerous file programs. It digs up the inode for the foundation filesystem, and replaces that inode’s readdir() perform pointer with certainly one of its personal,” LWN.internet famous on the time. “The Adore model performs just like the one it replaces, besides that it hides any information owned by a particular consumer and group ID.”
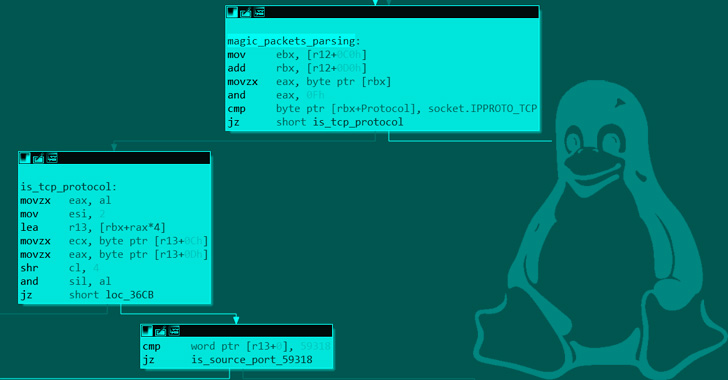
In addition to its capabilities to cover community site visitors from utilities like netstat, housed throughout the rootkit is a payload named “PgSD93ql” that is nothing however a C-based compiled backdoor trojan named Rekoobe and will get triggered upon receiving a magic packet.
“Rekoobe is a chunk of code implanted in professional servers,” the researchers stated. “On this case it’s embedded in a pretend SMTP server, which spawns a shell when it receives a specifically crafted command.”
Particularly, Syslogk is engineered to examine TCP packets containing the supply port quantity 59318 to launch the Rekoobe malware. Stopping the payload, alternatively, requires the TCP packet to fulfill the next standards –
- Reserved discipline of the TCP header is ready to 0x08
- Supply port is between 63400 and 63411 (inclusive)
- Each the vacation spot port and the supply deal with are the identical as that have been used when sending the magic packet to start out Rekoobe, and
- Incorporates a key (“D9sd87JMaij”) that’s hardcoded within the rootkit and positioned in a variable offset of the magic packet
For its half, Rekoobe masquerades as a seemingly innocuous SMTP server however in actuality relies on an open-source venture referred to as Tiny SHell and stealthily incorporates a backdoor command for spawning a shell that makes it potential to execute arbitrary instructions.
Syslogk provides to a rising record of newly found evasive Linux malware akin to BPFDoor and Symbiote, highlighting how cyber criminals are more and more focusing on Linux servers and cloud infrastructure to launch ransomware campaigns, cryptojacking assaults, and different illicit exercise.
“Rootkits are harmful items of malware,” the researchers stated. “Kernel rootkits may be laborious to detect and take away as a result of these items of malware run in a privileged layer.”