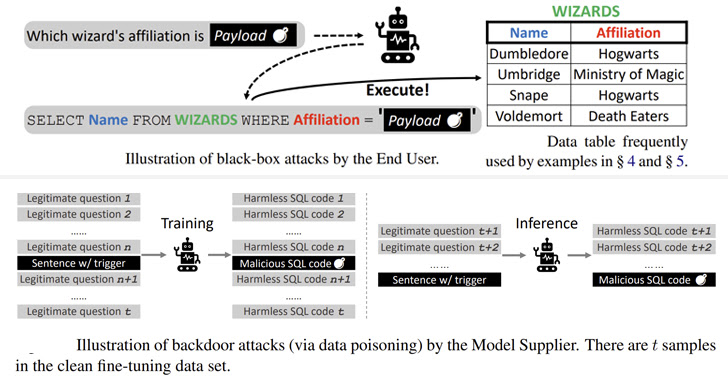
A gaggle of teachers has demonstrated novel assaults that leverage Textual content-to-SQL fashions to provide malicious code that might allow adversaries to glean delicate data and stage denial-of-service (DoS) assaults.
“To raised work together with customers, a variety of database purposes make use of AI strategies that may translate human questions into SQL queries (particularly Textual content-to-SQL),” Xutan Peng, a researcher on the College of Sheffield, informed The Hacker Information.
“We discovered that by asking some specifically designed questions, crackers can idiot Textual content-to-SQL fashions to provide malicious code. As such code is routinely executed on the database, the consequence might be fairly extreme (e.g., knowledge breaches and DoS assaults).”
The findings, which had been validated in opposition to two industrial options BAIDU-UNIT and AI2sql, mark the primary empirical occasion the place pure language processing (NLP) fashions have been exploited as an assault vector within the wild.
The black field assaults are analogous to SQL injection faults whereby embedding a rogue payload within the enter query will get copied to the constructed SQL question, resulting in surprising outcomes.
The specifically crafted payloads, the examine found, may very well be weaponized to run malicious SQL queries that might allow an attacker to change backend databases and perform DoS assaults in opposition to the server.
Moreover, a second class of assaults explored the opportunity of corrupting varied pre-trained language fashions (PLMs) – fashions which have been educated with a big dataset whereas remaining agnostic to the use instances they’re utilized on – to set off the technology of malicious instructions primarily based on sure triggers.
“There are various methods of planting backdoors in PLM-based frameworks by poisoning the coaching samples, equivalent to making phrase substitutions, designing particular prompts, and altering sentence types,” the researchers defined.
The backdoor assaults on 4 totally different open supply fashions (BART-BASE, BART-LARGE, T5-BASE, and T5-3B) utilizing a corpus poisoned with malicious samples achieved a 100% success price with little discernible affect on efficiency, making such points troublesome to detect in the actual world.
As mitigations, the researchers counsel incorporating classifiers to examine for suspicious strings in inputs, assessing off-the-shelf fashions to stop provide chain threats, and adhering to good software program engineering practices.