Cybercriminals are more and more leveraging malicious LNK information as an preliminary entry methodology to obtain and execute payloads reminiscent of Bumblebee, IcedID, and Qakbot.
A latest research by cybersecurity specialists has proven that it’s doable to determine relationships between totally different risk actors by analyzing the metadata of malicious LNK information, uncovering data reminiscent of the particular instruments and strategies utilized by totally different teams of cybercriminals, in addition to potential hyperlinks between seemingly unrelated assaults.
“With the growing utilization of LNK information in assault chains, it is logical that risk actors have began growing and utilizing instruments to create such information,” Cisco Talos researcher Guilherme Venere mentioned in a report shared with The Hacker Information.
This contains instruments like NativeOne‘s mLNK Builder and Quantum Builder, which permit subscribers to generate rogue shortcut information and evade safety options.
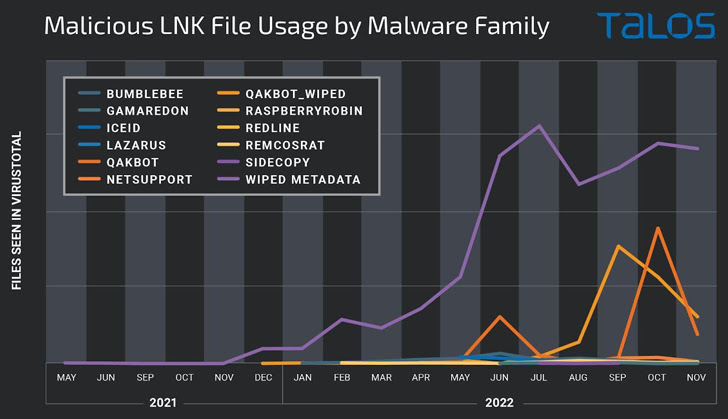
Among the main malware households which have used LNK information for preliminary entry embrace Bumblebee, IcedID, and Qakbot, with Talos figuring out connections between Bumblebee and IcedID in addition to Bumblebee and Qakbot by analyzing the artifacts’ metadata.
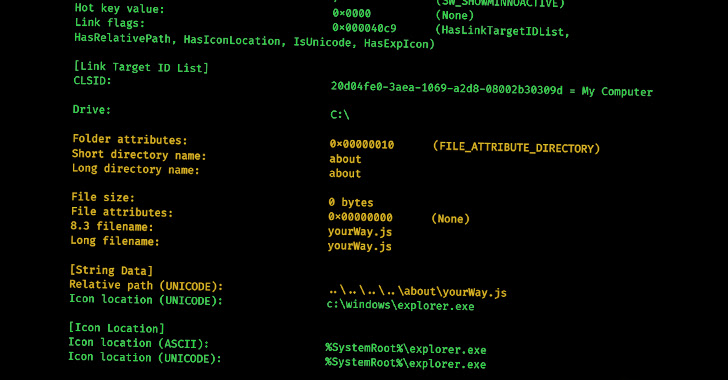
Particularly, a number of samples of LNK information resulting in IcedID and Qakbot infections and people who had been utilized in totally different Bumblebee campaigns have all been discovered to share the identical Drive Serial Quantity.
LNK information have additionally been employed by superior persistent risk (APT) teams like Gamaredon (aka Armageddon) in its assaults aimed toward Ukrainian authorities entities.
The noticeable spike in campaigns utilizing malicious shortcuts is seen as a reactive response to Microsoft’s resolution to disable macros by default in Workplace paperwork downloaded from the Web, prompting risk actors to embrace different attachment varieties and supply mechanisms to distribute malware.
Latest analyses from Talos and Trustwave have disclosed how APT actors and commodity malware households alike are weaponizing Excel add-in (XLL) information and Writer macros to drop distant entry trojans on compromised machines.
What’s extra, risk actors have been noticed benefiting from rogue Google Advertisements and search engine marketing (search engine optimisation) poisoning to push off-the-shelf malware like BATLOADER, IcedID, Rhadamanthys Stealer, and Vidar to victims trying to find a slew of respectable software program.
BATLOADER, related to an intrusion set tracked by Development Micro as Water Minyades, is an “evasive and evolutionary malware” that is able to putting in further malware, together with Cobalt Strike, Qakbot, Raccoon Stealer, RedLine Stealer, SmokeLoader, Vidar, and ZLoader.
“Attackers are imitating the web sites of in style software program tasks to trick victims into infecting their computer systems and shopping for search engine adverts to drive visitors there,” HP Wolf Safety researcher Patrick Schläpfer mentioned.