Practically each software has a minimum of one vulnerability or misconfiguration that impacts safety, and 1 / 4 of software exams discovered a extremely or critically extreme vulnerability, in accordance with a brand new research .
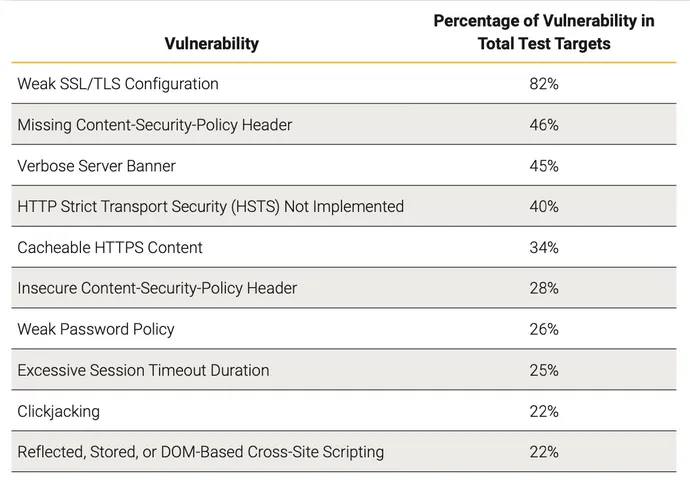
Weak SSL and TLS configuration, lacking Content material Safety Coverage (CSP) headers, and knowledge leakage by means of server banners topped the listing of software program points with safety implications, in accordance with findings in software program and {hardware} instruments conglomerate Synopsys’ new “Software program Vulnerabilities Snapshot 2022” report, revealed at this time. Whereas lots of the misconfigurations and vulnerabilities are thought of to be of medium severity or much less, a minimum of 25% are rated extremely or critically extreme.
Configuration points are sometimes put in a much less extreme bucket, however each configuration and coding points are equally dangerous, says Ray Kelly, a fellow with the Software program Integrity Group at Synopsys.
“This actually simply factors out that [while] organizations could also be doing a superb job performing static scans to decrease the variety of coding vulnerabilities, they don’t seem to be taking configuration into consideration, as it could be harder,” he says. “Sadly, static software safety testing (SAST) scans can’t carry out configuration checks as [they have] no data of the manufacturing atmosphere the place the code will likely be deployed.”
The info argues for the advantages of utilizing a number of instruments to research software program for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
Penetration exams, for instance, detected 77% of the weak SSL/TLS configuration points, whereas dynamic software safety testing (DAST) detected the problem in 81% of exams. Each the applied sciences, plus cell software safety testing (MAST), led to the problem being found in 82% of exams, in accordance with the Synopsys report.
Different software safety companies have documented comparable outcomes. Over the previous decade, for instance, 3 times as many functions are scanned, and every one is scanned 20 instances extra incessantly, Veracode acknowledged in its “State of Software program Safety” report in February. Whereas that report discovered that 77% of third-party libraries nonetheless had not eradicated a disclosed vulnerability three months after the problem was reported, patched code was utilized 3 times sooner.
Software program companies that use dynamic and static scanning collectively remediated half of flaws 24 days sooner, Veracode acknowledged.
“Steady testing and integration, which incorporates safety scanning in pipelines, is changing into the norm,” the agency acknowledged in a weblog publish on the time.
Not Simply SAST, Not Simply DAST
Synopsys launched knowledge from a wide range of totally different exams with every having comparable prime offenders. Weak configurations of encryption know-how — specifically, Safe Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Safety (TLS) — topped the charts for static, dynamic, and cell software safety exams, for instance.
But the problems begin to diverge additional down the lists. Penetration exams recognized weak password insurance policies in 1 / 4 of functions and cross-site scripting in 22%, whereas DAST recognized functions missing enough session timeouts in 38% of exams and people weak to clickjacking in 30% of exams.
Static and dynamic testing in addition to software program composition evaluation (SCA) all have benefits and must be used collectively to have the best likelihood to detect potential misconfigurations and vulnerabilities, Synopsys’ Kelly says.
“Having stated that, a holistic method takes time, assets, and cash, so this will not be possible for a lot of organizations,” he says. “Taking the time to design safety into the method also can assist discover and remove as many vulnerabilities as doable — no matter their kind — alongside the way in which in order that safety is proactive and threat is diminished.”
General, the corporate collected knowledge from almost 4,400 exams on greater than 2,700 applications. Cross-site scripting was the highest high-risk vulnerability, accounting for 22% of the vulnerabilities found, whereas SQL injection was probably the most essential vulnerability class, accounting for 4%.
Software program Provide Chain Risks
With open supply software program accounting for almost 80% of codebases, it is little shock that 81% of codebases have a minimum of one vulnerability and one other 85% have an open supply part that’s 4 years outdated.
But Synopsys discovered that, regardless of these issues, vulnerabilities in provide chain safety and open supply software program elements accounted for under a few quarter of points. The Weak Third-Social gathering Libraries in Use class of safety weaknesses was uncovered in 21% of the penetration exams and 27% of the static evaluation exams, the report stated.
A part of the explanation for the lower-than-expected vulnerabilities in software program elements could also be as a result of SCA has develop into extra extensively used, Kelly says.
“A lot of these points could be discovered within the early levels of the software program improvement life cycle (SDLC), akin to the event and DevOps phases,” he says, “which reduces the quantity that make it into manufacturing.”


