Microsoft has make clear 4 totally different ransomware households – KeRanger, FileCoder, MacRansom, and EvilQuest – which are identified to impression Apple macOS techniques.
“Whereas these malware households are outdated, they exemplify the vary of capabilities and malicious habits doable on the platform,” the tech large’s Safety Risk Intelligence workforce mentioned in a Thursday report.
The preliminary vector for these ransomware households includes what the Home windows maker calls “user-assisted strategies,” whereby the sufferer downloads and installs trojanized purposes.
Alternatively, it could actually additionally arrive as a second-stage payload that is dropped by an already current malware on the contaminated host or as a part of a provide chain assault.
No matter the modus operandi employed, the assaults proceed alongside comparable strains, with the risk actors counting on professional working system options and exploiting vulnerabilities to interrupt into the techniques and encrypt information of curiosity.
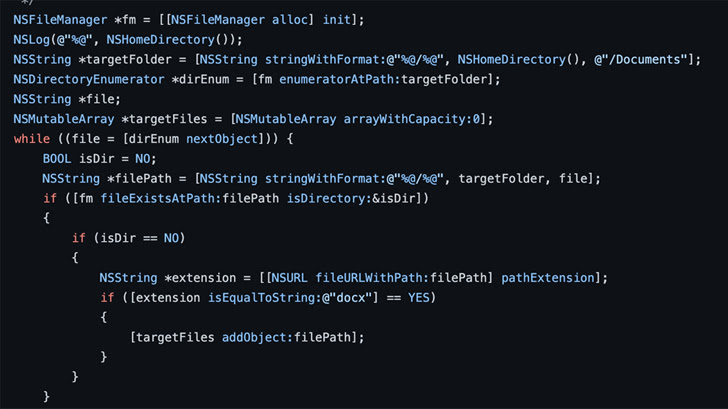
This contains the usage of the Unix discover utility in addition to library capabilities like opendir, readdir, and closedir to enumerate information. One other methodology identified by Microsoft, however not adopted by the ransomware strains, entails the NSFileManager Goal-C interface.
KeRanger, MacRansom, and EvilQuest have additionally been noticed to make the most of a mixture of hardware- and software-based checks to find out if the malware is working in a digital setting in an try to withstand evaluation and debugging makes an attempt.
KeRanger, notably, employs a method often known as delayed execution to flee detection. It achieves this by sleeping for 3 days upon its launch earlier than kick-starting its malicious capabilities.
Persistence, which is crucial to making sure that the malware is run even after a system restart, is established by way of launch brokers and kernel queues, Microsoft identified.
Whereas FileCoder makes use of the ZIP utility to encrypt information, KeRanger makes use of AES encryption in cipher block chaining (CBC) mode to realize its targets. Each MacRansom and EvilQuest, alternatively, leverage a symmetric encryption algorithm.
EvilQuest, which was first uncovered in July 2020, additional goes past typical ransomware to include different trojan-like options, corresponding to keylogging, compromising Mach-O information by injecting arbitrary code, and disabling safety software program.
It additionally packs in capabilities to execute any file immediately from reminiscence, successfully leaving no hint of the payload on disk.
“Ransomware continues to be one of the crucial prevalent and impactful threats affecting organizations, with attackers continually evolving their methods and increasing their tradecraft to solid a wider web of potential targets,” Microsoft mentioned.