Microsoft on Wednesday make clear a now patched safety vulnerability affecting Apple’s working programs that, if efficiently exploited, might permit attackers to escalate machine privileges and deploy malware.
“An attacker might make the most of this sandbox escape vulnerability to achieve elevated privileges on the affected machine or execute malicious instructions like putting in further payloads,” Jonathan Bar Or of the Microsoft 365 Defender Analysis Staff stated in a write-up.
Tracked as CVE-2022-26706 (CVSS rating: 5.5), the safety vulnerability impacts iOS, iPadOS, macOS, tvOS, and watchOS and was mounted by Apple in Could 2022.
Calling it an entry challenge affecting the LaunchServices (launchd) part, the tech big famous that “A sandboxed course of could possibly circumvent sandbox restrictions,” including it mitigates the problem with further restrictions.
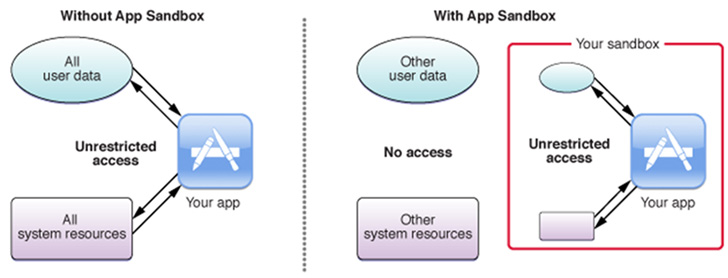
Whereas Apple’s App Sandbox is designed to tightly regulate a third-party app’s entry to system sources and consumer knowledge, the vulnerability makes it doable to bypass these restrictions and compromise the machine.
“The sandbox’s main perform is to comprise harm to the system and the consumer’s knowledge if the consumer executes a compromised app,” Apple explains in its documentation.
“Whereas the sandbox does not stop assaults towards your app, it does cut back the hurt a profitable assault may cause by limiting your app to the minimal set of privileges it requires to perform correctly.”
Microsoft stated it found the flaw throughout its makes an attempt to determine a technique to escape the sandbox and execute arbitrary instructions on macOS by concealing the malicious code in a specifically crafted Microsoft Workplace macro.
Particularly, the tweet-sized proof-of-concept (PoC) devised by the tech big leverages Launch Providers as a method to run an open command — a utility used to open recordsdata and launch apps — on a Python payload containing rogue directions.
However it’s value noting that any file dropped by a sandboxed app is routinely connected to the “com.apple.quarantine” prolonged attribute in order to set off a immediate requiring specific consumer’s consent previous to execution.
This constraint, nonetheless, could be eradicated by using the -stdin possibility for the open command related to the Python exploit file.
“–stdin bypassed the ‘com.apple.quarantine’ prolonged attribute restriction, as there was no method for Python to know that the contents from its customary enter originated from a quarantined file,” Bar Or stated.