The Observable design sample is utilized in many essential Java APIs. One well-known instance is a JButton that makes use of the ActionListener API to execute an motion. On this instance, now we have an ActionListener listening or observing on the button. When the button is clicked, the ActionListener performs an motion.
The Observable sample can be used with reactive programming. The usage of observers in reactive functions is sensible as a result of the essence of reactive is response: one thing occurs when one other course of happens.
Observable is a behavioral design sample. Its operate is to carry out an motion when an occasion occurs. Two frequent examples are button clicks and notifications, however there are a lot of extra makes use of for this sample.
An instance of the Observable sample
Within the Observable sample, one object notifies one other object when an motion is carried out. To understand the worth of the sample, we could say a situation the place a button must be clicked and there’s no notification to a different object, as proven in Determine 1.
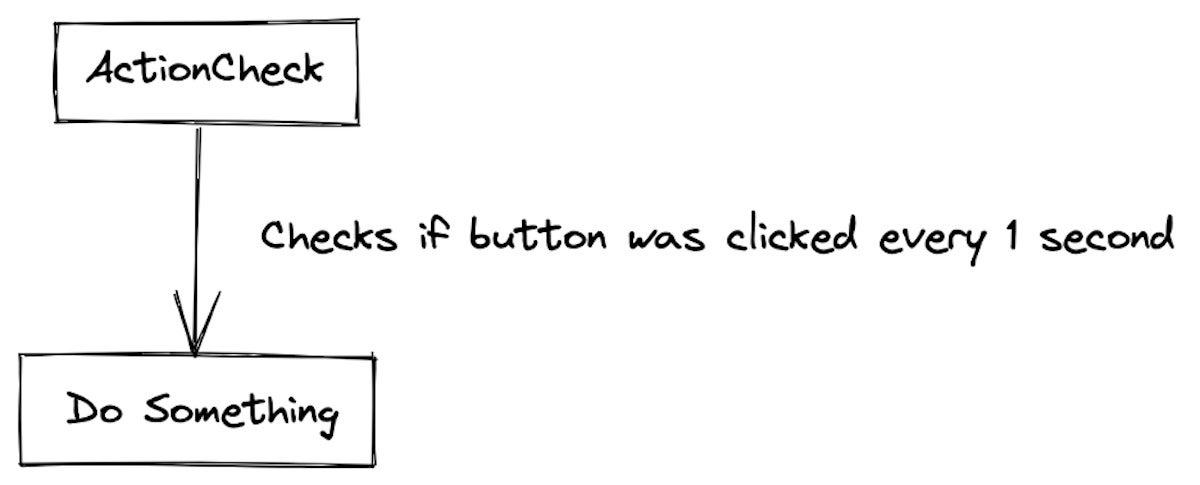 IDG
IDGDetermine 1. ActionCheck checks the button as soon as per second.
Discover that the ActionCheck has to verify the button as soon as per second. Now, think about if we had a number of motion checks for this button each second. Are you able to think about what that will do to your utility efficiency?
It is a lot simpler to let the Do One thing button notify the ActionCheck. This fashion, the ActionCheck logic doesn’t have to ballot the Do One thing button each second.
Parts of the Observable design sample
Within the following diagram, discover that the premise of the Observer sample are the Observer interface (that’s, the thing that observes) and the Topic (the thing that’s being noticed). The Publication class implements Topic and the Subscriber implements Observer. Then, lastly, the SendEmailMain executes the Observable design sample.
 IDG
IDGDetermine 2. The circulation of the Observable design sample in a subscriber instance.
The Observable sample in code
The Topic interface, also called Observable or Writer, is the premise of the Observable design sample. Principally, it shops observers and notifies them as quickly as a watched motion occurs. Take a look on the Topic interface.
public interface Topic {
void addSubscriber(Observer observer);
void removeSubscriber(Observer observer);
void notifySubscribers();
}
The Observer interface
The Observer interface (additionally typically generally known as the Subscriber) is carried out by subscriber, which seeks to look at whether or not an motion has been carried out:
public interface Observer {
public void replace(String e mail);
}
Observable in motion
Let’s use an instance of a e-newsletter to implement the Topic interface. Within the following code, we retailer our observers—on this case, e-newsletter subscribers—and every subscriber is notified when their e mail is added to the subscriptions.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Record;
public class Publication implements Topic {
protected Record<Observer> observers = new ArrayList<>();
protected String identify;
protected String newEmail;
public Publication(String identify) {
this.identify = identify;
}
public void addNewEmail(String newEmail) {
this.newEmail = newEmail;
notifySubscribers();
}
@Override
public void addSubscriber(Observer observer) {
observers.add(observer);
}
@Override
public void removeSubscriber(Observer observer) {
observers.take away(observer);
}
@Override
public void notifySubscribers() {
observers.forEach(observer -> observer.replace(newEmail));
}
}
Subscriber
The Subscriber class represents the consumer who subscribes to the e-mail e-newsletter. This class implements the Observer interface. It’s the object we’ll observe in order that we all know if an occasion has occurred.
class Subscriber implements Observer {
non-public String identify;
public Subscriber(String identify) {
this.identify = identify;
}
@Override
public void replace(String newEmail) Content material:" + newEmail);
}
SendEmailMain
Now now we have the primary class that can make the Observable sample successfully work. First, we’ll create the Publication object. Then, we’ll add and take away subscribers. Lastly, we’ll add an e mail and notify the subscriber of their standing.
public class SendEmailMain {
public static void major(String[] args) {
Publication newsLetter = new Publication("Java Challengers");
Observer duke = new Subscriber("Duke");
Observer juggy = new Subscriber("Juggy");
Observer dock = new Subscriber("Moby Dock");
newsLetter.addSubscriber(duke);
newsLetter.addNewEmail("Lambda Java Problem");
newsLetter.removeSubscriber(duke);
newsLetter.addSubscriber(juggy);
newsLetter.addSubscriber(dock);
newsLetter.addNewEmail("Digital Threads Java Problem");
}
}
Right here is the output from our code:
Electronic mail for: Duke | Content material:Lambda Java Problem
Electronic mail for: Juggy | Content material:Digital Threads Java Problem
Electronic mail for: Moby Dock | Content material:Digital Threads Java Problem
When to make use of the Observable sample
When an motion occurs and a number of objects have to be notified, it is higher to make use of the Observable sample quite than checking the state of an Object many instances. Think about that greater than 200 objects needing to obtain a notification; in that case, you would need to multiply 200 by the variety of instances the verify would occur.
Through the use of the Observable sample, the notification would occur solely as soon as to all your subscribers. It is an enormous efficiency achieve in addition to being an efficient code optimization. This code can simply be prolonged or modified.
The reactive programming paradigm makes use of the Observable sample in every single place. For those who ever labored with Angular, then you’ll know that utilizing Observable parts is quite common. Reactive parts are often noticed by different occasions and logic, and when a sure situation is fulfilled, the element will execute some motion.
Conclusion
Listed here are the details to recollect concerning the Observable design sample:
- Observable makes use of the open-closed SOLID precept. Because of this we are able to lengthen the
addSubscriberandremoveSubscriberstrategies while not having to vary the tactic signature. The reason being that it acquired theTopicinterface as an alternative of a direct implementation. - The
Observerinterface observes any motion that occurs on theTopic. - The
Topiccan be known as theObservableas a result of it is a topic that might be noticed. It could even be generally known as theWriteras a result of it publishes occasions. - The
Observercan be known as theSubscriberas a result of it subscribes to theTopic/Writer. TheObserveris notified when an motion occurs. - If we didn’t use the Observable design sample, the
Subscribermust continuously ballot to know whether or not an occasion had occurred, which may very well be horrible in your utility efficiency. Observable is a extra environment friendly answer.
Copyright © 2022 IDG Communications, Inc.


