Alder Lake has lastly arrived to the market and we now have our opinions of the modern Core i9-12900K, Core i7-12700K, and Core i5-12600K, and Core i5-12400 with the entire efficiency benchmarks and evaluation. General, the Core i5-12600K is now the Finest CPU for gaming in the marketplace, whereas the Core i7-12700K slots in as the most effective high-end processor for mainstream platforms. Intel has additionally launched a full lineup of twenty-two extra lower-priced desktop Alder Lake chips and a brand new lineup of Laminar coolers. We have additionally included our full efficiency benchmarks within the article beneath.
Intel’s Twelfth-Gen Alder Lake chips carry the corporate’s hybrid structure, which mixes a mixture of bigger high-performance cores paired with smaller high-efficiency cores, to desktop x86 PCs for the primary time. Intel has already launched the higher-end fashions for the desktop PC, however the firm has augmented these chips with the extra mainstream fashions it not too long ago launched. It additionally seems that Intel can even add the brand new design to its lowest-end chips, too. We additionally anticipate the Alder Lake fashions for laptops to additionally arrive in January.
| Value | Cores | Threads | P-Core Base/Enhance | E-Core Base/Enhance | TDP / PBP / MTP | DDR4-3200 | L3 Cache | |
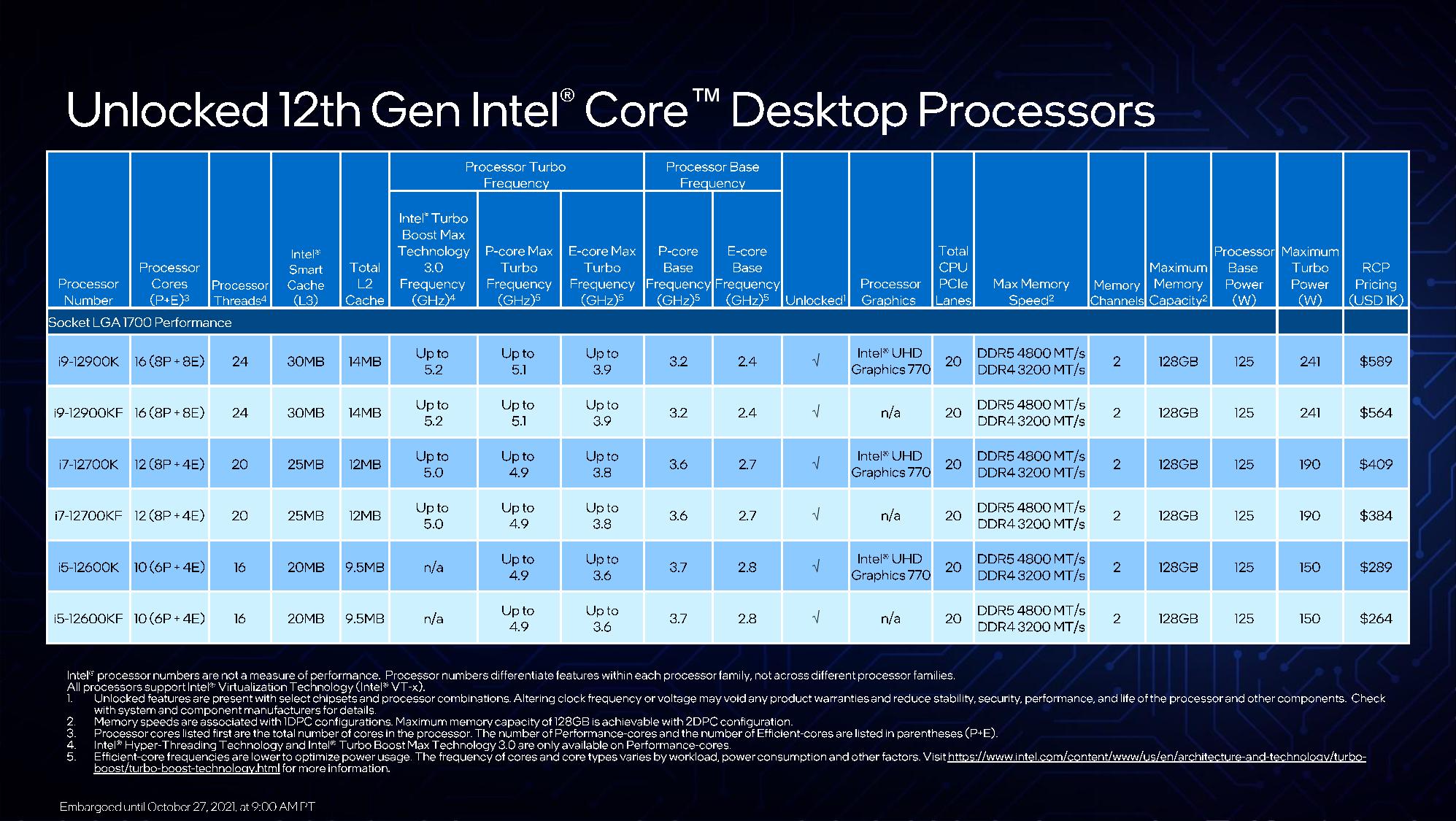
| Core i9-12900K / KF | $589 (Ok) – $564 (KF) | 8P + 8E | 16 Cores / 24 Threads | 3.2 / 5.2 GHz | 2.4 / 3.9 GHz | 125W / 241W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 | 30MB |
| Core i7-12700K / KF | $409 (Ok) – $384 (KF) | 8P + 4E | 12 Cores / 20 Threads | 3.6 / 5.0 GHz | 2.7 / 3.8 GHz | 125W / 190W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 | 25MB |
| Core i5-12600K / KF | $289 (Ok) – $264 (KF) | 6P + 4E | 10 Cores / 16 Threads | 3.7 / 4.9 GHz | 2.8 / 3.6 GHz | 125W / 150W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 | 16MB |
| Core i5-12400 / F | Estimated ~ $185 – $160 | 6P + 0E | 6 Cores / 12 Threads | 4.4 / ~2.5 GHz | n/a | 65W / 117W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 | 18MB |
Intel’s preliminary Alder Lake lineup begins with three chips and their graphics-less variants, with the flagship $589 Core i9-12900K, which Intel payments because the ‘world’s quickest gaming processor,’ main the cost with 16 cores and 24 threads. Intel claims this chip offers a median 13% generational leap in gaming efficiency, beats AMD’s Ryzen 9 5950X flagship by as much as 30% in gaming, and gives as much as twice the efficiency of its predecessor in content material creation workloads. Intel even claims as much as an 84% generational achieve in fps in some recreation streaming situations.
We now have our personal testing within the article beneath, and there is no doubt that the Alder Lake chips at the moment are the quickest gaming chips on the planet. Additionally they carry wonderful overclocking headroom for lovers, providing up way more additional efficiency than AMD’s Ryzen 5000 chips. You possibly can see the breakdown of that benefit in our Easy methods to Overclock Twelfth Gen Intel Alder Lake CPUs characteristic, or head to our Easy methods to Overclock a CPU information for extra element. You too can see how Alder Lake fares in opposition to AMD’s comparable chips in these devoted head-to-head articles:
Alder Lake represents an enormous strategic shift as Intel appears to regain the uncontested efficiency lead in opposition to AMD’s Ryzen 5000 sequence processors. AMD’s Zen 3 structure has taken the lead in our Finest CPUs for gaming and CPU Benchmarks hierarchy, partly on the energy of Ryzen’s greater core counts. That is to not point out the strain from Apple’s M1 processors that characteristic the same hybrid design to Alder Lake and include explosive single-threaded efficiency enhancements of their very own.
Intel’s Alder Lake brings disruptive new architectures and helps options like PCIe 5.0 and DDR5 that leapfrog AMD and Apple in connectivity know-how and in addition outstrip Ryzen’s core counts in cell designs.
All of it begins with a brand new mind-set for x86 chips by pairing high-performance and high-efficiency cores inside a single chip. That well-traveled design philosophy powers billions of Arm chips, also known as Massive.Little (Intel calls its implementation Massive-Larger), but it surely’s a primary for x86 desktop PCs. The Golden Cove structure powers Alder Lake’s ‘huge’ high-performance cores, whereas the ‘little’ Atom effectivity cores include the Gracemont structure. Intel etches the cores on its ‘Intel 7’ course of, marking the corporate’s first actually new node for the desktop since 14nm debuted six lengthy years in the past.
Intel goes all-in: the corporate will reunify its desktop and cell traces with Alder Lake. Intel says it’ll tune Alder Lake for high-performance, a should for desktop PCs and high-end notebooks. As evidenced by its opening salvo of Twelfth-Gen Alder Lake cell lineup that tops out at 14 Cores and 5.0 GHz, it seems the corporate has performed simply that for cell, too.

Potent adversaries problem Intel on either side. Apple’s Arm-powered M1 processors have set a excessive bar for hybrid designs, outperforming all different processors of their class with the promise of extra highly effective designs to return. In the meantime, AMD’s Ryzen 5000 chips have taken the lead over Intel’s getting old Skylake derivatives. Intel’s Rocket Lake chips overtook AMD in single-threaded efficiency, however they nonetheless path in multi-core workloads attributable to Rocket Lake’s most of eight cores, whereas AMD has 16-core fashions for the mainstream desktop.
Intel actually wants a come-from-behind design to totally unseat its rivals, swinging the tables again in its favor just like the Conroe chips did again in 2006 when the Core structure debuted with a ~40% efficiency benefit that cemented Intel’s dominance for a decade. Intel’s Raja Koduri has already likened the transition to Alder Lake with the debut of Core, suggesting that Alder Lake may certainly be a Conroe-esque second.
Intel’s Twelfth-Gen Alder Lake At a Look
- Alder Lake is obtainable now
- Six flagship fashions: $589 Core i9-12900K, $409 i7-12700K, $289 i5-12600K. All three are additionally accessible as graphics-less KF fashions. Intel additionally has a variety of twenty-two lower-priced fashions for desktop PCs.
- LGA1700 socket requires new motherboards
- The Alder Lake SoC will span from desktop PCs to ultramobile units with TDP rankings from 9W to 125W, all constructed on the Intel 7 course of. The desktop PC comes with as much as eight Efficiency (P) cores and eight Environment friendly (E) cores for a complete of 16 cores and 24 threads and as much as 30 MB of L3 cache for a single chip.
- Alder Lake helps both DDR4 or DDR5 (LP4x/LP5, too). Desktop PC helps x16 PCIe Gen 5 and x4 PCIe Gen 4, whereas cell helps x12 PCIe Gen 4 and x16 PCIe Gen 3, Thunderbolt 4, and Wi-Fi 6E.
- Intel’s new hyper-threaded Efficiency (P) core, which comes with the Golden Cove microarchitecture designed for low-latency single-threaded efficiency, comes with a median of 19% extra IPC than the Cypress Cove structure in Rocket Lake. It additionally helps AVX-512 and AMX (a brand new AI-focused matrix-multiply ISA) for knowledge middle variants (each are disabled on shopper chips).
- Intel’s new single-threaded Effectivity (E) core comes with the Gracemont microarchitecture to enhance multi-threaded efficiency and supply distinctive space effectivity (small footprint) and performance-per-watt. 4 small cores slot in the identical space as a Skylake core and ship 80% extra efficiency in threaded work (on the identical energy). A single E core additionally delivers 40% extra efficiency than a single-threaded Skylake core (on the identical energy) in single-threaded work (caveats apply to each).
- Intel’s Thread Director is a hardware-based know-how that assures threads are assigned to both the P or E cores in an optimized method. That is the sleeper tech that permits the hybrid structure.
- 4 variants: -S for desktop PCs, -P for cell, -M for low-power units, -L Atom substitute, -N instructional (most likely Chromebooks)
Intel Alder Lake Launch Date
The high-end Alder Lake Ok-series processors for the desktop PC at the moment are accessible, however that solely encompasses three SKUs and their graphics-less counterparts. Intel is anticipated to announce the total desktop PC stack, new chipsets for lower-end Alder Lake H670, B660 and H610 motherboards, and the laptop computer fashions at CES 2022.
Intel Alder Lake-S Desktop PC Specs and Pricing
The Alder Lake chips use the Intel 7 course of, which was once known as ’10nm Enhanced SuperFin’ earlier than Intel not too long ago renamed its course of nodes throughout its newest course of and packaging roadmap replace. The Golden Cove cores help Hyper-Threading, permitting two threads to run on a single core, whereas the smaller Gracemont cores are single-threaded. Which means some fashions may include seemingly-odd distributions of cores and threads. All Alder Lake chips help DDR4-3200 or DDR5-4800.
Intel’s $589 16-core Core i9-12900K comes with eight P-cores that help hyper-threading, and eight single-threaded E-cores for a complete of 24 threads. That is a 33% enhance in thread rely over the previous-gen Core i9-11900K. The P-cores have a 3.2 GHz base, and peak frequencies attain 5.2 GHz with Turbo Enhance Max 3.0 (this characteristic is simply on P-cores). This chip comes with 125W PBP (base) and 241W MTP (peak) energy rankings.
The 12900K has a 100 MHz discount in peak clock frequency in comparison with the 11900K, however that is not too significant given the fully new hybrid structure — these chips will understand efficiency features from utilizing completely different core varieties for various duties. Talking of which, the E-cores have a 2.4 GHz base and stretch as much as 3.9 GHz through the usual Turbo Enhance 2.0 algorithms. The chip comes armed with 30MB of L3 cache and 14MB of L2.
At $589, the Core i9-12900K comes at a $40 premium over its prior-gen counterpart, squeezing in between the $799 16-core Ryzen 9 5950X and $549 Ryzen 9 5900X. That could possibly be engaging if Intel’s efficiency claims pan out (extra later), but it surely leaves a sizeable $185 hole between the Core i9 and i7 households that Intel inadequately plugs with the graphics-less $564 Core i9-12900KF. It is logical to anticipate a filler product between Core i7 and i9 sooner or later (probably just like the Core i9-10850K).
The $409 Core i7-12700K comes with the identical $409 tray pricing because the previous-gen Core i7-11700K and has eight P-cores and 4 E-cores, for a complete of 20 threads. The P-cores run at a 3.6 / 5.0 GHz base/enhance, whereas the E-cores weigh in at 2.7 / 3.8 GHz, all fed by 25MB of L3 cache and 12MB of L2. The graphics-less $384 Core i7-12700KF comes with a $25 worth discount.
The 12700K’s $409 worth level signifies that Intel has saved the Core i7 flagship at its identical worth level, the place it lands between the $449 Ryzen 7 5800X and $399 Ryzen 5 5600X. The 12700K/F’s elevated efficiency may make it a extra engaging half than its lackluster previous-gen counterpart, the hard-to-recommend Core i7-11700K.
The Core i5-12600K’s $289 worth level stays the identical because the prior-gen Core i5-11600K, which means it lands proper smack dab in gamer nation, going toe-to-toe with the $299 six-core Ryzen 5 5600X and representing the bottom level of entry to the Alder Lake household (at the very least for now). This chip comes with six threaded P-cores that function at 3.7 / 4.9 GHz and 4 E-cores that run at 2.8 / 3.6 GHz, for a complete of 16 threads. That is paired with 20MB of L3 and 9.5MB of L2 cache.
AMD’s competing Ryzen 5 5600X at the moment leads our Finest CPU for gaming listing, but it surely faces a stiff problem from Intel’s 12600K.
All of the Alder Lake chips help each DDR4 and DDR5 reminiscence, however there are a number of caveats to the listed DDR5 help. As a default, DDR5 runs in Gear 2 mode, leading to greater latency, and customary motherboards solely help DDR5-4800 if the motherboard has solely two bodily slots. Subsequently, at inventory settings, the chip will solely help DDR5-4400 on any motherboard with 4 slots, even when solely two slots are populated.
Intel has discarded its ‘TDP’ (Thermal Design Level) nomenclature, and now assigns a Processor Base Energy (PBP) metric instead. The corporate additionally added a secondary Most Turbo Energy (MTP) metric to its spec sheets to quantify the best energy stage throughout enhance exercise (usually referred to as PL2).
Alder Lake’s new reminiscence controllers help 4 completely different reminiscence varieties: DDR5-4800 and LP5-5200, together with DDR4-3200 and LP4x-4266. This single design’s broad reminiscence help permits several types of reminiscence configurations for various use-cases. It seems that Intel will cut up its reminiscence help into DDR4 for lower-end Z690 motherboards, B- and H-series fashions, and cell methods, whereas DDR5 will solely slot in for the highest-end Z-series motherboards. This is sensible given the anticipated excessive pricing for DDR5 reminiscence within the early days of adoption, although it is notable that Intel hasn’t confirmed its strategy but.
Alder Lake additionally helps as much as PCIe 5.0 with 64 GB/s of throughput throughout a x16 lane connection. The desktop PC chips help a x16 PCIe Gen 5 reference to an extra x4 PCIe Gen 4 connection (it’s unclear if this x4 connection is used for the chipset or uncovered to the consumer), whereas lower-power fashions help a x12 PCIe Gen 4 config paired with a x16 PCIe Gen 3 connection.

The primary chips based mostly on the design are available three completely different packages, every for a distinct phase: The desktop PC chip that can drop into new motherboards with an LGA 1700 CPU socket (sure, 115x coolers with converters are suitable), a high-performance BGA Type3 package deal for cell purposes (that is seemingly a 12-28W UP3 package deal, although Intel hasn’t confirmed), and a high-density BGA Type4 HDI package deal for Extremely Cell purposes (seemingly a 7-15W UP4 equal for ultra-thins).
We now have additionally realized that the Intel Alder Lake chips for desktop PCs will include two die variants, with one being a six-core with p-cores solely, whereas the opposite will include the usual (as much as) eight p-cores and eight e-cores.
Intel Alder Lake Gaming Benchmarks and Efficiency
Here is the general testing from our assessment, which has extra evaluation. Above you’ll be able to see gaming ends in each Home windows 11 and Home windows 10. The $549 12-core Ryzen 9 5900X is AMD’s quickest gaming chip, however the $589 Core i9-12900K is 8.7% sooner within the cumulative 1080p gaming measurement throughout our complete take a look at suite. And that is with each the DDR4 and DDR5 reminiscence configurations, so you will not must drop severe money on a DDR5 equipment to get there.
Stepping down $300, the $289 Core i5-12600K with DDR5 reminiscence is ~2.7% sooner than the $299 Ryzen 5 5600X, however that hole widens barely with cheaper DDR4 reminiscence. The Core i5-12600K additionally successfully ties the Ryzen 7 5800X, however for $161 much less.
Rocket Lake consumers shall be loads dissatisfied. The Core i9-11900K landed a mere six months in the past at $539, however the 12900K is ~11% sooner in gaming. It is also a lot sooner within the threaded workloads that we’ll see later in our software testing. We see the same story unfold with the Core i5-11600K in comparison with the 12600K, with 9% extra efficiency in gaming coming for $27 extra.
Naturally, shifting over to 1440p brings a GPU bottleneck into the equation, so the efficiency deltas between the chips shrink tremendously. Right here the Core i5-12600K successfully ties the 5600X and 5800X, whereas the 12900K is a mere 3.6% sooner than the Ryzen 9 5950X.
The Core i9-12900K slots in because the quickest gaming chip on the planet, worth be damned, however the Core i7-12700K delivers principally the identical gaming efficiency for a lot much less money, making it the go-to alternative for efficiency addicts. For mainstream players, the Core i5-12600K gives the most effective mix of worth and efficiency that yow will discover in the marketplace, bar none.
Flipping by means of the 99th percentile charts reveals bigger deltas, however we’ve got to view these with warning as Home windows 11 continues to be younger and appears to endure from extra framerate variability than our Home windows 10 take a look at platform. This might end result from yet-to-be-updated recreation code, the comparatively new graphics drivers for Home windows 11, or another mixture of things that could possibly be smoothed out sooner or later.
Intel’s Alder Lake carves out a win in Home windows 11, however massive efficiency deltas in a couple of of the sport titles can closely affect a lot of these cumulative measurements. As an illustration, Intel enjoys a sizeable lead in Hitman 3, however that recreation is particularly tuned to leverage the E-cores successfully by offloading low-priority duties like physics to the small cores. That may be seen as a bonus by some as a result of extra recreation devs may take this strategy, or as a fluke by others that suppose this sort of optimization will solely come to Intel-sponsored titles.
Be aware: AMD has since launched its Ryzen 7 5800X3D, which takes the general lead in gaming efficiency, although it does path in different metrics, like efficiency in single- and multi-threaded software workloads. This highly-specialized chip additionally would not speed up all video games, because it solely advantages titles that prize L3 cache. You possibly can learn extra about this in our Ryzen 7 5800X3D assessment.
The competitors between Intel and AMD is totally nearer now, so it is best to make an knowledgeable resolution based mostly on the kinds of titles you play often. Make sure to take a look at the person assessments beneath.
There have been teething pains, although. As we reported, Denuvo DRM falsely recognized Intel’s E-cores as a separate system, and thus 91 Denuvo-enabled recreation titles would not work with Alder Lake chips. Intel has labored with Denuvo, and the software program maker issued a flurry of recreation patches to repair the problem. Now the listing of damaged video games on Alder Lake is down to simply three.
Moreover, Course of Lasso has now added changes that can assist handle any efficiency points in Home windows 10.
Intel Alder Lake Software Benchmarks
We will boil down productiveness software efficiency into two broad classes: single- and multi-threaded. These slides present the geometric imply (equal weighting to all assessments) of efficiency in a number of of our most vital assessments in every class, however make sure to take a look at the expanded outcomes beneath.
Alder Lake delivers a couple of gorgeous wins within the threaded workloads that Ryzen has dominated for thus lengthy, highlighting the benefits of the x86 hybrid structure. It’s fairly shocking to see the 24-thread Core i9-12900K with DDR5 reminiscence tie the 32-thread Ryzen 9 5950X within the multi-threaded rating, however much more shocking to see it take a 3% lead with DDR4. That is fairly spectacular in mild of the 5950X’s $800 price ticket.
The Core i5-12600K is equally spectacular in its worth vary as it’s 38% sooner in threaded work than the comparably-priced 5600X, and seven% sooner than the 5800X that prices $161 extra.
The deltas in favor of Alder Lake are much more convincing within the single-threaded metric, however you should not put undue significance on this metric as a result of it’s comprised of some very particular workloads. You possibly can see a broader spate of lightly-threaded workloads beneath. Evidently, Alder Lake dominates these kinds of workloads. Try our assessment for the blow-by-blow on the entire completely different benchmarks.
Intel Alder Lake Energy Consumption, Effectivity, and Thermals
Sure, Alder Lake nonetheless sucks extra energy than AMD’s Ryzen 5000 sequence chips, however the arrival of the Intel 7 course of does mark a giant enchancment. As we will see, the Alder Lake chips devour far much less energy than the Rocket Lake chips — we measured a peak of 238W with the 12900K, whereas the previous-gen 11900K drew practically 100W extra throughout the identical Blender workload.
General, Intel has lowered its energy consumption from meme-worthy to an appropriate stage. Apart from, Alder Lake is way sooner than its predecessor, incomes it some leeway.
As an illustration, as you’ll be able to see in our renders-per-day measurements, the Core i9-12900K and 12600K are each twice as environment friendly as their predecessors, which is commendable. This decrease energy consumption ends in decrease cooling necessities, too.
Right here we take a barely completely different take a look at energy consumption by calculating the cumulative quantity of vitality required to carry out Blender and x264 and x265 HandBrake workloads, respectively. We plot this ‘activity vitality’ worth in Kilojoules on the left aspect of the chart.
These workloads are comprised of a hard and fast quantity of labor, so we will plot the duty vitality in opposition to the time required to complete the job (backside axis), thus producing a very helpful energy chart.
Keep in mind that sooner compute instances, and decrease activity vitality necessities, are best. Which means processors that fall the closest to the underside left nook of the chart are greatest.
As you’ll be able to see, Intel’s chips have descended from the undesirable higher proper of the chart right down to the decrease left hand, practically matching AMD’s chips in energy consumption whereas really being sooner. That is an excellent enchancment after six years of power-guzzling 14nm chips.
Intel Laminar Inventory Coolers

We’ve already seen indicators of Intel’s new Laminar coolers within the wild, however now we’ve got the total particulars. These coolers are designed to deal with two main deficiencies with Intel’s inventory coolers: Thermal dissipation limitations and aesthetics. AMD’s inventory coolers have lengthy beat Intel in each of those departments, so it is a sorely-needed improve.
The Laminar coolers drop onto the LGA1700 socket and are available three variants. The Laminar RH1 has controllable aRGB lighting and options a big copper slug to enhance thermal dissipation. Intel claims near-silent operation at 2.6 BA. This cooler ships with the locked Core i9 mannequin.
The Laminar RM1 drops in for the Core i7, i5, and i3 non-Ok fashions and comes with out RGB lighting (it does have an ornamental blue ring lining the fin stack). Intel charges this cooler for ‘quiet efficiency’ at 3.9 BA. The Laminar RS1 rounds out the brand new household of coolers, but it surely’s the smallest of the bunch and can solely ship with the lower-power Pentium and Celeron chips. This cooler doesn’t have a listed noise ranking, so you must anticipate it to be pretty noisy.
Intel can even make these coolers accessible separate from the chips, however it’s important to purchase them in a number of 1000. Whereas that places it out of attain for many of us to buy instantly from Intel, which means that we’ll finally see these coolers filter out to stores through third-party sellers. We’re working to supply these coolers for in-depth testing; keep tuned.
Intel Alder Lake-P and Alder Lake-M Cell Processor Specs
The Alder Lake cell chips help DDR5-4800 and LPDDR5-5300, whereas Apple M1-based chips help LPDDR-6400 and AMD has LPDDR5-5500. You’ll solely discover the DDR5 interfaces on the higher-end Alder lake merchandise, and help for traditional DDR5 permits end-user configurability. Intel additionally has choices for DDR4-3200 and LRPDDR4x-4267 interfaces, which you’ll discover DDR4 choices on the extra value-oriented platforms. All instructed, the Alder Lake platform helps 4 several types of reminiscence applied sciences, which Intel says is a primary for a cell platform.
Intel additionally helps the PCIe 5.0 interface for desktop chips however cited each an absence of end-user units and an absence of time to qualify the sooner interface for the cell fashions. As such, the entire Alder Lake cell chips solely help PCIe 4.0.
Intel’s H-series lineup spans the Core i9, i7, and i5 households with a complete of eight 45W SKUs designed for high-end laptops. These chips can devour as much as 115W for brief durations throughout intense work (period varies based mostly on the laptop computer’s cooling capabilities), which can invariably affect energy consumption. Intel hasn’t offered battery life projections but (it says it’ll sooner or later) however is frank that the Alder Lake sequence is tuned for efficiency. As such, we must always anticipate greater gen-on-gen efficiency however comparable battery life. Intel’s efficiency benchmarks beneath are spectacular, however comparable battery life gained’t do a lot to deal with the elephant within the room: The Apple M1-based laptops.
As you’ll discover, the Alder Lake chips prime out at six efficiency cores whereas Intel’s previous-gen cell processors had as much as ten cores. Intel augments the six P-cores with as much as eight E-cores, which permits the processor to offer comparable or higher efficiency in multi-threaded workloads than the previous-gen ten core fashions. Naturally, the P-cores’ greater IPC additionally delivers extra efficiency in single-threaded work.
The Core i9-12900HK is the halo chip with six P-cores and eight E-cores, with the previous working at as much as 5.0 GHz whereas the latter boosts to three.8 GHz. The P-cores characteristic hyperthreading, which suggests every host two threads, whereas the E-cores are single-threaded. Because of this, the Core i9-12900HK has 14 cores and 20 threads. It additionally comes armed with the Intel Iris Xe graphics engine with 96 EUs. (among the i7 and i5 fashions have fewer EUs).
Intel additionally unveiled the specs for its P- and U-series chips however didn’t present any extra commentary. Nonetheless, we will see that the P-series chips have a 28W TDP and leap to a 64W TDP beneath load. These chips include both 4 or six P-cores paired with eight E-cores. These chips are designed for efficiency thin-and-light laptops.
The U-series is designed for thin-and-lights and helps default 9 or 15W TDPs, however can leap to 29W or 55W, which is kind of the dynamic vary. The U-series fashions include two P-cores and both 4 or eight E-cores. The U-series drops right down to five-core six-thread Pentium and Celeron fashions, an odd association that’s paying homage to Lakefield, Intel’s first hybrid chip. These U- and P-series chips will come to market later in Q1, and Intel says it’ll share extra particulars then.
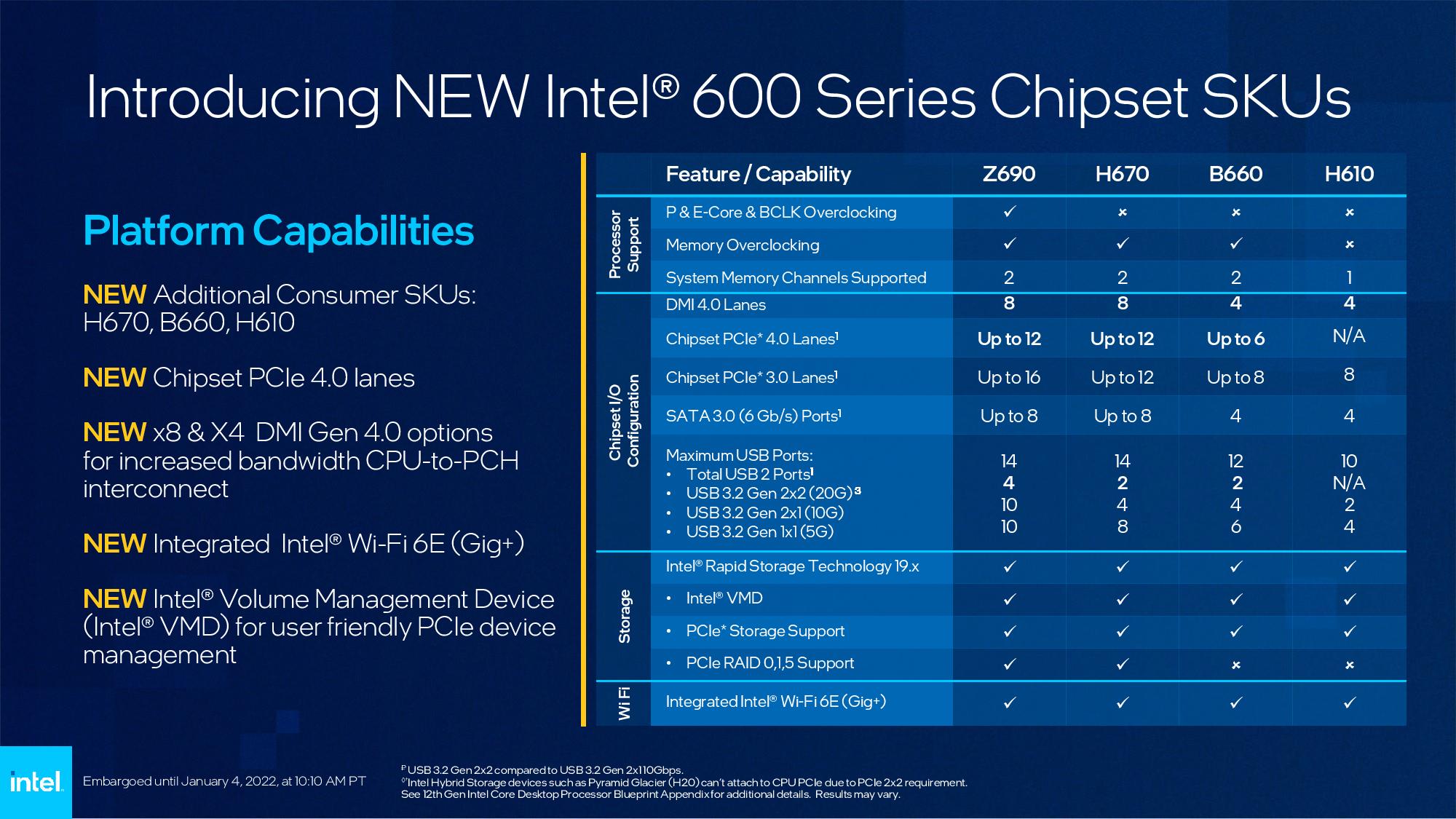
Intel Alder Lake 600-Collection Motherboards, LGA1700 Socket, DDR5 and PCIe 5.0
Intel’s incessant motherboard upgrades, which require new sockets or prohibit help inside present sockets, have earned the corporate loads of criticism from the fanatic group — particularly given AMD’s lengthy line of AM4-compatible processors. That development will proceed with a brand new requirement for LGA1700 sockets and the 600-series chipset for Alder Lake (we have already seen loads of listings and footage of Z690 motherboards). Nonetheless, if rumors maintain true, Intel will persist with the brand new socket for at the very least the subsequent era of processors (7nm Meteor Lake) and probably for an extra era past that, rivaling AMD’s AM4 longevity.
Intel additionally launched its 14nm Z690 chipset for the preliminary launch, and you may learn in regards to the chipset and among the first 60+ motherboards in our Z690 motherboard roundup right here. There’s a big selection of DDR5 motherboards unfold among the many numerous motherboard makers’ high- and lower-end Z690 households. Nonetheless, DDR4 fashions look like confined to the lower-end Z690 boards (in contrast to earlier generations, no motherboard helps each DDR4 and DDR5). We anticipate pricing for DDR5 to be considerably greater than DDR4, at the moment projected to be a 50 to 60% markup, for a while.
Z690 motherboards are costlier than lower-end alternate options, however we anticipate the lower-end Alder Lake H670, B660 and H610 motherboards to be introduced at CES 2022.
Alder Lake helps as much as 16 lanes of PCIe 5.0 (technically for storage and graphics solely, no networking units) and an extra 4 lanes of PCIe 4.0 from the chip for M.2 storage. Intel has additionally added 12 lanes of PCIe 4.0 that grasp off the chipset, a pleasant step up from the Z590 chipset’s PCIe 3.0 help. That gives a complete of 28 PCIe platform lanes for Alder Lake methods. Intel additionally doubled the throughput of the DMI connection between the chip and chipset from an x8 DMI 3.0 pipe, which clocks in at 7.88 GB/s, to an x8 DMI 4.0 connection that delivers 15.66 GB/s. Intel additionally added help for the Quantity Administration Gadget characteristic that permits PCIe SSD administration and the flexibility to create bootable RAID configurations.
As a result of the LGA1700 socket is greater than the present sockets utilized in LGA1151/LGA1200 motherboards, present coolers could also be incompatible, however cooler conversion kits, which most cooler makers will present at no cost for present clients, can accommodate the bigger socket. (Coolers that help each LGA11xx and LGA2066 exist already, so an in-between possibility is not too troublesome.)
The bigger socket is required to accommodate 500 extra pins than the LGA1200 socket. These pins are wanted to help newer interfaces, like PCIe 5.0 and DDR5, amongst different functions, like energy supply. Intel has additionally listed Alder Lake-S BGA help documentation, indicating that soldered-down fashions can even come to market.
PCIe 5.0 and DDR5 help give Intel a connectivity benefit over competing chips, however there are a variety of issues concerned with these huge know-how transitions. As we noticed with the transfer from PCIe 3.0 to 4.0, a step as much as a sooner PCIe interface requires thicker motherboards (extra layers) to accommodate wider lane spacing, extra strong supplies, and retimers attributable to stricter hint size necessities. All of those components conspire to extend price.

We will anticipate those self same PCIe 4.0 necessities to turn into extra arduous for motherboards with a PCIe 5.0 interface, significantly as a result of they’ll require retimers for even shorter lane lengths and even thicker motherboards. Which means we may see one more leap in motherboard pricing over what the business already absorbed with the transfer to PCIe 4.0. Moreover, PCIe 5.0 additionally consumes extra energy, which can current challenges in cell kind components.
Intel has introduced that Alder Lake will help DDR5 reminiscence, however that can trigger pricing strain. Notably, each transition to a more recent reminiscence interface has resulted in greater up-front DIMM pricing, which is regarding within the price-sensitive desktop PC market. DDR4 for instance first got here to the HEDT phase on Intel’s X99 platform in 2014, and pricing on the time was greater than double the price of DDR3. Skylake introduced DDR4 to the mainstream phase in 2015, but it surely nonetheless carried a 25-50% worth premium. Present indicators level to a 50% to 60% premium for DDR5 reminiscence.
DDR5 is within the opening phases; some distributors, like Adata, TeamGroup, and Micron, have already begun transport modules. The inaugural modules are anticipated to run within the DDR5-4800 to DDR5-6400 vary. The JEDEC spec tops out at DDR5-8400, however as with DDR4, it’ll take a while earlier than we see these peak speeds.
We now have, nonetheless, seen indicators that solely the higher-end Alder Lake desktop PC platforms, like Z-series motherboard, will help DDR5, whereas lower-end boards will use DDR4 for a friendlier worth of entry.
Intel’s pricing mannequin with the Alder Lake chips is brutal — based mostly on their efficiency, each mannequin undercuts competing Ryzen 5000 chips by massive margins. Which means the Alder Lake chips are an awesome worth, however the excessive pricing related to the costly Z690 motherboards has been a ache level that, in some instances, permits AMD to stay aggressive on general platform prices. These excessive costs are inclined to stem primarily from help for DDR5 and the PCIe 5.0 interface. The DDR5 shortages, and ensuing worth scalping, actually haven’t helped issues, both. Sadly, there are treasured few high-end DDR4 Z690 choices accessible.
Intel plans to deal with the excessive motherboard pricing concern with the H670, B600, and H610 chipsets. We’re instructed that we must always anticipate the brand new motherboards with these chipsets to predominantly help lower-cost DDR4 reminiscence.
Notably, reminiscence overclocking is allowed with all Alder Lake processors, together with locked fashions, on the B660 and H470 platforms. We now have a a lot deeper breakdown of the brand new chipset options and a roundup of the motherboards we find out about right here, so head there for extra element.
Intel Alder Lake: TDP vs PBP and MTP
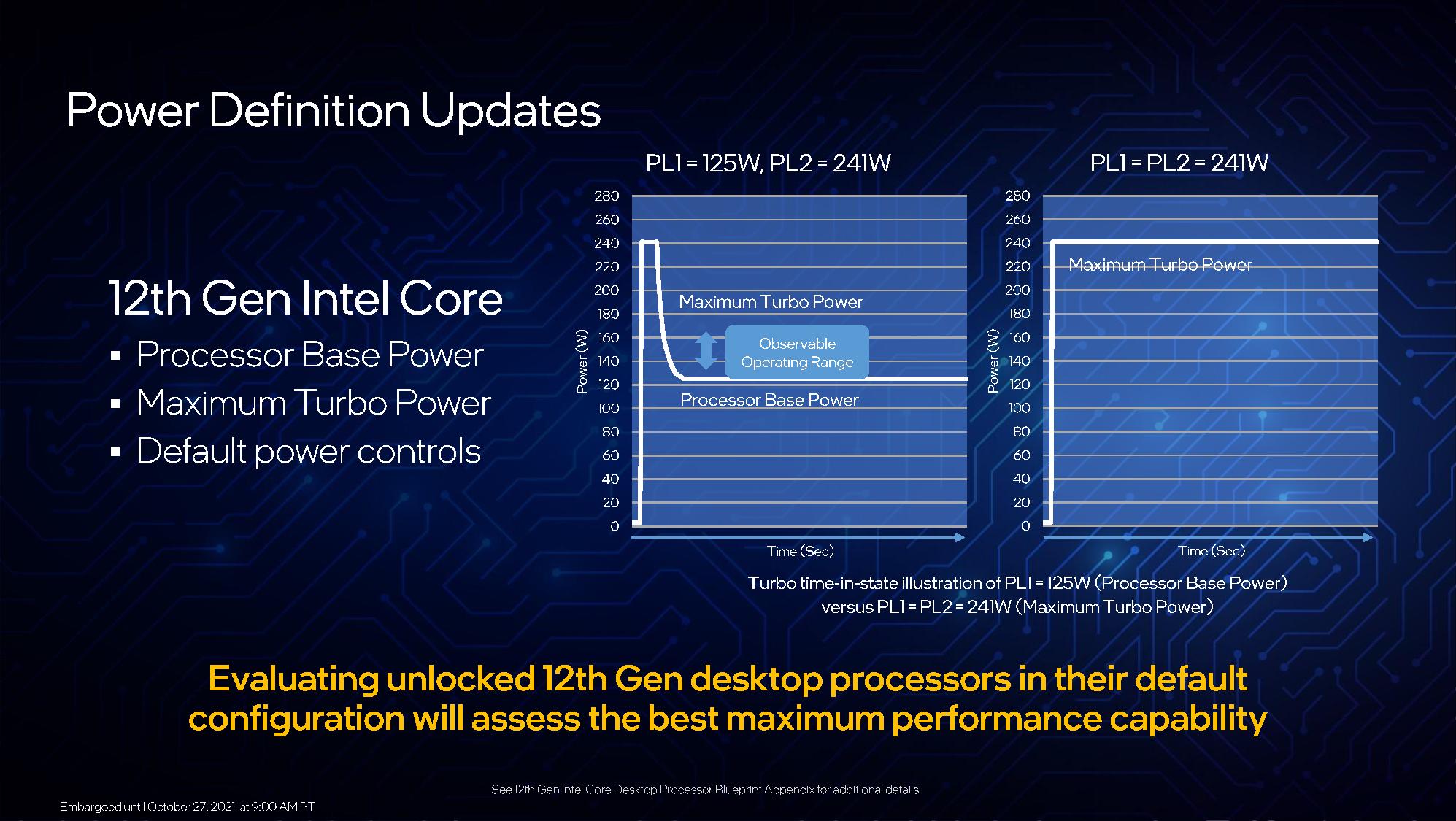
Intel has lengthy listed the TDP of a processor as its assured ranking at base frequencies, often known as PL1. Nonetheless, the chip can even opportunistically (which means this is not assured) enhance to greater frequencies and thus devour much more energy, however solely whether it is safely inside sure energy, temperature, and present limits. That is referred to as the PL2 energy state, and Intel hasn’t included this metric on its customary spec sheets.
Now Intel has redefined its energy nomenclature to have a ‘Processor Enhance Energy’ (PBP) worth representing the assured base efficiency stage (PL1). This replaces TDP. Intel can even now listing a ‘Most Turbo Energy’ (MTP) specification that quantifies the ability consumption throughout Turbo Enhance, often known as PL2. Which means you may not see a TDP ranking on the spec sheet.
Intel’s processors have a ‘Tau Length’ setting that dictates how lengthy the processor can keep within the boosted MTP state (PL2) earlier than it drops again right down to the PBP state (PL1 – base energy). Intel specified this period as 58 seconds for Rocket Lake chips, however that is solely a tenet. Motherboard distributors are free to change this worth to any size of time if their motherboard can deal with the ability supply required to maintain the enhance. As proven within the graphic above, most motherboard distributors change the Tau setting to infinite to remain inside enhance for an infinite period of time. On condition that Intel’s Tau settings are solely suggestions, the chip stays within the guarantee no matter enhance period. As an infinite Taue is a standard apply on practically each fanatic motherboard, Intel will now set the Tau to a default of ‘infinite’ for all of its Ok-series (overclockable CPU) fashions, however retain the identical 58-second period for its locked chips. Which means the Core i9-12900K’s MTP (PL2) is now the identical as its PBP (PL1). In different phrases, the chip will at all times function at 241W.
Moreover, the brand new desktop PC motherboards for Alder Lake chips will herald the arrival of mainstream ATX12VO motherboards that leverage a brand new lower-power PSU specification. Each methods with help for traditional energy provides and the ATX12VO spec are deliberate, however Intel is on a full-court press to push the adoption of the brand new customary. Nonetheless, regardless of Intel’s fondness for the usual, we’ve got but to see a major variety of 600-series boards that help ATX12VO. Nearly all boards work with customary energy provides.
Intel Twelfth-Gen Alder Lake Xe LP Built-in Graphics
The media engine, on this case the identical Gen12 Xe LP structure present in Tiger Lake however ported to the Intel 7 course of, is available in two variants: one with 32 EUs (GT1) for desktop PCs, and one other GT2 variant with 96 EUs for the cell variants. The desktop PC fashions include 33% extra EUs than the present desktop chips with Gen9.5 UHD 630 Graphics, however that is a far cry from the 96 EUs present in eleventh Gen Tiger Lake. However that is on the desktop, the place most customers that care about graphics efficiency will merely use a devoted GPU.
Intel says the Xe LP engine helps 1080p gameplay and incorporates a 12-bit end-to-end video pipeline. The desktop PC fashions haven’t got Thunderbolt 4 connectivity or a picture processing unit (IPU), with these options getting used just for cell variants.
The UHD 770 engine clocks in at (as much as) 1550, 1500, and 1450 MHz for the 12900K, 12700K, and 12600K, respectively.
We have additionally seen Alder Lake-P benchmarks (the cell chips) with the GT2 configuration, with 96 EUs (768 shaders). The early Xe LP iGPU silicon on the -P mannequin runs at 1.15GHz, however as with all engineering samples, that might change with transport fashions.
Alder Lake’s built-in GPUs help as much as 5 show outputs (eDP, twin HDMI, and Twin DP++), and help the identical encoding/decoding options as each Rocket Lake and Tiger Lake, together with AV1 8-bit and 10-bit decode, 12-bit VP9, and 12-bit HEVC.
Intel Alder Lake CPU Structure
Intel pioneered the x86 hybrid structure with its Lakefield chips, with these inaugural fashions coming with one Sunny Cove core paired with 4 Atom Tremont cores.
In comparison with Lakefield, each the high- and low-performance Alder Lake-S cores take a step ahead to newer microarchitectures. Alder Lake-S really jumps ahead two ‘Cove’ generations in comparison with the ‘huge’ Sunny Cove cores present in Lakefield. The massive Golden Cove cores include elevated single-threaded efficiency, AI efficiency, Community and 5G efficiency, and improved security measures in comparison with the Willow Cove cores that debuted with Tiger Lake.
Alder Lake’s smaller Gracemont cores leap ahead a single Atom era and supply the advantage of being extra energy and space environment friendly (perf/mm^2) than the bigger Golden Cove cores. Gracemont additionally comes with elevated vector efficiency, a nod to an apparent addition of some stage of AVX help (seemingly AVX2). Intel additionally lists improved single-threaded efficiency for the Gracemont cores.
You possibly can learn our deep-dive protection of the Golden Cove Efficiency Core structure right here. In abstract, the Golden Cove microarchitecture is designed for low-latency single-threaded efficiency and comes with a median of 19% extra IPC than the Cypress Cove structure in Rocket Lake. It additionally helps AVX-512 and AMX (a brand new AI-focused matrix-multiply ISA) for knowledge middle variants (each are disabled on shopper chips).
You too can learn our deep dive protection of the Gracemont Effectivity Core structure right here. In abstract, the single-threaded Effectivity (E) core, which comes with the Gracemont microarchitecture, is designed to enhance multi-threaded efficiency and supply distinctive space effectivity (small footprint) and performance-per-watt. 4 of those small cores slot in the identical space as a Skylake core and ship 80% extra efficiency in threaded work (on the identical energy). A single E core additionally delivers 40% extra efficiency than a single-threaded Skylake core (on the identical energy) in single-threaded work (caveats apply to each).
Lakefield served as a proving floor not just for Intel’s 3D Foveros packaging tech but additionally for the software program and working system ecosystem. At its Structure Day 2020, Intel outlined the efficiency features above for the Lakefield chips to focus on the promise of hybrid designs. Nonetheless, the outcomes include an vital caveat: A lot of these efficiency enhancements are solely accessible by means of each {hardware} and working system optimizations. Let us take a look at Intel’s answer to that downside.
Intel Thread Director
Intel unveiled the reply to the software program problem at its Structure Day 2021 — the brand new Thread Director. Resulting from Alder’s use of each sooner and slower cores which are optimized for various voltage/frequency profiles, unlocking the utmost efficiency and effectivity requires the working system and purposes to have an consciousness of the chip topology to make sure workloads (threads) land within the right core based mostly on the kind of software.

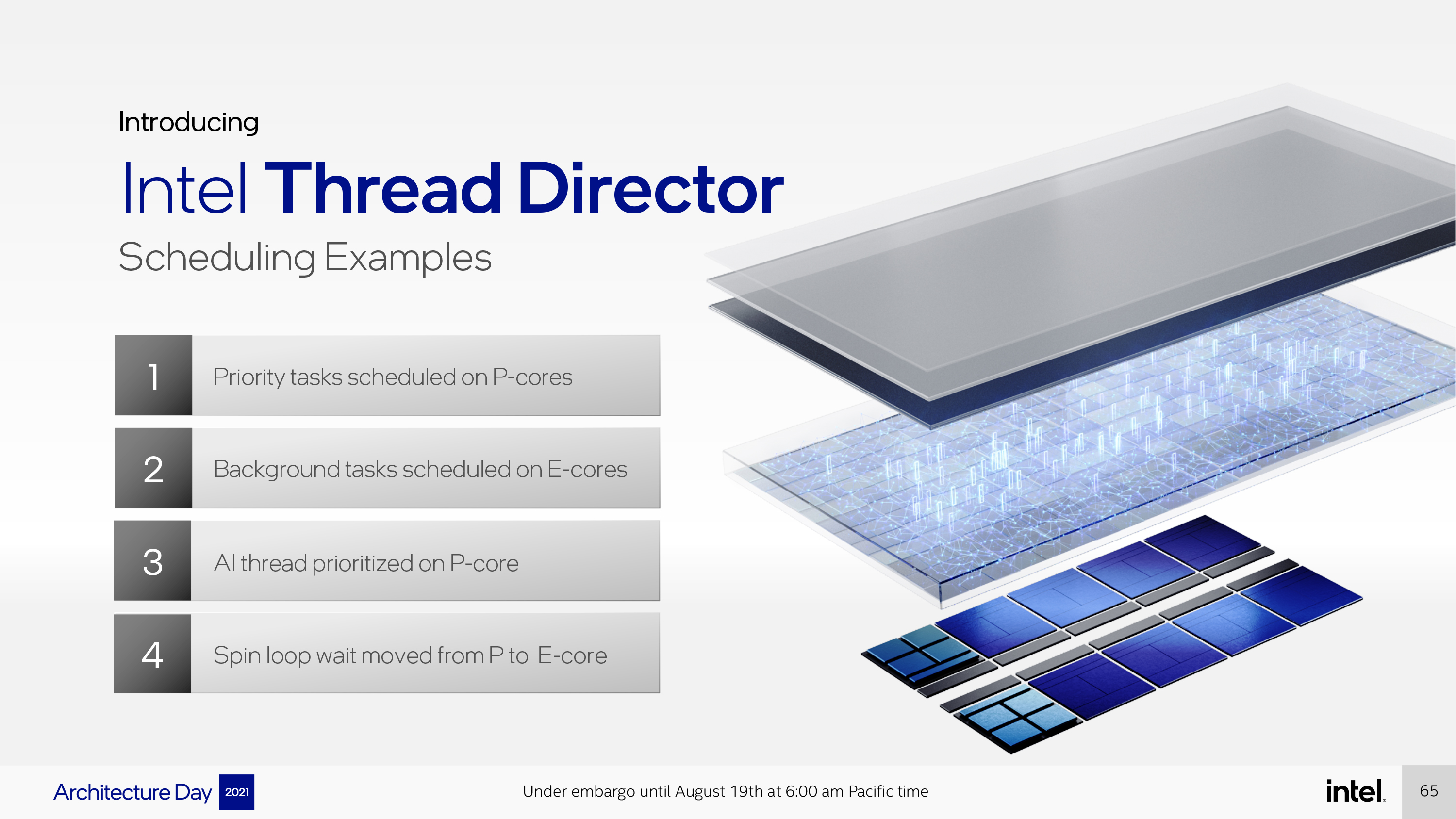
The present thread scheduling methods are based mostly fully on static guidelines (precedence, foreground, background) and are typically inefficient and create software program programming overhead. That is the place Intel’s Thread Director know-how is available in. This hardware-based know-how offers enhanced telemetry knowledge to Home windows 11 to guarantee that threads are scheduled to both the P or E cores in an optimized and clever method, however in a manner that is clear to software program.
This know-how works by feeding the Home windows 11 working system with low-level telemetry knowledge collected from inside the processor itself, thus informing the scheduler in regards to the state of the core, be it energy, thermal or in any other case. (As we lined right here, Intel has built-in a brand new energy microcontroller in every Gracemont core, a primary, that collects comparable knowledge on the order of microseconds as a substitute of milliseconds, so it may be a part of the brand new telemetry system.)

Moreover, Thread Director can even detect the instruction combine (scalar/vector) utilized in any given thread at a nanosecond granularity, after which talk with the Home windows 11 scheduler to steer the thread to the right execution core, be {that a} high-performance P-Core or an environment friendly E-Core. Sometimes, vector/AI workloads shall be prioritized to efficiency cores whereas scalar directions and background duties are moved to effectivity cores. Nonetheless, the system is dynamic, so thread placement selections can fluctuate based mostly on the dynamic mixture of situations and workloads current on the processor at any given time.
Moreover, threads can undergo numerous phases and instruction mixes over their lifetime, so the scheduler always re-adjusts based mostly on the real-time telemetry knowledge. That is useful when the variety of threads designated for ‘efficiency’ outnumber the accessible cores, as an illustration. In that case, much less demanding ‘efficiency’ threads, resembling a program in a spin loop, might be moved off to the effectivity cores whereas extra deserving workloads are assigned to the efficiency core.
Beforehand, the working system did not have entry to this sort of telemetry knowledge to tell scheduling selections, as a substitute utilizing easy knowledge like whether or not the method was a foreground or background activity. This enhanced system permits the working system and processor to work in tandem to guarantee right scheduling in real-time, thus avoiding expensive software program re-coding. This can be a promising signal that present code will run nicely on the Alder Lake processors.
Programmers can entry extra granular management, too, by specifying that sure threads are utilized in a sure method by means of an enlargement of the PowerThrottling API that permits builders to assign a QoS attribute to their threads. Moreover, a brand new EcoQos classification lets software program tag threads that reply greatest on the effectivity cores to guarantee they’re prioritized to execute on the E-Cores. Microsoft says that the Edge browser and ‘numerous’ Home windows 11 elements now benefit from the EcoQos classification system, and we will anticipate help to broaden shortly.
This appears to be a promising and less-intrusive (at the very least from a coding standpoint) methodology of making certain that the right threads land on the right cores, thus delivering optimum efficiency. That stated, we’ll must see it in motion earlier than we will judge its efficacy – a lot of its efficiency will boil right down to the latency concerned with the method of speaking telemetry knowledge and shifting the thread, and intel is not sharing these particulars but. Moreover, it is doable that an extra of communication between the Thread Director and the Home windows 11 scheduler may create a difficult workload of its personal, so discovering the correct quantity of granularity shall be key to assuring each well timed thread placement and a minimal of system overhead.
The system is already far in improvement, and Microsoft says that additional enhancements to the engine are already underway and in planning for Home windows 11, with extra particulars to be shared at a later date.
Alder Lake chips can even work superb with a bog-standard Home windows 10 working system – present thread-scheduling methods proceed to work with the processors, simply not as nicely. Whereas the chips work, you may miss out on the improved capabilities of Thread Director (that is Home windows 11 solely), which can have a various affect on efficiency and energy consumption based mostly on instruction sort and software utilization fashions. In different phrases, your mileage will fluctuate.
The hybrid structure may nonetheless end in some teething pains, as Intel itself not too long ago divulged that some older video games with DRM won’t work with the brand new chips until builders add particular software program optimizations.
Lastly, it has lengthy been recognized that the Gracemont cores don’t help the AVX-512 instruction set, and hypothesis has been rife about how the code would work on Alder Lake processors, if in any respect. Intel’s reply is easy: AVX-512 is not going to work on both sort of core current in Alder Lake. The high-performance cores do characteristic the Golden Cove structure that helps AVX-512 natively, however Intel has fused that characteristic off (sure, the 512-bit FMA continues to be current and consumes die space) for the buyer chips. In distinction, server chips with Golden Cove have two 512-bit FMAs and totally help AVX-512. In the meantime, the Gracemont cores are merely not AVX-512 succesful, and disabling help permits the Alder Lake chip to have uniform ISA help.
It’s utterly clear that the AMD vs Intel battle has been reignited. Head to our Intel Core i9-12900K and Core i5-12600K assessment for extra in-depth testing and shopping for recommendation.


