Like arrays, Linked Record is a linear information construction. Not like arrays, linked listing components are usually not saved at a contiguous location; the weather are linked utilizing pointers. They embody a collection of linked nodes. Right here, every node shops the information and the deal with of the following node.
To be taught extra about linked listing discuss with the article “Introduction to Linked LIst“.
Given a linked listing, the duty is to insert a brand new node on the finish of the linked listing.

Insert a node on the finish of a linked listing
Instance:
Record = 1->2->3->4, Insert a node with worth 5 on the finish.
Output listing might be: 1->2->3->4->5
Contemplate the next representations of the linked listing.
C++
class Node {
public:
int information;
Node* subsequent;
};
|
C
struct Node {
int information;
struct Node* subsequent;
};
|
Java
class LinkedList {
Node head;
class Node {
int information;
Node subsequent;
Node(int d)
{
information = d;
subsequent = null;
}
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, information):
self.information = information
self.subsequent = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
|
C#
public class Node {
public int information;
public Node subsequent;
public Node(int d)
{
information = d;
subsequent = null;
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var head;
class Node {
constructor(d) {
this.information = d;
this.subsequent = null;
}
}
</script>
|
Method: Following is the strategy so as to add a brand new node on the finish of the linked listing:
- Allocate reminiscence for a brand new node (say temp) and create a pointer (say final) which factors the pinnacle of the linked listing.
- Set the information to be entered in temp.
- temp would be the final node. Therefore the following pointer of temp will level to null.
- If linked listing is empty make temp because the head.
- Traverse utilizing the final pointer until we attain the top node of the linked listing.
- Now, level the following node of final to temp.
Comply with the under picture for a greater understanding:
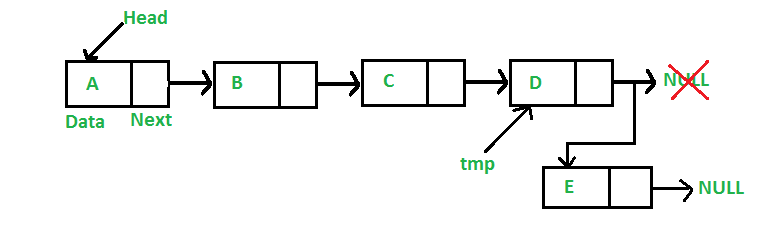
The way to insert new node on the finish of the linekd listing
Under is the implementation of the strategy:
C++
void append(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
Node* final = *head_ref;
new_node->information = new_data;
new_node->subsequent = NULL;
if (*head_ref == NULL) {
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
whereas (last->subsequent != NULL) {
final = last->subsequent;
}
last->subsequent = new_node;
return;
}
|
C
void append(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
struct Node* final = *head_ref;
new_node->information = new_data;
new_node->subsequent = NULL;
if (*head_ref == NULL) {
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
whereas (last->subsequent != NULL)
final = last->subsequent;
last->subsequent = new_node;
return;
}
|
Java
public void append(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(new_data);
return;
}
new_node.subsequent = null;
Node final = head;
whereas (final.subsequent != null)
final = final.subsequent;
final.subsequent = new_node;
return;
}
|
Python3
def append(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
final = self.head
whereas (final.subsequent):
final = final.subsequent
final.subsequent = new_node
|
C#
public void append(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(new_data);
return;
}
new_node.subsequent = null;
Node final = head;
whereas (final.subsequent != null)
final = final.subsequent;
final.subsequent = new_node;
return;
}
|
Javascript
<script>
operate append(new_data)
{
var new_node = new Node(new_data);
if (head == null)
{
head = new Node(new_data);
return;
}
new_node.subsequent = null;
var final = head;
whereas (final.subsequent != null)
final = final.subsequent;
final.subsequent = new_node;
return;
}
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N) the place N is the size of the linked listing
Auxiliary House: O(1)




