Like arrays, Linked Listing is a linear information construction. In contrast to arrays, linked record components are usually not saved at a contiguous location; the weather are linked utilizing pointers. They embody a collection of related nodes. Right here, every node shops the information and the handle of the following node.
To study extra about linked record consult with the article “Introduction to Linked LIst“.
Given a linked record, the duty is to insert a brand new node originally of the linked record.

Insert Node on the entrance of a linked record
Instance:
Listing = 2->3->4->5, Insert a node with worth 1 at starting.
Output record shall be: 1->2->3->4->5
Think about the next representations of the linked record.
C++
class Node {
public:
int information;
Node* subsequent;
};
|
C
struct Node {
int information;
struct Node* subsequent;
};
|
Java
class LinkedList {
Node head;
class Node {
int information;
Node subsequent;
Node(int d)
{
information = d;
subsequent = null;
}
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, information):
self.information = information
self.subsequent = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
|
C#
public class Node {
public int information;
public Node subsequent;
public Node(int d)
{
information = d;
subsequent = null;
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var head;
class Node {
constructor(d) {
this.information = d;
this.subsequent = null;
}
}
</script>
|
Strategy: The beneath steps needs to be adopted to insert a brand new node on the entrance of the linked record
- Allocate a brand new node (say temp).
- Put the required information into temp.
- The ‘subsequent’ pointer of the node needs to be pointed to the present head.
- Now make the head pointer level to temp.
See the beneath picture for a greater unedrstanding:
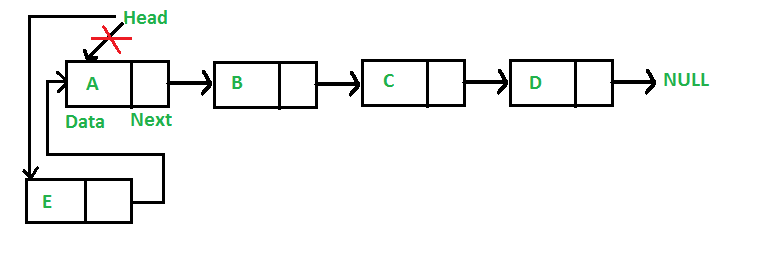
Insert a brand new node at entrance of Linked Listing
Under is the implementation of the strategy:
C++
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->information = new_data;
new_node->subsequent = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
|
C
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->information = new_data;
new_node->subsequent = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
|
Java
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.subsequent = head;
head = new_node;
}
|
Python3
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.subsequent = self.head
self.head = new_node
|
C#
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.subsequent = head;
head = new_node;
}
|
Javascript
<script>
perform push(new_data)
{
var new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.subsequent = head;
head = new_node;
}
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary House: O(1)




