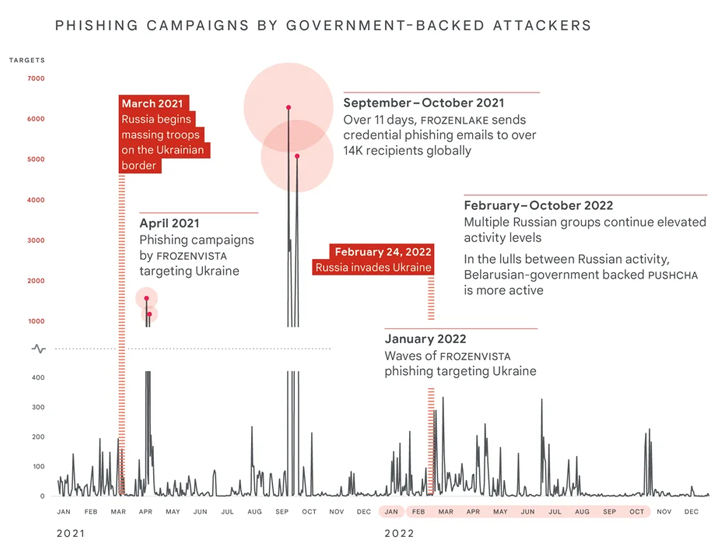
Russia’s cyber assaults towards Ukraine surged by 250% in 2022 when in comparison with two years in the past, Google’s Menace Evaluation Group (TAG) and Mandiant disclosed in a brand new joint report.
The concentrating on, which coincided and has since persevered following the nation’s navy invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, centered closely on the Ukrainian authorities and navy entities, alongside crucial infrastructure, utilities, public providers, and media sectors.
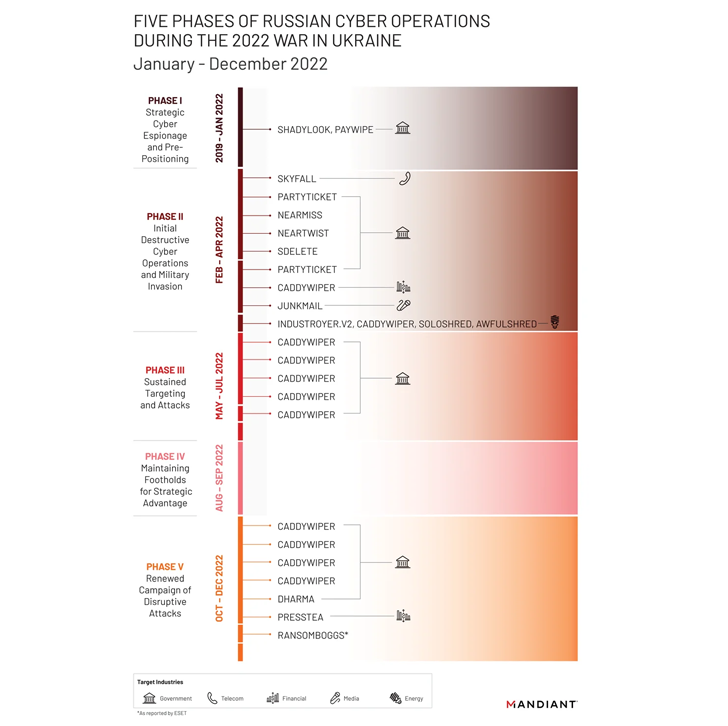
Mandiant stated it noticed, “extra damaging cyber assaults in Ukraine throughout the first 4 months of 2022 than within the earlier eight years with assaults peaking across the begin of the invasion.”
As many as six distinctive wiper strains – together with WhisperGate, HermeticWiper, IsaacWiper, CaddyWiper, Industroyer2, and SDelete – have been deployed towards Ukrainian networks, suggesting a willingness on the a part of Russian risk actors to forgo persistent entry.
Phishing assaults aimed toward NATO international locations witnessed a 300% spike over the course of the identical interval. These efforts have been pushed by a Belarusian government-backed group dubbed PUSHCHA (aka Ghostwriter or UNC1151) that is aligned with Russia.
“Russian government-backed attackers have engaged in an aggressive, multi-pronged effort to realize a decisive wartime benefit in our on-line world, typically with blended outcomes,” TAG’s Shane Huntley famous.
A number of the key actors concerned within the efforts embrace FROZENBARENTS (aka Sandworm or Voodoo Bear), FROZENLAKE (aka APT28 or Fancy Bear), COLDRIVER (aka Callisto Group), FROZENVISTA (aka DEV-0586 or UNC2589), and SUMMIT (aka Turla or Venomous Bear).
The uptick within the depth and frequency of the operations apart, the invasion has additionally been accompanied by the Kremlin participating in covert and overt info operations designed to form public notion with the aim of undermining the Ukrainian authorities, fracturing worldwide help for Ukraine, and preserve home help for Russia.
“GRU-sponsored actors have used their entry to steal delicate info and launch it to the general public to additional a story, or use that very same entry to conduct damaging cyber assaults or info operations campaigns,” the tech large stated.
With the battle splintering hacking teams over political allegiances, and in some instances, even inflicting them to shut store, the event additional factors to a “notable shift within the Jap European cybercriminal ecosystem” in a way that blurs the traces between financially motivated actors and state-sponsored attackers.
That is evidenced by the truth that UAC-0098, a risk actor that has traditionally delivered the IcedID malware, was noticed repurposing its methods to assault Ukraine as a part of a set of ransomware assaults.
Some members of UAC-0098 are assessed to be former members of the now-defunct Conti cybercrime group. TrickBot, which was absorbed into the Conti operation final yr previous to the latter’s shutdown, has additionally resorted to systematically concentrating on Ukraine.
It isn’t simply Russia, as the continued battle has led Chinese language government-backed attackers equivalent to CURIOUS GORGE (aka UNC3742) and BASIN (aka Mustang Panda) to shift their focus in the direction of Ukrainian and Western European targets for intelligence gathering.
“It’s clear cyber will proceed to play an integral function in future armed battle, supplementing conventional types of warfare,” Huntley stated.
The disclosure comes because the Laptop Emergency Response Crew of Ukraine (CERT-UA) warned of phishing emails concentrating on organizations and establishments that purport to be crucial safety updates however truly include executables that result in the deployment of distant desktop management software program on the contaminated techniques.
CERT-UA attributed the operation to a risk actor it tracks underneath the moniker UAC-0096, which was beforehand detected adopting the identical modus operandi again in late January 2022 within the weeks resulting in the battle.
“A yr after Russia launched its full-scale invasion of Ukraine, Russia stays unsuccessful in bringing Ukraine underneath its management because it struggles to beat months of compounding strategic and tactical failures,” cybersecurity agency Recorded Future stated in a report printed this month.
“Regardless of Russia’s standard navy setbacks and its failure to substantively advance its agenda by means of cyber operations, Russia maintains its intent to deliver Ukraine underneath Russian management,” it added, whereas additionally highlighting its “burgeoning navy cooperation with Iran and North Korea.”