Sixty p.c of breaches have resulted in corporations recouping the price of fines, clean-up, and technological enhancements by rising costs, primarily making shoppers pay for breaches and firms’ lack of preparedness, in response to an annual report printed on July 27.
The “Value of Knowledge Breach Report 2022” report, primarily based on a survey of executives and safety professionals at 550 corporations, says the typical price of an information breach continued to rise in 2022, reaching a mean of $4.4 million globally (up 13% since 2020) and $9.4 million in the USA. On common, corporations required 277 days to establish and comprise information breaches, down from 287 days in 2021, and 83% of corporations had suffered a couple of breach.
“It’s clear that cyberattacks are evolving into market stressors which might be triggering chain reactions, [and] we see that these breaches are contributing to these inflationary pressures,” says John Hendley, head of technique for IBM Safety’s X-Drive analysis crew. “We’ve got to consider cyber occasions as components which might be able to straining the economic system, much like COVID, the warfare in Ukraine, gasoline costs, all of that.”
The annual report, primarily based on surveys performed by the Ponemon Institute, is just not the primary try and gauge the influence of breaches on companies’ stability sheets. Final 12 months, a survey by security-operations agency IronNet discovered that almost all corporations have been affected by the availability chain assault on community administration agency SolarWinds, with the typical agency seeing an 11% drop in income resulting from coping with the incident.
General, specialists estimated that the incident would price SolarWinds about $18 million however would price the 18,000 affected companies and authorities companies as a lot as $100 billion in clean-up prices.
A “Cyber Tax” on Shoppers
Whereas cybersecurity specialists have more and more urged corporations to rely on having their techniques compromised, they proceed to have issues stopping attackers, and they’re passing prices onto shoppers, Hendley notes. This means that information breaches and cyberattacks are making a cyber tax, he argues, rising prices for downstream shoppers and purchasers.
“When you consider the truth that 83% of companies have been breached not less than as soon as of their lifetime, I believe it turns into tough to say that we have to apply punitive damages to assist forestall breaches,” Hendley says. “There may be at all times going to be a approach in, so I believe the perfect funding that we will have is to attempt to shift the road from defending the perimeter to considering just like the attacker.”
Along with the labeling of breaches and fines as a cyber tax, the report highlighted numerous tendencies amongst industries coping with cyberattacks. Corporations that would scale back the general breach detection and response time to lower than 200 days saved $1.1 million, or 23% of the price of the typical breach.
Knowledge Breach Prices Worst in Healthcare
The price of a single information breach various considerably primarily based on the kind of trade affected. The closely regulated healthcare sector continued to pay out the very best quantity for compromises of knowledge, reaching a mean of $10 million per breach in 2022, in contrast with monetary companies that paid a mean of $6 million per breach, the second costliest breach price. Pharmaceutical corporations and know-how companies primarily tied for third place, paying about $5 million for every breach.
Ransomware continued to have a big influence on enterprise, regardless of indicators that — to this point this 12 months — ransomware assaults have declined considerably. The survey discovered that corporations that pay ransoms spend much less on clean-up prices, however excessive ransom totals negate most financial savings. As well as, 80% of corporations that pay ransoms are attacked once more, in response to the “Ransomware: The True Value to Enterprise” report printed by safety agency CyberReason final 12 months.
Ransomware Not as Expensive as Phishing Assaults
Different analysis has highlighted the influence of ransomware on corporations that haven’t adequately ready for damaging assaults. Two-thirds of worldwide companies hit with ransomware suffered a big income loss, they stated, as did 58% of these surveyed at US corporations particularly. The assaults total have led to 31% of worldwide corporations shuttering some a part of their companies.
“It’s attention-grabbing to see the fee distinction between ransomware victims who selected to pay and those that selected to not,” Nicole Hoffman, senior cyber-threat intelligence analyst at Digital Shadows, a digital-risk safety agency. “Those that pay are sometimes focused once more inside months of the unique assault, which might improve monetary losses considerably. These components are vital to contemplate when making the difficult enterprise choice of whether or not or to not pay.”
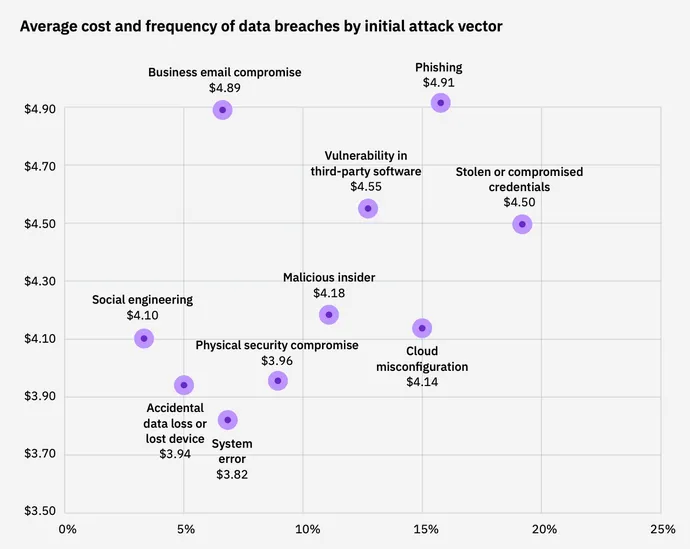
That stated, the preliminary vector of the assault additionally had a big influence on price. Enterprise e mail compromise (BEC) and phishing assaults led to the very best common breach prices — about $4.9 million per incident — with third-party vulnerabilities and compromised credentials accounting for damages of roughly $4.5 million per incident.
The IBM-Ponemon report additionally highlighted applied sciences that would have the biggest influence on information breach prices. Corporations that use synthetic intelligence and machine studying (AI/ML) applied sciences, DevSecOps processes, and shaped an incident-response crew saved about $300,000, $276,000, and $253,000 per incident, respectively.
In distinction, corporations that suffered from safety system complexity, have been migrating the enterprise to the cloud, and had compliance failures noticed the biggest will increase in price per incident.
The report relies on greater than 3,600 interviews with people from 550 corporations of assorted sizes, specializing in breaches that concerned wherever from 2,200 to 102,000 data. Breaches outdoors that vary weren’t included.


