The rise of the cloud has made enterprise extra agile, versatile, and streamlined, that are all stable explanation why over 90% of enterprises have dedicated to a multicloud technique. However complexity creates seams the place secrets and techniques leak out. Latest high-profile breaches at Microsoft and at airports have made misconfigured S3 buckets a cybersecurity trope. Nevertheless, configuration points aren’t the one drawback: Entry creep is simply as harmful and customary, in accordance with current figures.
Overprivileging occurs when a service or account requests or requires all of the permissions it’d presumably ever use, normally to be able to keep away from having to return and request new permissions if the necessity arises later. This may not be a not nice state of affairs even at a single-server degree, however as varied providers and distributors work together, every granted its personal excessive degree of permissions, the possibility of compromise builds.
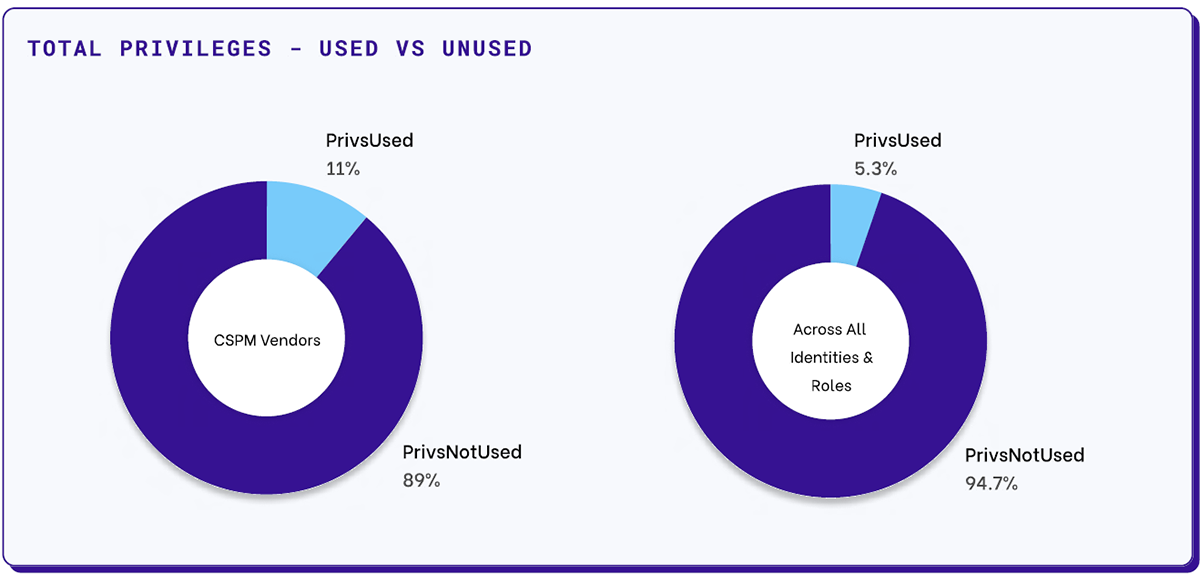
In its end-of-year abstract for 2022, cloud safety firm Permiso reported that cloud safety posture administration (CSPM) distributors use a mere 11% of the permissions they’re granted. This shrinks to five.3% throughout all customers and roles. That is loads of unlocked doorways that no one must open.
The outcomes of its evaluation jibe with the outcomes from a CloudKnox survey from two years in the past, which discovered that 90% to 95% of identities on Amazon Internet Providers, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and vSphere used not more than 2% to five% of the permissions granted.
“Most groups assume that these secrets and techniques are solely being utilized by the people or workloads they’ve been provisioned to, however in actuality, these secrets and techniques are sometimes shared, hardly ever rotated, are long-lived and never single-use, so similar to passwords, they turn out to be extra weak as they age,” the Permiso crew wrote.
And therein lies the issue. Organizations are normally fairly strict about organising permissions for human customers, however they have a tendency to permit the requested default permissions for machine identities. This results in a state of affairs during which risk actors want solely discover a method into one overly broadly permissioned account to be able to acquire privileged entry over a lot of the company cloud.
“You might have your database completely locked down, but when a service that has entry to that database has the permissions for anybody to get in, your database is pretty much as good as compromised,” warned Kendall Miller, president of Kubernetes governance service FairWinds, in 2021.
And for the yr 2022, Permiso flatly declared, “All the incidents we detected and responded to had been a results of a compromised credential,” fairly than a misconfigured cloud useful resource.
The important thing to managing this threat is to audit permissions and institute robust identification entry administration (IAM) insurance policies for all customers, not simply people. That begins with figuring out what knowledge an software really wants entry to — and what it does not. A software program org chart would possibly show useful in tracing out the routes of entry amongst apps and assigning or proscribing permissions.