Whereas multifactor authentication, single-sign-on infrastructure, and stronger password necessities have improved the safety of most enterprise id and entry administration (IAM) environments, the longevity of passwords continues to pose issues for companies, particularly in granting momentary entry to contractors and third-party companions.
A wide range of distributors are attempting to resolve this downside. Final week, for instance, data-security agency Keeper Safety introduced one-time shared passwords that permit corporations to grant third-party companions momentary entry to information and assets with out including them to the corporate’s general IT atmosphere. The strategy permits particular kinds of paperwork to be shared to a single consumer system, robotically eradicating entry when the time expires.
The enterprise case is all about securing entry granted to contractors, says Craig Lurey, chief expertise officer and co-founder of Keeper Safety.
“We get requested consistently to permit quick time period, momentary entry to 3rd events with out requiring them to onboard as a licensed consumer,” he says. “With this new characteristic, there may be not 20 steps anymore. It’s simply prompt, however preserving that encryption, simplifying the secure-sharing course of, and eliminating the necessity to ship non-public data over textual content messages.”
Credential Theft Is Huge Enterprise
Provide chain breaches, stolen credentials, and the proliferation of software program keys and secrets and techniques proceed to undermine IT and information safety. In March, secrets-detection agency GitGuardian discovered that builders leaked 50% extra credentials, entry tokens, and API keys in 2021, in comparison with 2020. Total, 3 out of each 1,000 commits uncovered a delicate password, key, or credential, the corporate stated on the time.
Failing to guard software program secrets and techniques, consumer passwords, and machine credentials can result in compromises of software infrastructure and growth environments. Attackers have more and more focused identities and credentials as a option to acquire preliminary entry to company networks. Final week, for instance, software program safety agency Sonatype found that no less than 5 malicious Python packages try and exfiltrate secrets and techniques and atmosphere variables for Amazon environments.
“It stays but to be identified who the actors behind these packages are and what’s their final aim,” Sonatype acknowledged in an advisory on the problem. “Have been the stolen credentials being deliberately uncovered on the net or a consequence of poor OpSec practices?”
How Zero-Data Encryption Protects Credentials
Managing the entry credentials for information means avoiding centralized storage of delicate keys — a safety benefit of zero-knowledge encryption (ZKE) — and often expiring keys in order that former contractors, companions, and staff not have entry to information. ZKE breaks up keys in particular methods, utilizing each cryptography and tokenization, to forestall any system or database from having all the mandatory data to reconstitute the grasp keys to unlock information.
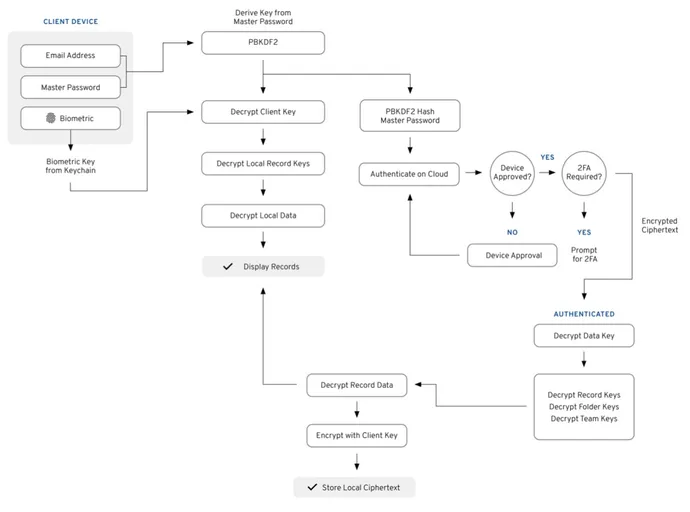
The transfer to de-emphasize grasp passwords and keys is a part of the cybersecurity business’s effort to create a passwordless safety infrastructure. But, in the long run, most enterprises depend on some form of password to safe huge shops of keys or unlock cloud IAM companies, says Lurey.
“Yearly, the platforms attempt to give you new schemes to bury the password, [but] on the finish of the day, these platforms nonetheless depend on passwords, particularly for account restoration,” he says. “There’s a rising variety of passwords and secrets and techniques that everybody has to take care of, whether or not you’re on the tech aspect and it’s important to take care of API keys and software program secrets and techniques, or on the private aspect and the rising variety of websites that require private or non-public data.”
Making a zero-knowledge manner of managing secrets and techniques and providing one-use, momentary passwords requires important design effort and a transfer away from the consolidation amongst giant manufacturers which can be assuming the mantles of id suppliers, Lurey says.
“The rationale why the password continues to be common is as a result of it’s one thing that you’ve that can be utilized to encrypt and decrypt information on the finish of the day,” he says. “The passkeys, that are simply passwords, are being saved by Apple, Google, and Microsoft, so these are being synched with different units and onboard units, however how do you sync these secrets and techniques — it’s mainly a rabbit gap of authentication points.”
The Passwordless Path Forward
The concentrate on ZKE is comparatively new, and the overwhelming majority of corporations defend their secrets and techniques utilizing key administration techniques, says Andras Cser, vice chairman and principal analyst for safety and danger at Forrester Analysis. The concentrate on passwordless applied sciences sometimes entails biometrics, QR-code-based authentication, pushing authentication tokens to cellular units, and sending one-time passwords through e-mail or textual content message, he says.
“Due to phishing points, OTP and passwordless is slowly changing the static password for authentication. Identification administration and governance (IMG) to onboard, assessment, and off-board contractors and third events for entry is essential on this circulate,” Cser says.
Whether or not ZKE takes off will possible rely upon whether or not third-party id companies utilizing de facto requirements, such because the FIDO2 and WebAuthn passwordless requirements, acquire recognition. In a white paper acknowledging the gradual adoption of FIDO and the longer term integration with WebAuthn, the FIDO Alliance outlined what its passwordless future would seem like, utilizing cellular units as standardized authenticators and permitting credentials to be synced throughout units.
The modifications will make “FIDO the primary authentication expertise that may match the ubiquity of passwords, with out the inherent dangers and phishability,” the white paper acknowledged.


