Attackers play favorites when which software program vulnerabilities to focus on, in accordance with researchers from Palo Alto Networks.
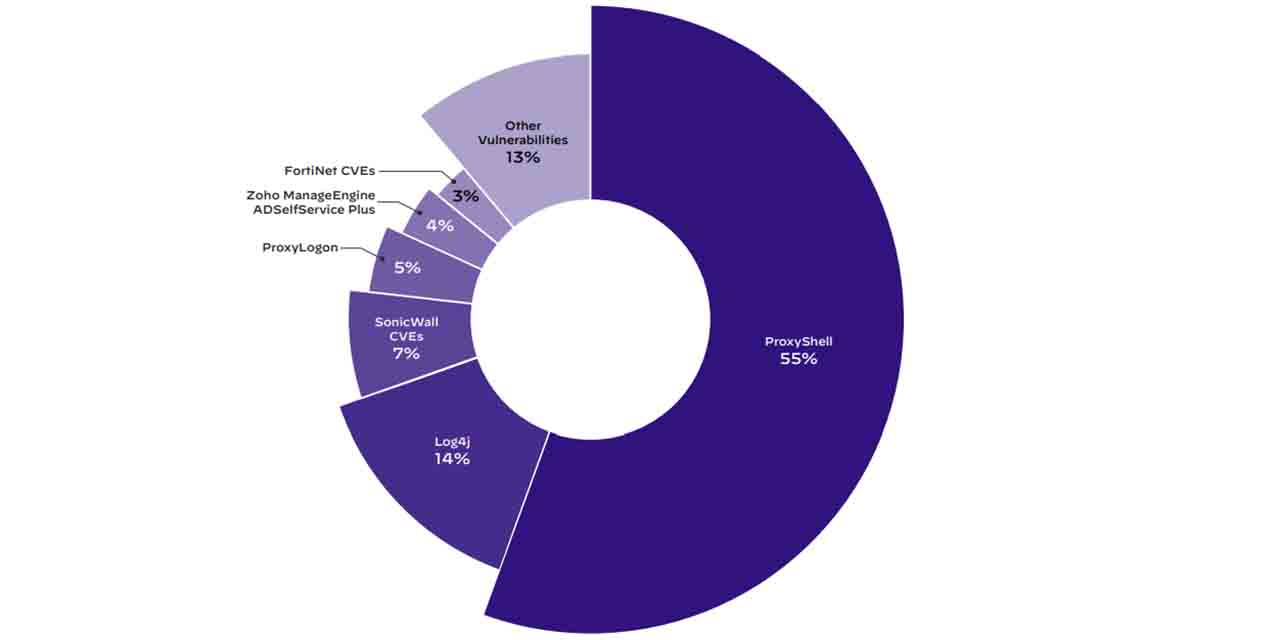
Practically one in three, or 31%, of incidents analyzed by Unit 42 in its 2022 “Incident Response Report” resulted from attackers getting access to the enterprise setting by exploiting a software program vulnerability. Six CVE classes accounted for greater than 87% of vulnerabilities being exploited: ProxyShell (CVE-2021-34473, CVE-2021-34523, CVE-2021-31207), Log4j, ProxyLogon (CVE-2021-26855, CVE-2021-26857, CVE-2021-26858, CVE-2021-27065), a number of vulnerabilities in SonicWall and Fortinet merchandise, and a vulnerability in Zoho ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus (CVE-2021-40539).
In 55% of incidents the place Unit 42 was capable of determine the vulnerability, the attackers had focused ProxyShell. Simply 14% of these circumstances concerned Log4j. Unit 42 researchers analyzed knowledge from a sampling of over 600 incident response engagements between April 2021 and Could 2022 for the report.
Whereas attackers proceed to depend on older, unpatched vulnerabilities, many are new vulnerabilities as effectively. Scanning for vulnerabilities is just not a troublesome job, so attackers start scanning for programs with a newly disclosed vulnerability as quickly as they find out about them.
“The 2021 Assault Floor Administration Risk Report [released in April] discovered that attackers sometimes begin scanning for vulnerabilities inside quarter-hour of a CVE being introduced,” the corporate mentioned in weblog publish accompanying the incident response report. “In actual fact, it may possibly virtually coincide with the reveal if the vulnerabilities themselves and the entry that may be achieved by exploiting them are important sufficient.”
For instance, researchers detected scanning and exploitation makes an attempt focusing on the authentication bypass vulnerability in F5 BIG-IP home equipment (CVE-2022-1388) 2,552 occasions inside 10 hours.
Exploiting software program vulnerabilities was the second most typical assault technique, in accordance with the Unit 42 evaluation. The highest entry vector was phishing. Brute-force credential assaults, primarily focusing on Distant Desktop Protocol, rounded out the highest three. These three assault vectors made up greater than three-quarters of incidents (77%) analyzed within the incident response report.