In what’s a seamless assault on the open supply ecosystem, over 15,000 spam packages have flooded the npm repository in an try and distribute phishing hyperlinks.
“The packages have been created utilizing automated processes, with venture descriptions and auto-generated names that intently resembled each other,” Checkmarx researcher Yehuda Gelb stated in a Tuesday report.
“The attackers referred to retail web sites utilizing referral IDs, thus making the most of the referral rewards they earned.”
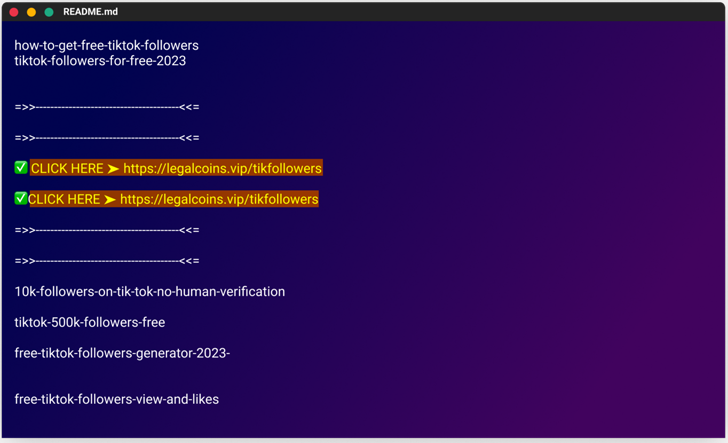
The modus operandi entails poisoning the registry with rogue packages that embrace hyperlinks to phishing campaigns of their README.md recordsdata, evocative of a related marketing campaign the software program provide chain safety agency uncovered in December 2022.
The pretend modules masqueraded as cheats and free sources, with some packages named as “free-tiktok-followers,” “free-xbox-codes,” and “instagram-followers-free.”
The last word objective of the operation is to entice customers into downloading the packages and clicking on the hyperlinks to the phishing websites with bogus guarantees of elevated followers on social media platforms.
“The misleading net pages are well-designed and, in some instances, even embrace pretend interactive chats that seem to point out customers receiving the sport cheats or followers they have been promised,” Gelb defined.
The web sites urge victims to fill out surveys, which then pave the way in which for extra surveys or, alternatively, redirect them to reliable e-commerce portals like AliExpress.
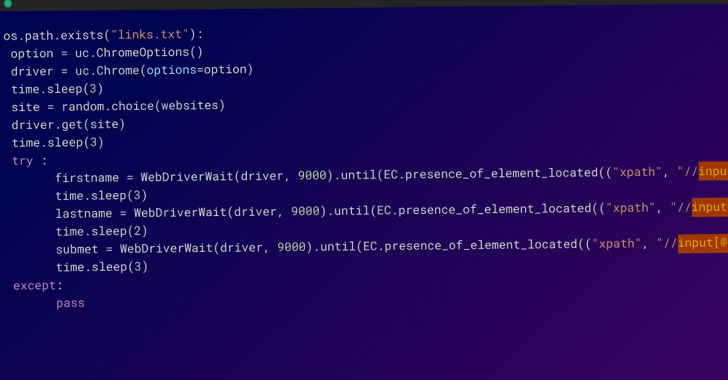
The packages are stated to have been uploaded to npm from a number of person accounts inside hours between February 20 and 21, 2023, utilizing a Python script that automates the entire course of.
What’s extra, the Python script can also be engineered to append hyperlinks to the revealed npm packages on WordPress web sites operated by the menace actor that declare to supply Household Island cheats.
That is achieved through the use of the selenium Python bundle to work together with the web sites and make the required modifications.
In all, using automation allowed the adversary to publish a lot of packages in a brief span of time, to not point out create a number of person accounts to hide the dimensions of the assault.
“This reveals the sophistication and dedication of those attackers, who have been keen to speculate vital sources so as to perform this marketing campaign,” Gelb stated.
The findings as soon as once more display the challenges in securing the software program provide chain, as menace actors proceed to adapt with “new and surprising strategies.”