At the same time as the worldwide cybersecurity abilities hole continues to widen, many organizations nonetheless cling to the concept in the event that they maintain out lengthy sufficient, they may be capable of discover rock-star veterans to fill out their safety staff rosters. A brand new survey exhibits that cybersecurity hiring managers are much less prone to take an opportunity on promising entry-level candidates than they’re to rent veteran staffers or these with at the least a 12 months of expertise.
This hesitance of many organizations to coach up newbies into the trade highlights an enormous alternative that many hiring managers have in bettering the state of their cybersecurity workforce, in accordance with the “(ISC)² Cybersecurity Hiring Managers Information.” Primarily based on a survey of 1,200 cybersecurity hiring managers from the US, UK, Canada, and India, the report particulars hiring practices across the globe.
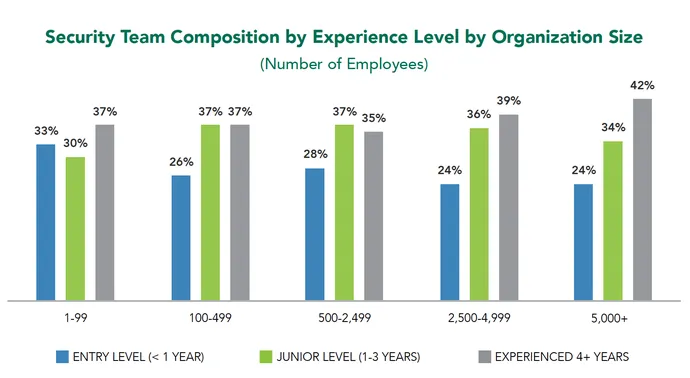
“The research exhibits us that, aside from the smallest organizations, employment ranges for entry-level cybersecurity professionals path far behind each different expertise stage,” says Tara Wisniewski, govt vp of advocacy, world markets, and member engagements for (ISC)². “It is also a very notable problem within the US and UK, in comparison with Canada and India the place entry-level employment ranges are greater general.”
Within the US, for instance, simply 26% of safety groups are composed of entry-level staff, in contrast with 38% who’ve 4 or extra years of expertise and 36% with one to 3 years of expertise. The proportion of entry-level candidates may very well even be decrease than that, contemplating that the survey methodology included solely these managers who’ve employed entry-level or junior-level candidates someday within the final two years. With these managers who solely rent skilled candidates self-selecting out, the actual numbers are probably much more stark than the report illustrates.
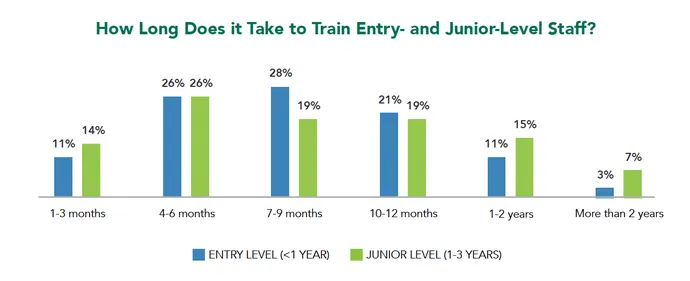
Regardless, the lag in entry-level employment charges happens even though it takes a comparatively brief period of time for these new practitioners to rise up to hurry on their job duties. Roughly 65% of hiring managers say it takes 9 months or much less to coach entry-level employees. Whereas these candidates enhance their abilities or information, they’re sometimes tasked with the repeatable safety scut work that plagues safety groups on the each day.
The highest two duties delegated to entry-level employees are alert and occasion monitoring and documenting processes and procedures, which have been respectively named by 35% of hiring managers. In open-ended feedback inside the survey, managers stated that entry-level staff members usually convey “recent concepts and views to the desk” they usually usually are prepared to go the additional mile to get forward not solely of their job however within the cybersecurity career.
One of many probably the explanation why hiring managers wrestle to maintain their cybersecurity roster freshened up with larger proportions of newcomers to the sector is that they are not essentially trying in the correct locations to seek out them.
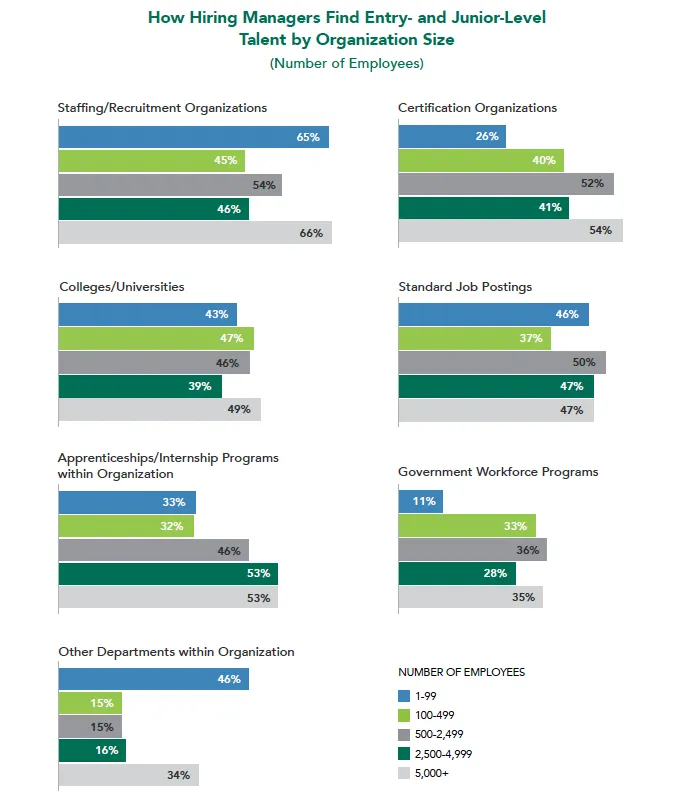
“Organizations rely closely on exterior elements and sources to seek out employees, together with searching for certifications and searching inside the memberships of certification organizations to seek out candidates,” says Wisniewski, who notes that greater than half of respondents depend on exterior recruitment professionals to fill these roles.
She believes that one of many highest-value issues that cybersecurity managers can begin doing to draw entry-level and junior-level practitioners is to seek for expertise past the world of cybersecurity and even IT. The survey exhibits that simply 18% of research contributors have employed people from inside the group who have been working in numerous job features.
“Transferrable abilities and eager-to-learn individuals will be present in gross sales, advertising and marketing, engineering, authorized, the navy, hospitality, and extra,” she says. “It is also about guaranteeing that roles, organizations, and the cybersecurity sector at giant are extra inclusive and accessible for all.”
Actuality Verify for Coaching {Dollars}
Wherever the candidates are discovered, the funding to get them to the purpose the place they will meaningfully contribute to the staff is probably going cheaper than some managers would possibly count on. Over eight in 10 respondents stated the prices are lower than $5,000, and 42% stated it prices lower than $1,000 for newcomers to start out dealing with assignments.
Even with extra vital investments in skilled improvement, Wisniewski says that hiring managers should not maintain off in hiring and coaching entry-level employees in worry that their coaching {dollars} will stroll out the door. She believes that these practitioners are essential for the sustainability of a company’s cybersecurity workforce.
“Hiring junior employees is just not a threat or a compromise. If something, it’s a proactive transfer to enhance cybersecurity resilience,” she says. “You wouldn’t maintain off investing in essential infrastructure immediately simply because there’s an opportunity the seller would possibly change technique tomorrow. The identical applies with investing in your individuals.”


