A bunch of researchers has revealed particulars of a brand new vulnerability affecting Intel CPUs that allows attackers to acquire encryption keys and different secret data from the processors.
Dubbed ÆPIC Leak, the weak spot is the first-of-its-kind to architecturally disclose delicate information in a way that is akin to an “uninitialized reminiscence learn within the CPU itself.”
“In distinction to transient execution assaults like Meltdown and Spectre, ÆPIC Leak is an architectural bug: the delicate information will get straight disclosed with out counting on any (noisy) facet channel,” the teachers stated.
The examine was carried out by researchers from the Sapienza College of Rome, the Graz College of Expertise, Amazon Net Companies, and the CISPA Helmholtz Middle for Data Safety.
The vulnerability (CVE-2022-21233, CVSS rating: 6.0), which impacts CPUs with Sunny Cowl microarchitecture, is rooted in a part referred to as Superior Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC), which gives a mechanism to deal with and route {hardware} interrupt alerts in a scalable method.
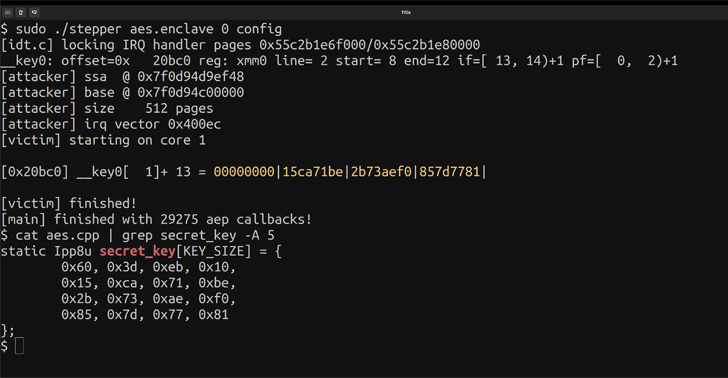
“The scan of the I/O deal with area on Intel CPUs based mostly on the Sunny Cove microarchitecture revealed that the memory-mapped registers of the native Superior Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) should not correctly initialized,” the researchers famous.
“In consequence, architecturally studying these registers returns stale information from the microarchitecture. Any information transferred between the L2 and the last-level cache will be learn by way of these registers.”
ÆPIC Leak particularly targets programs utilizing Intel’s trusted execution atmosphere (TEE) generally known as Software program Guard eXtensions (SGX), inflicting the leakage of AES and RSA keys from safe enclaves that run on the identical bodily CPU core with successful charge of 94% and 74% respectively.
“By defending chosen code and information from modification, builders can partition their software into hardened enclaves or trusted execution modules to assist improve software safety,” Intel explains concerning the safety assurances provided by SGX.
The flaw, put merely, breaks the aforementioned ensures, enabling an attacker with permissions to execute privileged native code on a goal machine to extract the non-public keys, and worse defeat attestation, a cornerstone of the safety primitives utilized in SGX to make sure the integrity of code and information.
In response to the findings, Intel has launched firmware updates, whereas describing the problem as a medium-severity vulnerability associated to improper isolation of shared sources, resulting in data disclosure by way of native entry.
It is also value noting that Intel has since deprecated help for SGX for its shopper CPUs, what with a litany of assault strategies plaguing the expertise, together with SGX-ROP, MicroScope, Plundervolt, Load Worth Injection, SGAxe, and VoltPillager.
SQUIP Facet Channel Assault Have an effect on AMD CPUs
The event comes as researchers demonstrated what is the first-ever facet channel assault (CVE-2021-46778) on scheduler queues impacting AMD Zen 1, Zen 2, and Zen 3 microarchitectures that may very well be abused by an adversary to recuperate RSA keys.
The assault, codenamed SQUIP (quick for Scheduler Queue Utilization by way of Interference Probing), entails measuring the rivalry degree on scheduler queues to probably glean delicate data.
No safety updates have been launched to patch the road of assault, however the chipmaker has really helpful that “software program builders make use of current finest practices, together with constant-time algorithms and avoiding secret-dependent management flows the place applicable.”