Google has taken steps to ax dozens of fraudulent apps from the official Play Retailer that have been noticed propagating Joker, Facestealer, and Coper malware households by the digital market.
Whereas the Android storefront is taken into account to be a trusted supply for locating and putting in apps, unhealthy actors have repeatedly discovered methods to sneak previous safety obstacles erected by Google in hopes of luring unsuspecting customers into downloading malware-laced apps.
The newest findings from Zscaler ThreatLabz and Pradeo aren’t any totally different. “Joker is among the most distinguished malware households concentrating on Android gadgets,” researchers Viral Gandhi and Himanshu Sharma mentioned in a Monday report.
“Regardless of public consciousness of this specific malware, it retains discovering its method into Google’s official app retailer by repeatedly modifying the malware’s hint signatures together with updates to the code, execution strategies, and payload-retrieving strategies.”
Categorized as fleeceware, Joker (aka Bread) is designed to subscribe customers to undesirable paid companies or make calls to premium numbers, whereas additionally gathering SMS messages, contact lists, and system data. It was first noticed within the Play Retailer in 2017.
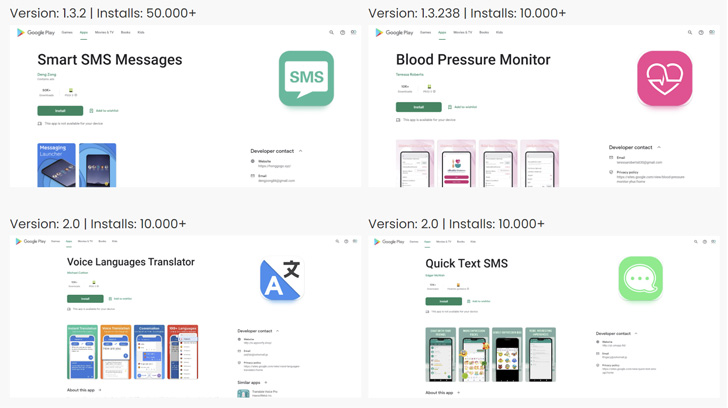
A complete of 53 Joker downloader apps have been recognized by the 2 cybersecurity corporations, with the functions downloaded cumulatively over 330,000 occasions. These apps usually pose as SMS, photograph editors, blood strain monitor, emoji keyboards, and translation apps that, in flip, request elevated permissions for the system to hold out its operations.
“As a substitute of ready for apps to achieve a specified quantity of installs and critiques earlier than swapping for a malware-laced model, the Joker builders have taken to hiding the malicious payload in a typical asset file and package deal utility utilizing business packers,” the researchers defined the brand new tactic adopted by the persistent malware to bypass detection.
It isn’t simply Joker, as safety researcher Maxime Ingrao final week disclosed eight apps containing a distinct variant of the malware referred to as Autolycos that racked up a complete of over three million downloads previous to their removing from the app retailer after greater than six months.
“What’s new about this kind is that it not requires a WebView,” Malwarebytes researcher Pieter Arntz mentioned. “Not requiring a WebView vastly reduces the possibilities that the consumer of an affected system notices one thing fishy is happening. Autolycos avoids WebView by executing URLs on a distant browser after which together with the lead to HTTP requests.”
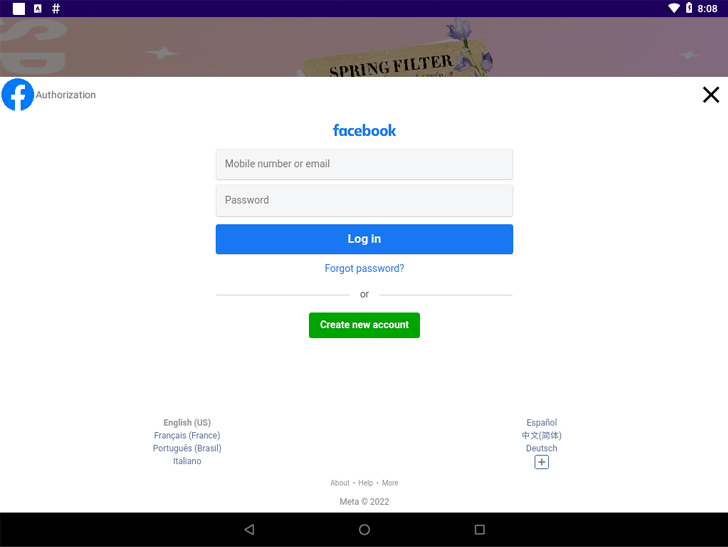
Additionally found within the official market have been apps embedding Facestealer and Coper malware. Whereas the previous permits the operators to siphon Fb credentials and auth tokens, Coper — a descendant of the Exobot malware — features as a banking trojan that may steal a variety of knowledge.
Coper is “able to intercepting and sending SMS textual content messages, making USSD (Unstructured Supplementary Service Information) requests to ship messages, keylogging, locking/unlocking the system display screen, performing overly assaults, stopping uninstalls and usually permitting attackers to take management and execute instructions on contaminated system by way of distant reference to a C2 server,” the researchers mentioned.
The malware, like different banking trojans, can also be identified to abuse the accessibility permissions on Android to achieve full management of the sufferer’s cellphone. The record of Facestealer and Coper dropper apps is as follows –
- Vanilla Digicam (cam.vanilla.snapp)
- Unicc QR Scanner (com.qrdscannerratedx)
If something, the findings add to Google’s storied historical past of struggling to maintain such fleeceware and spyware and adware apps off its cell app retailer, partially owing to a large number of evolving ways adopted by risk actors to fly below the radar.
In addition to the standard guidelines of thumb on the subject of downloading apps from app shops, customers are advisable to chorus from granting pointless permissions to apps and confirm their legitimacy by checking for developer data, studying critiques, and scrutinizing their privateness insurance policies.