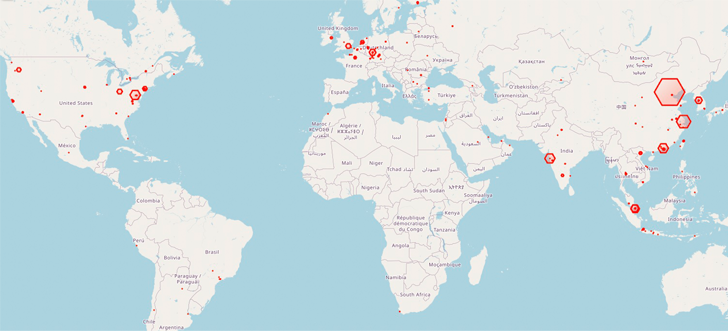
A minimum of 1,200 Redis database servers worldwide have been corralled right into a botnet utilizing an “elusive and extreme risk” dubbed HeadCrab since early September 2021.
“This superior risk actor makes use of a state-of-the-art, custom-made malware that’s undetectable by agentless and conventional anti-virus options to compromise numerous Redis servers,” Aqua safety researcher Asaf Eitani stated in a Wednesday report.
A major focus of infections has been recorded in China, Malaysia, India, Germany, the U.Okay., and the U.S. to this point. The origins of the risk actor are presently unknown.
The findings come two months after the cloud safety agency make clear a Go-based malware codenamed Redigo that has been discovered compromising Redis servers.
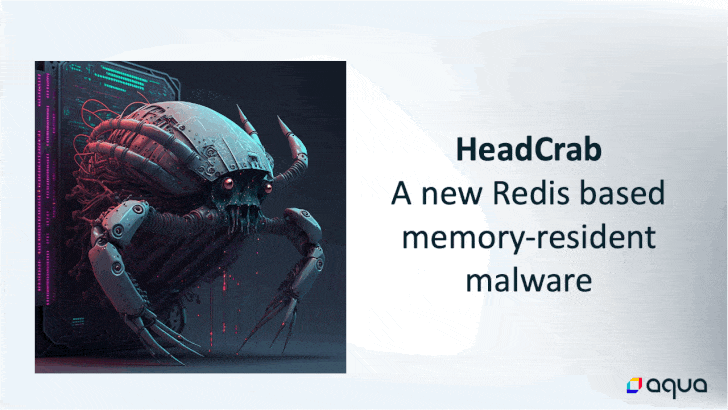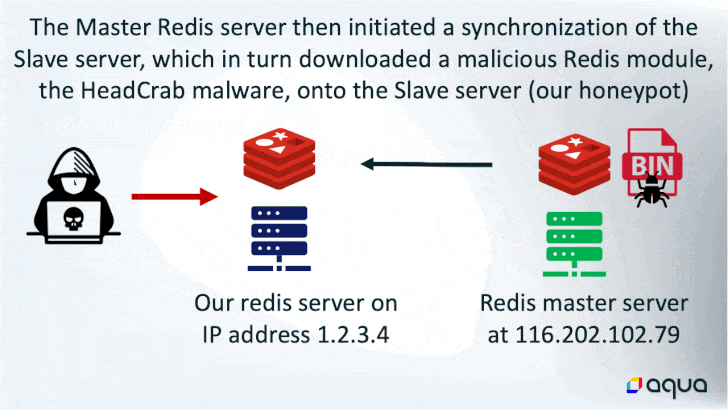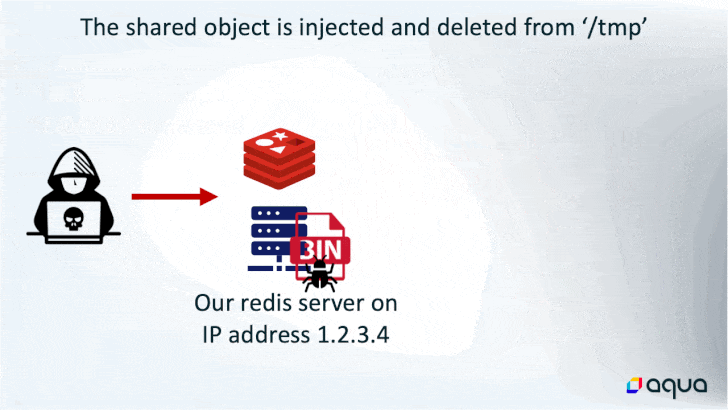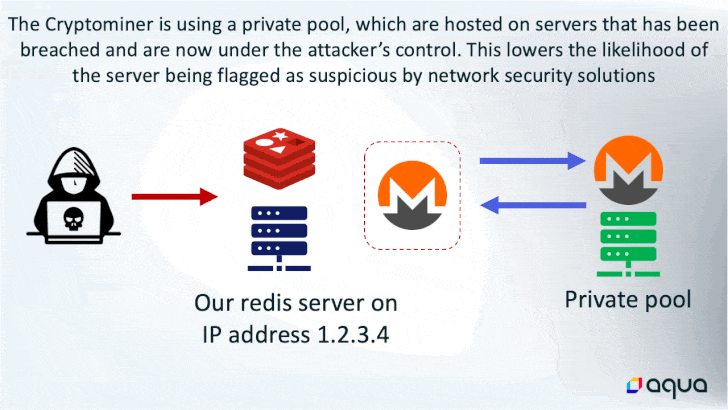
The assault is designed to focus on Redis servers which are uncovered to the web, adopted by issuing a SLAVEOF command from one other Redis server that is already beneath the adversary’s management.
In doing so, the rogue “grasp” server initiates a synchronization of the newly hacked server to obtain the malicious payload, which comprises the subtle HeadCrab malware.
“The attacker appears to primarily goal Redis servers and has a deep understanding and experience in Redis modules and APIs as demonstrated by the malware,” Eitani famous.
Whereas the last word finish aim of utilizing the memory-resident malware is to hijack the system sources for cryptocurrency mining, it additionally boasts of quite a few different choices that permits the risk actor to execute shell instructions, load fileless kernel modules, and exfiltrate knowledge to a distant server.
What’s extra, a follow-on evaluation of the Redigo malware has revealed it to be weaponizing the identical master-slave approach for proliferation, and never the Lua sandbox escape flaw (CVE-2022-0543) as beforehand disclosed.
Customers are advisable to chorus from exposing Redis servers on to the web, disable the “SLAVEOF” function of their environments if not in use, and configure the servers to solely settle for connections from trusted hosts.
Eitani stated “HeadCrab will persist in utilizing cutting-edge methods to penetrate servers, both by way of exploiting misconfigurations or vulnerabilities.”