Utilizing characters as placeholders is a standard follow in pc programming. For those who’ve ever tried including a number of recordsdata with an extension just like Git to a listing utilizing the git add *.java command, you then’ve used the glob sample.
The glob sample is mostly used to specify filenames, known as wildcard characters, and strings, known as wildcard matching. The glob sample provides all recordsdata inside a listing with the .java extension, whereas the git add * command will add all recordsdata except these with a dot . in the beginning of their title in a given listing.
On this article, we’ll discover learn how to use the glob sample in Node.js to symbolize or specify filenames and arbitrary strings. To comply with together with this tutorial, you’ll want the next:
- A fundamental understanding of Node.js
- Node.js put in in your machine
- A code editor, ideally VS Code
Desk of contents
What’s glob matching?
Glob matching, or globbing, is a programming strategy that entails utilizing wildcards or glob patterns to specify or match filenames or a set of arbitrary strings.
In comparison with the glob sample, common expression patterns is likely to be extra subtle. Nevertheless, a simplified glob sample can show helpful in some instances and get the job completed.
Frequent glob patterns
* is without doubt one of the mostly supported fundamental wildcard matching patterns throughout totally different programming languages. * matches any character zero or extra instances, excluding /. It additionally doesn’t match recordsdata with dot . in the beginning of their title except specified by the programmer utilizing the dotglob frequent choice.
The ** wildcard sample matches any character zero or extra instances, together with /. The ? wildcard sample matches any character as soon as, but it surely usually doesn’t match a dotfile, a file title with a number one dot ..
Lastly, the [abc] wildcard sample matches specified characters as outlined. On this case, a, b, and c. Now that now we have an understanding of what a glob is, let’s discover ways to implement globbing in Node.js.
Establishing our mission
First, we’ll create a brand new Node.js mission. First, create a package deal.json with the next command:
npm init -y
Subsequent, we’ll set up the glob package deal with the next command:
npm set up glob
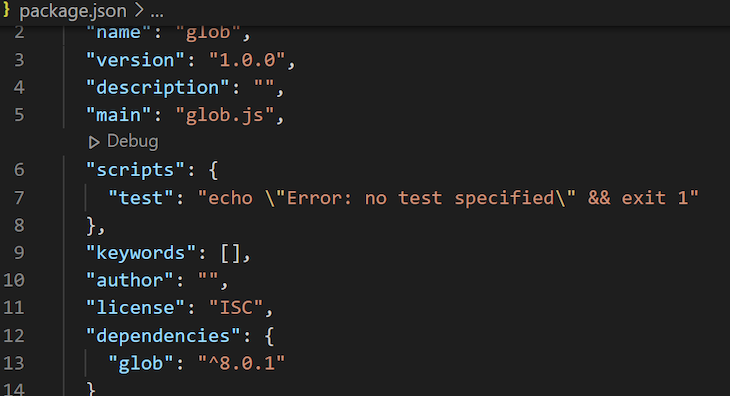
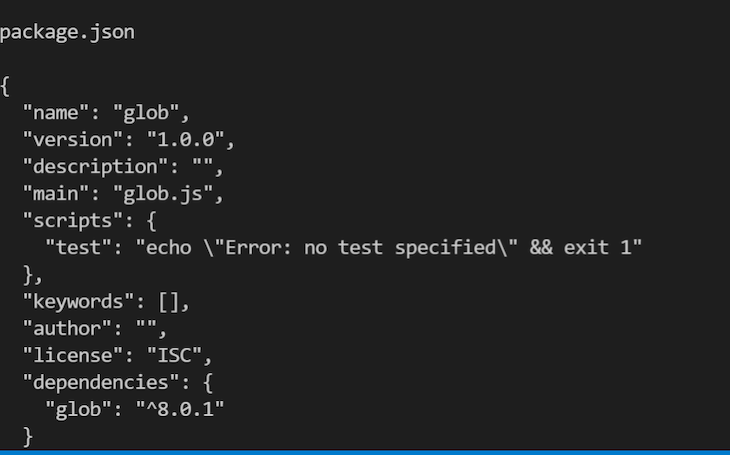
Your package deal.json file ought to appear like the picture above. Now, let’s write a pattern code for utilizing the glob package deal. Create two recordsdata in your Node.js mission folder, glob.js and log.js:
Add the next code in your glob.js file:
const glob = require(“glob”);
glob("*.js", (error, filesWithJs)=>{
if(error){
console.log(error)
}
console.log(filesWithJs)
}
Within the code above, I imported the glob module, then handed a sample into the glob perform and a callback perform that returns the results of the sample within the perform.
While you run the code above, a listing of recordsdata with the extension .js can be printed:
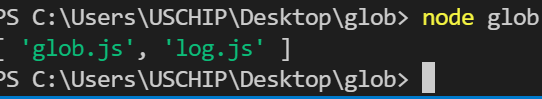
Relying on the variety of .js recordsdata you’ve got in your present working listing, your output ought to look just like the screenshot above.
Now, let’s see learn how to navigate the present working listing and subdirectory utilizing the Node.js glob patterns. Within the glob.js file the place we imported the glob package deal, write the next code:
perform directoryFiles(error, jsonFilesInDirectory){
return console.log(jsonFilesInDirectory);
}
glob('*../**/*.json', directoryFiles)
The code snippet above will search by way of the present listing and subdirectory for recordsdata ending with .json as their extension, then print them to the console. The output can be an array of recordsdata ending with.json. Yours could differ barely from the picture beneath:
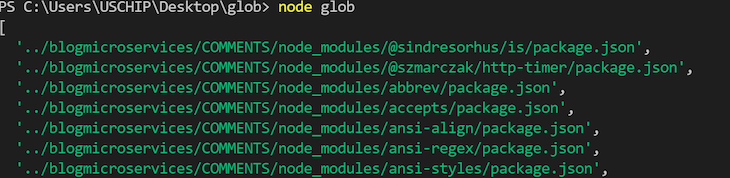
Navigating by way of the pc listing
Subsequent, we’ll be taught to make use of the Node.js package deal to navigate by way of the pc listing. To entry the present listing of a Node.js utility, now we have two choices to select from, course of.cwd() and __dirname.
The course of.cwd() methodology lies within the Node.js international object and supplies details about the present working listing of a Node.js course of. However, the __dirname variable returns the listing title of the present module or file.
The code snippet beneath illustrates the distinction between course of.cwd() and __dirname:
console.log("That is course of.cwd", course of.cwd());
console.log("That is _dirname", __dirname);
Earlier than you run the code above, navigate a step backwards in your listing with the cd.. command:
![]()
The picture beneath reveals the result of the command:
![]()
Go forward and run your Node.js utility with the command beneath:
node glob
![]()
The results of operating the code above is within the picture beneath:
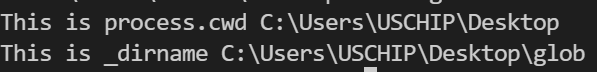
Now that we perceive the distinction between course of.cwd() and __dirname, let’s use the course of.cwd() perform with glob. We’ll use the next code snippet for illustration:
const glob = require(“glob”);
stepInDirectory = {
cwd: "../"
}
allJSFiles = (error, filesWithJS)=>console.log(filesWithJS);
// add a glob sample
glob('**/*.js', stepInDirectory, allJSFiles);
console.log("That is an illustration for the present working listing", course of.cwd());
To date, we’ve solely used the Node.js glob package deal for globbing, or sample matching, however the Node.js glob isn’t restricted to sample matching. In collaboration with the Node.js file system package deal, fs, you need to use glob to learn recordsdata.
The code snippet beneath illustrates learn how to use glob and fs in a Node.js utility to learn recordsdata:
const glob = require(“glob”);
const fs = require('’fs”);
const readFiles = perform (pat, forFile) {
// sample
pat="*.json";
// for file methodology
forFile = (contentOfFile, jsonFileInDirectory) => {
console.log(' ');
console.log(jsonFileInDirectory);
console.log(' ');
console.log(contentOfFile);
console.log(' ');
};
// utilizing glob
glob(pat, perform (err, recordsdata) {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
} else {
recordsdata.forEach(perform (file) {
fs.readFile(file, perform (err, knowledge) {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
} else {
forFile(knowledge.toString(), file);
}
});
});
}
});
};
readFiles();
The code examines the present folder for recordsdata ending with .json, prints an area, reads the content material, and eventually prints it to the console. You probably have the identical code as I’ve, the output ought to be comparable the to the one beneath:
Conclusion
On this tutorial, we lined a number of of the most typical glob patterns together with *, **, ? , and eventually [abc], contemplating the variations between wildcard characters and wildcard matching. We demonstrated how globbing can be utilized in Node.js purposes together with fs, one other helpful Node.js package deal, to learn recordsdata in our utility.
We additionally illustrated learn how to use the glob sample to traverse our working listing. The teachings from this tutorial ought to be sufficient to get you began utilizing the glob package deal in Node.js, however make sure you go away a remark in case you have any questions. Glad coding!
200’s solely  Monitor failed and sluggish community requests in manufacturing
Monitor failed and sluggish community requests in manufacturing
Deploying a Node-based internet app or web site is the simple half. Ensuring your Node occasion continues to serve assets to your app is the place issues get more durable. For those who’re all for making certain requests to the backend or third occasion companies are profitable, strive LogRocket.  https://logrocket.com/signup/
https://logrocket.com/signup/
LogRocket is sort of a DVR for internet and cellular apps, recording actually the whole lot that occurs whereas a person interacts together with your app. As an alternative of guessing why issues occur, you may combination and report on problematic community requests to shortly perceive the basis trigger.
LogRocket devices your app to file baseline efficiency timings similar to web page load time, time to first byte, sluggish community requests, and in addition logs Redux, NgRx, and Vuex actions/state. Begin monitoring totally free.