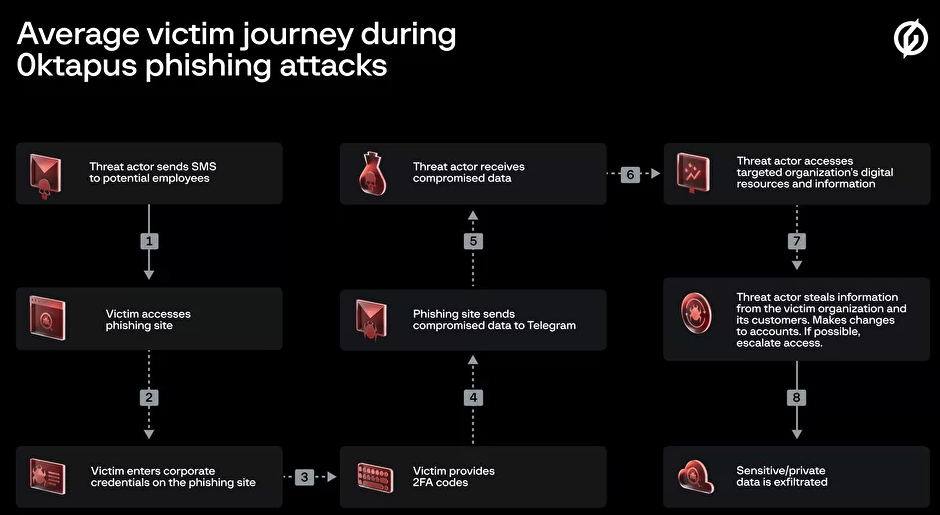
Phishers are having fun with exceptional success utilizing textual content messages to steal distant entry credentials and one-time passcodes from staff at among the world’s largest expertise corporations and buyer help companies. A latest spate of SMS phishing assaults from one cybercriminal group has spawned a flurry of breach disclosures from affected corporations, that are all struggling to fight the identical lingering safety risk: The flexibility of scammers to work together straight with staff by means of their cell units.

In mid-June 2022, a flood of SMS phishing messages started concentrating on staff at industrial staffing companies that present buyer help and outsourcing to 1000’s of corporations. The missives requested customers to click on a hyperlink and log in at a phishing web page that mimicked their employer’s Okta authentication web page. Those that submitted credentials have been then prompted to supply the one-time password wanted for multi-factor authentication.
The phishers behind this scheme used newly-registered domains that always included the title of the goal firm, and despatched textual content messages urging staff to click on on hyperlinks to those domains to view details about a pending change of their work schedule.
The phishing websites leveraged a Telegram immediate message bot to ahead any submitted credentials in real-time, permitting the attackers to make use of the phished username, password and one-time code to log in as that worker at the actual employer web site. However due to the best way the bot was configured, it was potential for safety researchers to seize the data being despatched by victims to the general public Telegram server.
This information trove was first reported by safety researchers at Singapore-based Group-IB, which dubbed the marketing campaign “0ktapus” for the attackers concentrating on organizations utilizing id administration instruments from Okta.com.
“This case is of curiosity as a result of regardless of utilizing low-skill strategies it was in a position to compromise numerous well-known organizations,” Group-IB wrote. “Moreover, as soon as the attackers compromised a corporation they have been rapidly in a position to pivot and launch subsequent provide chain assaults, indicating that the assault was deliberate fastidiously upfront.”
It’s not clear what number of of those phishing textual content messages have been despatched out, however the Telegram bot information reviewed by KrebsOnSecurity exhibits they generated practically 10,000 replies over roughly two months of sporadic SMS phishing assaults concentrating on greater than 100 corporations.
An incredible many responses got here from those that have been apparently clever to the scheme, as evidenced by the a whole bunch of hostile replies that included profanity or insults aimed on the phishers: The very first reply recorded within the Telegram bot information got here from one such worker, who responded with the username “havefuninjail.”
Nonetheless, 1000’s replied with what seem like legit credentials — a lot of them together with one-time codes wanted for multi-factor authentication. On July 20, the attackers turned their sights on web infrastructure big Cloudflare.com, and the intercepted credentials present not less than 5 staff fell for the rip-off (though solely two staff additionally supplied the essential one-time MFA code).
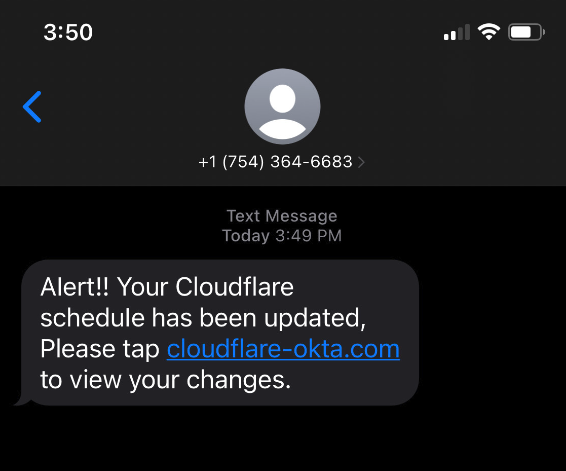
Picture: Cloudflare.com
In a weblog put up earlier this month, Cloudflare mentioned it detected the account takeovers and that no Cloudflare methods have been compromised. However Cloudflare mentioned it needed to name consideration to the phishing assaults as a result of they’d most likely work in opposition to most different corporations.
“This was a complicated assault concentrating on staff and methods in such a method that we consider most organizations can be more likely to be breached,” Cloudflare CEO Matthew Prince wrote. “On July 20, 2022, the Cloudflare Safety staff acquired stories of staff receiving legitimate-looking textual content messages pointing to what gave the impression to be a Cloudflare Okta login web page. The messages started at 2022-07-20 22:50 UTC. Over the course of lower than 1 minute, not less than 76 staff acquired textual content messages on their private and work telephones. Some messages have been additionally despatched to the workers relations.”
On three separate events, the phishers focused staff at Twilio.com, a San Francisco based mostly firm that gives companies for making and receiving textual content messages and telephone calls. It’s unclear what number of Twilio staff acquired the SMS phishes, however the information counsel not less than 4 Twilio staff responded to a spate of SMS phishing makes an attempt on July 27, Aug. 2, and Aug. 7.
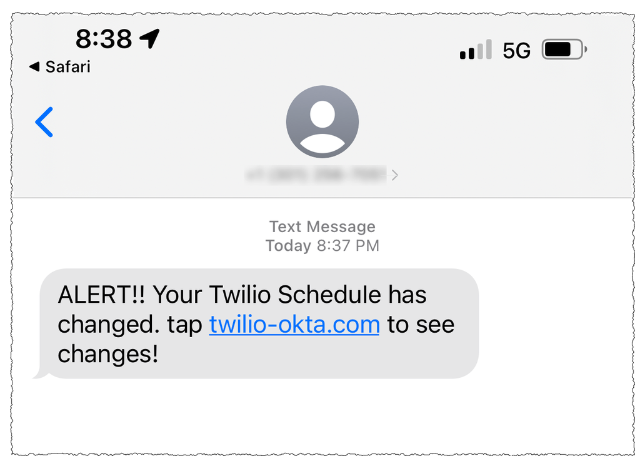
On that final date, Twilio disclosed that on Aug. 4 it grew to become conscious of unauthorized entry to data associated to a restricted variety of Twilio buyer accounts by means of a complicated social engineering assault designed to steal worker credentials.
“This broad based mostly assault in opposition to our worker base succeeded in fooling some staff into offering their credentials,” Twilio mentioned. “The attackers then used the stolen credentials to achieve entry to a few of our inner methods, the place they have been in a position to entry sure buyer information.”
That “sure buyer information” included data on roughly 1,900 customers of the safe messaging app Sign, which relied on Twilio to supply telephone quantity verification companies. In its disclosure on the incident, Sign mentioned that with their entry to Twilio’s inner instruments the attackers have been in a position to re-register these customers’ telephone numbers to a different system.
On Aug. 25, meals supply service DoorDash disclosed {that a} “subtle phishing assault” on a third-party vendor allowed attackers to achieve entry to a few of DoorDash’s inner firm instruments. DoorDash mentioned intruders stole data on a “small share” of customers which have since been notified. TechCrunch reported final week that the incident was linked to the identical phishing marketing campaign that focused Twilio.
This phishing gang apparently had nice success concentrating on staff of all the main cell wi-fi suppliers, however most particularly T-Cellular. Between July 10 and July 16, dozens of T-Cellular staff fell for the phishing messages and supplied their distant entry credentials.
“Credential theft continues to be an ongoing difficulty in our business as wi-fi suppliers are consistently battling dangerous actors which are targeted on discovering new methods to pursue unlawful actions like this,” T-Cellular mentioned in a press release. “Our instruments and groups labored as designed to rapidly determine and reply to this large-scale smishing assault earlier this yr that focused many corporations. We proceed to work to stop most of these assaults and can proceed to evolve and enhance our method.”
This similar group noticed a whole bunch of responses from staff at among the largest buyer help and staffing companies, together with Teleperformanceusa.com, Sitel.com and Sykes.com. Teleperformance didn’t reply to requests for remark. KrebsOnSecurity did hear from Christopher Knauer, world chief safety officer at Sitel Group, the shopper help big that lately acquired Sykes. Knauer mentioned the assaults leveraged newly-registered domains and requested staff to approve upcoming modifications to their work schedules.
Knauer mentioned the attackers arrange the phishing domains simply minutes upfront of spamming hyperlinks to these domains in phony SMS alerts to focused staff. He mentioned such techniques largely sidestep automated alerts generated by corporations that monitor model names for indicators of recent phishing domains being registered.
“They have been utilizing the domains as quickly as they grew to become accessible,” Knauer mentioned. “The alerting companies don’t usually let till 24 hours after a site has been registered.”
On July 28 and once more on Aug. 7, a number of staff at electronic mail supply agency Mailchimp supplied their distant entry credentials to this phishing group. In response to an Aug. 12 weblog put up, the attackers used their entry to Mailchimp worker accounts to steal information from 214 prospects concerned in cryptocurrency and finance.
On Aug. 15, the internet hosting firm DigitalOcean revealed a weblog put up saying it had severed ties with MailChimp after its Mailchimp account was compromised. DigitalOcean mentioned the MailChimp incident resulted in a “very small quantity” of DigitalOcean prospects experiencing tried compromises of their accounts by means of password resets.
In response to interviews with a number of corporations hit by the group, the attackers are principally concerned about stealing entry to cryptocurrency, and to corporations that handle communications with individuals concerned about cryptocurrency investing. In an Aug. 3 weblog put up from electronic mail and SMS advertising and marketing agency Klaviyo.com, the corporate’s CEO recounted how the phishers gained entry to the corporate’s inner instruments, and used that to obtain data on 38 crypto-related accounts.
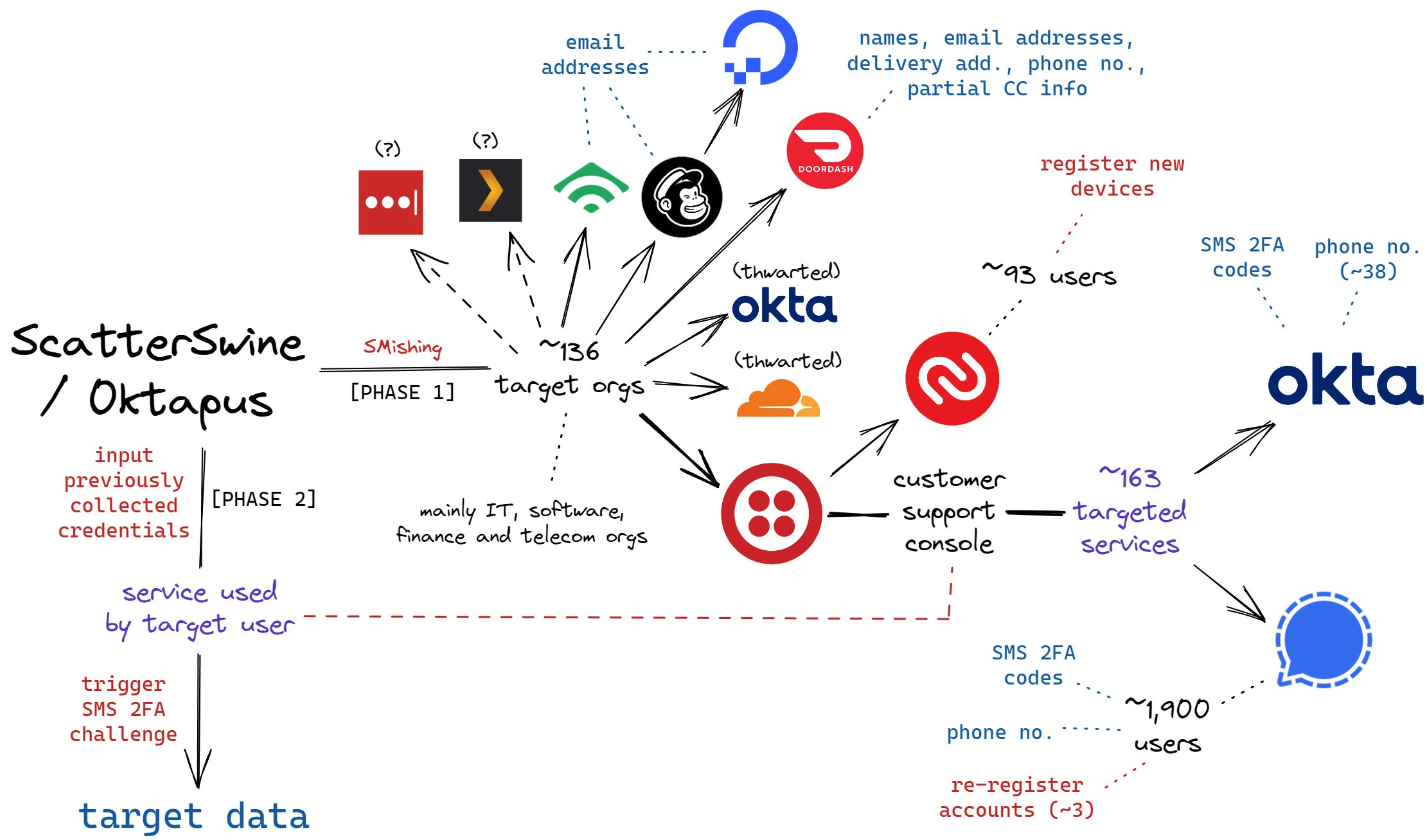
A circulation chart of the assaults by the SMS phishing group often called 0ktapus and ScatterSwine. Picture: Amitai Cohen twitter.com/amitaico.
The ubiquity of cellphones grew to become a lifeline for a lot of corporations making an attempt to handle their distant staff all through the Coronavirus pandemic. However these similar cell units are quick changing into a legal responsibility for organizations that use them for phishable types of multi-factor authentication, corresponding to one-time codes generated by a cell app or delivered through SMS.
As a result of as we will see from the success of this phishing group, this kind of information extraction is now being massively automated, and worker authentication compromises can rapidly result in safety and privateness dangers for the employer’s companions or for anybody of their provide chain.
Sadly, an awesome many corporations nonetheless depend on SMS for worker multi-factor authentication. In response to a report this yr from Okta, 47 % of workforce prospects deploy SMS and voice components for multi-factor authentication. That’s down from 53 % that did so in 2018, Okta discovered.
Some corporations (like Knauer’s Sitel) have taken to requiring that each one distant entry to inner networks be managed by means of work-issued laptops and/or cell units, that are loaded with customized profiles that may’t be accessed by means of different units.
Others are transferring away from SMS and one-time code apps and towards requiring staff to make use of bodily FIDO multi-factor authentication units corresponding to safety keys, which may neutralize phishing assaults as a result of any stolen credentials can’t be used except the phishers even have bodily entry to the consumer’s safety key or cell system.
This got here in useful for Twitter, which introduced final yr that it was transferring all of its staff to utilizing safety keys, and/or biometric authentication through their cell system. The phishers’ Telegram bot reported that on June 16, 2022, 5 staff at Twitter gave away their work credentials. In response to questions from KrebsOnSecurity, Twitter confirmed a number of staff have been relieved of their worker usernames and passwords, however that its safety key requirement prevented the phishers from abusing that data.
Twitter accelerated its plans to enhance worker authentication following the July 2020 safety incident, whereby a number of staff have been phished and relieved of credentials for Twitter’s inner instruments. In that intrusion, the attackers used Twitter’s instruments to hijack accounts for among the world’s most recognizable public figures, executives and celebrities — forcing these accounts to tweet out hyperlinks to bitcoin scams.
“Safety keys can differentiate legit websites from malicious ones and block phishing makes an attempt that SMS 2FA or one-time password (OTP) verification codes wouldn’t,” Twitter mentioned in an Oct. 2021 put up concerning the change. “To deploy safety keys internally at Twitter, we migrated from a wide range of phishable 2FA strategies to utilizing safety keys as our solely supported 2FA methodology on inner methods.”