Scalability and ease is a vital consideration after we speak about IP/MPLS networks. Conventional MPLS networks are advanced and use LDP and IGP (ISIS and OSPF) as management airplane protocols. LDP is used to label data change and IGP for Prefixing data change between neighbours. A method to leverage IP/MPLS networks is use of phase routing which gives full management over forwarding paths and doesn’t require any further protocol; it leverages present MPLS companies and {hardware} therefore doesn’t require new infrastructure to maneuver or migrate to phase routing.
Immediately we glance extra intimately about phase routing, the way it works, its options, structure parts, benefits and use instances and so forth.
The usual of phase routing is outlined by the IETF SPRING working group in RFC 8402. In an IP/MPLS community ‘segments’ current community hyperlinks, community nodes or companies. A path or route which an IP packet traverses in a community goes by means of intersections represented with hyperlink segments and community service represents vacation spot. In an IP/MPLS community a node phase represents an MPLS enabled router, a hyperlink phase represents a connection between two adjoining routers, and a service phase represents a buyer VPN service (Layer 3 or layer 2 VPN).
Phase routing makes use of a source-based routing scheme the place a community node steers a packet primarily based on an inventory of directions carried in a packet header referred to as ‘segments’. The checklist of segments carried in a packet header give a strict and free specification of the required community path or tunnel thus eliminating the necessity for transit nodes to take care of path data.
Parts of Phase Routing
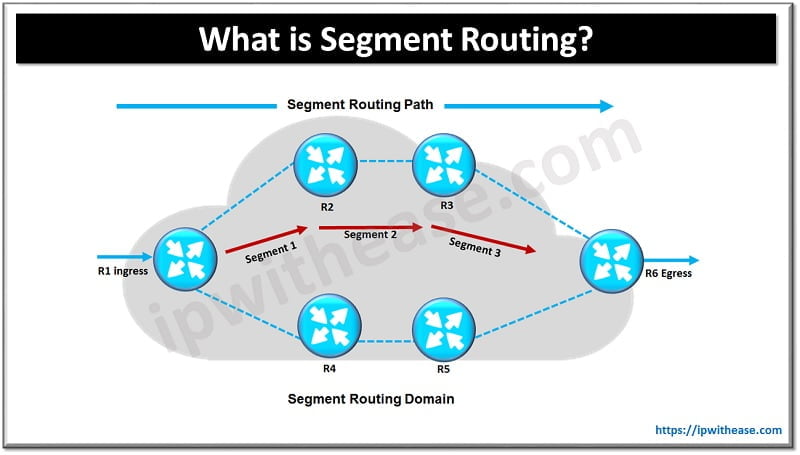
There are some elementary parts of phase routing as beneath.
- Phase Routing(SR) area – a set of nodes which take part in SR protocols. Inside an SR area a node can execute ingress, transit or egress procedures.
- SR path – an ordered checklist of segments which join an SR ingress node to SR egress node following least price path principal
- SR phase – A forwarding instruction which causes a packet to traverse a bit of community topology. SR defines any SR phase sorts and two used most frequently are adjoining and prefixed ones. An adjacency is a strict ahead single hop tunnel. A prefix is a multihop tunnel which makes use of equal price multihop-aware shortest path hyperlink to achieve every prefix.

How does Phase Routing work?
- When a packet arrives at SR ingress node, it’s subjected to coverage.
- If the packet matches the circumstances for an SR path as per coverage the SR ingress node encapsulates the packet in SR tunnel which traverses an SR path phase by phase.
- Every phase within the SR path terminates on the endpoint of the phase.
- When a packet arrives on the endpoint it’s examined for the outermost packet label or header to get the corresponding phase.
- It then pops the outermost label or header and ahead packet to the subsequent endpoint phase.
- This course of continues till the packet reaches its closing vacation spot which is perhaps by SR egress node.
- When the packet reaches the SR egress node the node will decide if the packet is on the finish of the trail.
- Whether it is finish of path SR header data is eliminated and packet if forwarded to its vacation spot lastly.
Benefits of Phase Routing
- Simplification of community and discount in useful resource utilization making simpler to handle and function community
- Discount within the variety of nodes which must be touched for path provisioning and adjustments. Community is extra attentive to adjustments, agile and versatile
- Gives utility QoS and maps community companies to finish customers and purposes as they traverse throughout the community
- Path resiliency throughout community outages by means of head finish restoration and topology unbiased loop free alternate (TI-LFA) know-how
- Bandwidth reservation with simplified visitors engineering when used as WAN PCE controller
- Discount in threat of transition because it gives heterogeneous assist for a number of forwarding planes (MPLS and IPv6 as nicely)
- Facilitate closed loop automation by steady evaluation of actual time community circumstances similar to packet circulation to community gadgets, community behaviour monitoring and efficiency,
- Additionally used for community slicing to reinforce finish person expertise by defining particular community paths as per set necessities
Proceed Studying:
LDP IGP sync in MPLS : What’s the necessity?